Many Apple customers imagine the macOS working system is so safe that no cyberthreats can hurt them, so that they don’t want to fret about defending their units. Nevertheless, that is removed from the case: whereas there is much less malware for macOS, it’s nonetheless rather more widespread than Apple gadget homeowners wish to assume.
On this put up, we talk about present threats dealing with macOS customers and the right way to successfully defend your Mac. As an instance the truth that viruses for macOS do exist, we’ll take a look at three latest research on a number of malware households which were printed over the previous few weeks.
BlueNoroff assaults macOS customers and steals cryptocurrency
In late October 2023, our researchers found a brand new macOS Trojan that’s believed to be related to BlueNoroff, the “industrial wing” of the Lazarus APT group working for North Korea. This subgroup makes a speciality of monetary assaults and particularly focuses on two issues: firstly, assaults on the SWIFT system — together with the infamous heist of the Bangladesh Central Financial institution — and secondly, stealing cryptocurrencies from organizations and people.
The found macOS Trojan downloader is distributed inside malicious archives. It’s disguised as a PDF doc titled “Crypto-assets and their dangers for monetary stability”, with an icon that mimics a preview of this doc.

Cowl web page of the misleading PDF that the Trojan downloads and exhibits to the person when launching the file from an contaminated archive. Supply
As soon as the person clicks on the Trojan (masquerading as a PDF), a script is executed that truly downloads the corresponding PDF doc from the web and opens it. However, after all, that’s not all that occurs. The Trojan’s predominant job is to obtain one other virus, which gathers details about the contaminated system, sends it to the C2, after which waits for a command to carry out one in all two doable actions: self-deletion or saving to a file and executing malicious code despatched in response from the server.
Proxy Trojan in pirated software program for macOS
In late November 2023, our researchers found one other malware occasion that threatens Mac customers — a proxy Trojan, distributed alongside pirated software program for macOS. Particularly, this Trojan was added to the PKG information of cracked video enhancing applications, information restoration instruments, community utilities, file converters, and numerous different software program. The total listing of contaminated installers found by our consultants might be discovered on the finish of the report printed on Securelist.
As talked about earlier, this malware belongs to the class of proxy Trojans — malware that units up a proxy server on the contaminated laptop, basically creating a number to redirect web visitors. Subsequently, cybercriminals can use such contaminated units to construct a paid community of proxy servers, incomes cash from these looking for such companies.
Alternatively, the Trojan’s homeowners may straight use the contaminated computer systems to hold out felony actions within the sufferer’s title — whether or not it’s attacking web sites, firms or different customers, or buying weapons, medicine or different unlawful items.
Atomic stealer in pretend Safari browser updates
Additionally in November 2023, a brand new malicious marketing campaign was found to unfold one other Trojan for macOS, often known as Atomic and belonging to the class of stealers. Such a malware searches for, extracts, and sends to its creators all types of useful info discovered on the sufferer’s laptop, significantly information saved in browsers. Logins and passwords, financial institution card particulars, crypto pockets keys, and comparable delicate info are of specific worth to stealers.
The Atomic Trojan was first found and described again in March 2023. What’s new is that now the attackers have began utilizing pretend updates for the Safari and Chrome browsers to unfold the Atomic Trojan. These updates are downloaded from malicious pages that very convincingly mimic the unique Apple and Google web sites.
A website with pretend Safari browser updates that truly comprise the Atomic stealer. Supply
As soon as working on a system, the Atomic Trojan makes an attempt to steal the next info from the sufferer’s laptop:
- cookies
- logins, passwords, and financial institution card particulars saved within the browser
- passwords from the macOS password storage system (Keychain)
- information saved on the onerous drive
- saved information from over 50 standard cryptocurrency extensions
Zero-day vulnerabilities in macOS
Sadly, even if you happen to don’t obtain any suspicious information, you keep away from opening attachments from unknown sources, and customarily chorus from clicking on something suspicious, this doesn’t assure your safety. It’s vital to keep in mind that any software program all the time has vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit to contaminate a tool, and which require little or no lively person motion. And the macOS working system isn’t any exception to this rule.
Not too long ago, two zero-day vulnerabilities have been found within the Safari browser — and in accordance with Apple’s announcement, cybercriminals have been already exploiting them by the point they have been found. By merely luring the sufferer to a malicious webpage, attackers can infect their gadget with none extra person motion, thereby gaining management over the gadget and the flexibility to steal information from it. These vulnerabilities are related for all units utilizing the Safari browser, posing a risk to each iOS/iPadOS customers and Mac homeowners.
It is a widespread state of affairs: as Apple’s working methods share many parts, vulnerabilities usually apply not simply to one of many firm’s opertaing methods however to all of them. Thus, it’s a case of Macs being betrayed by the iPhone’s reputation: iOS customers are the first targets, however these vulnerabilities can simply as simply be used to assault macOS.
A complete of 19 zero-day vulnerabilities have been found in Apple’s working methods in 2023 which might be identified to have been actively exploited by attackers. Of those, 17 affected macOS customers — together with over a dozen with high-risk standing, and one labeled as crucial.
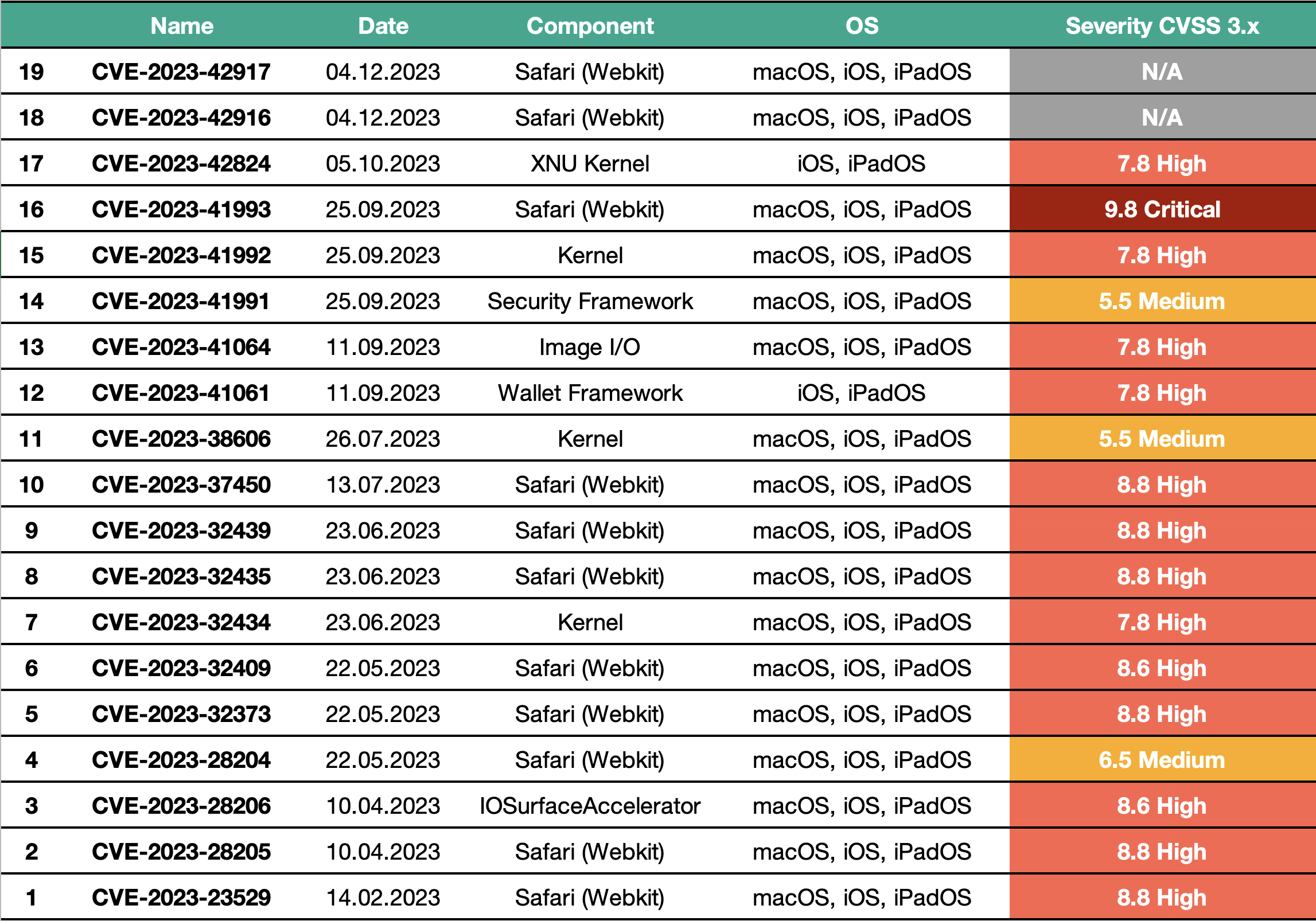
Zero-day vulnerabilities in macOS, iOS, and iPadOS found in 2023, which have been actively exploited by cybercriminals
Different threats and the right way to defend your Mac
What’s vital to recollect is that there are quite a few cyberthreats that don’t depend upon the working system however that may be no much less harmful than malware. Specifically, take note of the next threats:
- Phishing and pretend web sites. Phishing emails and web sites work the identical manner for each Home windows customers and Mac homeowners. Alas, not all pretend emails and web sites are simply recognizable, so even skilled customers usually face the chance of getting their login credentials stolen.
- Net threats, together with net skimmers. Malware can infect not solely the person’s gadget but additionally the server it communicates with. For instance, attackers usually hack poorly protected web sites, particularly on-line shops, and set up net skimmers on them. These small software program modules are designed to intercept and steal financial institution card information entered by guests.
- Malicious browser extensions. These small software program modules are put in straight into the browser and function inside it, so that they don’t depend upon the OS getting used. Regardless of being seemingly innocent, extensions can do rather a lot: learn the content material of all visited pages, intercept info entered by the person (passwords, card numbers, keys to crypto wallets), and even substitute displayed web page content material.
- Visitors interception and man-in-the-middle (MITM) assaults. Most fashionable web sites use encrypted connections (HTTPS), however you possibly can nonetheless generally come throughout HTTP websites the place information trade might be intercepted. Cybercriminals use such interception to launch MITM assaults, presenting customers with pretend or contaminated pages as an alternative of reliable ones.
To guard your gadget, on-line service accounts and, most significantly, the precious info they comprise, it’s essential to make use of complete safety for each Mac computer systems and iPhones/iPads. Such safety should be capable to counteract your entire vary of threats — for instance options like our Kaspersky Premium, whose effectiveness has been confirmed by quite a few awards from impartial testing laboratories.



