One of many largest challenges in constructing an API is authentication. This is likely one of the most important assault surfaces an API has. Correct authentication helps keep away from safety threats and ensures that solely the proper customers can entry the required information.
Authentication was simple when groups had been working with server-side functions. A easy session validation on the server was sufficient to make sure person permissions for operations. Nevertheless, the appearance of APIs has led to a major shift in these authentication challenges.
However with an API, you may’t implement periods. You possibly can’t assure that your API will at all times be invoked utilizing an internet browser, so you may’t depend on cookies to safe an API. One of many important options of an API is that it’s stateless, that means that each request despatched to an API doesn’t rely upon any earlier or subsequent requests. Subsequently, you want an method able to carrying the authentication/authorization info essential to validate a request.
One efficient API authentication approach is utilizing JSON Internet Tokens (JWTs). On this article, we’ll delve into the small print of JWTs and supply a complete information on implement a REST API utilizing Node.js, with JWTs because the safety measure.
Key Takeaways
- Implementing JWTs for safe communication. The article gives an in-depth information on implementing JWTs for authentication in net functions. This consists of token era, transmission and verification. By doing so, it enhances the general API safety by stopping damaged entry management and by letting solely the approved folks entry the information.
- Position-based entry management in JWT. This text showcases an summary of role-based entry management through which particular API endpoints are restricted for sure roles. For instance, an administrator can view all customers, whereas a buyer can’t. This was applied on this article by managing customized claims inside within the JWT Token.
- Implementation of JWT in a REST API. The article gives a step-by-step method to constructing a easy REST API utilizing Node.js, Specific, and the jsonwebtoken library for JWT authentication. It consists of establishing the venture, putting in mandatory libraries, making a primary person database, and implementing login and person information endpoints. The method entails producing a token upon person login and validating this token in subsequent requests to authorize or deny entry primarily based on the person’s function.
What’s a JSON Internet Token (JWT)?
A JSON Internet Token (JWT) is an open customary (RFC 7519) that defines a technique of transferring info between two events, a consumer and a server, as a JSON object. It’s essential to notice that the data being transferred between the 2 events is digitally signed utilizing a personal signature. Subsequently, that is thought of verified and secure to make use of information.
Notice: usually, JWT is used to construct authentication and authorization flows for an API.
As an illustration, info that can be utilized to affiliate a person with a request is commonly wrapped in a JWT. This might embody a person ID and a job, and your API may use this info to find out if the person sending the request is permitted to take action.
When Ought to You Use JWT?
There are sometimes two essential eventualities through which it’s best to think about using a JWT Token.
- Authentication/authorization. This is likely one of the most generally accepted use circumstances of JWT. You possibly can construct an authentication token to validate requests in your API and be certain that approved customers are performing approved actions.
- Info change. You can even leverage JWTs to change info between events securely. They function a very good type of legitimate and accepted information as JWTs might be signed. For instance, utilizing public/non-public key pairs, you might be certain the senders are who they are saying they’re. This allows you to make extra checks to make sure your info hasn’t been tampered with.
Construction of a JWT Token
To realize all the performance, the JWT token is structured in a sure method. It has three key parts:
- Header. The header consists of two components: the token kind, JWT, and the signing algorithm getting used, resembling HMAC SHA256 or RSA.
- Payload. The payload accommodates your claims. Claims are info that describes the entity you’re issuing the token. For instance, in case you had been issuing a token for a person, you’d have claims just like the person ID and function. Aside from that, a JWT token has a typical set of claims such because the issuer, the time of issuing, the expiration time and extra.
- Signature. That is one thing that it is advisable create. To create the signature, it’s a must to take the encoded header, the encoded payload, a secret, and the algorithm specified within the header and signal that. That is carried out to make sure the message wasn’t modified alongside the best way.
Notice: your JWT token is a plan base64 string that contains of those three parts the place every part is seperated utilizing a ..
For instance, a easy token would possibly look one thing like this:
header.payload.signatureMoreover, your decoded token would really like one thing like pictured under.
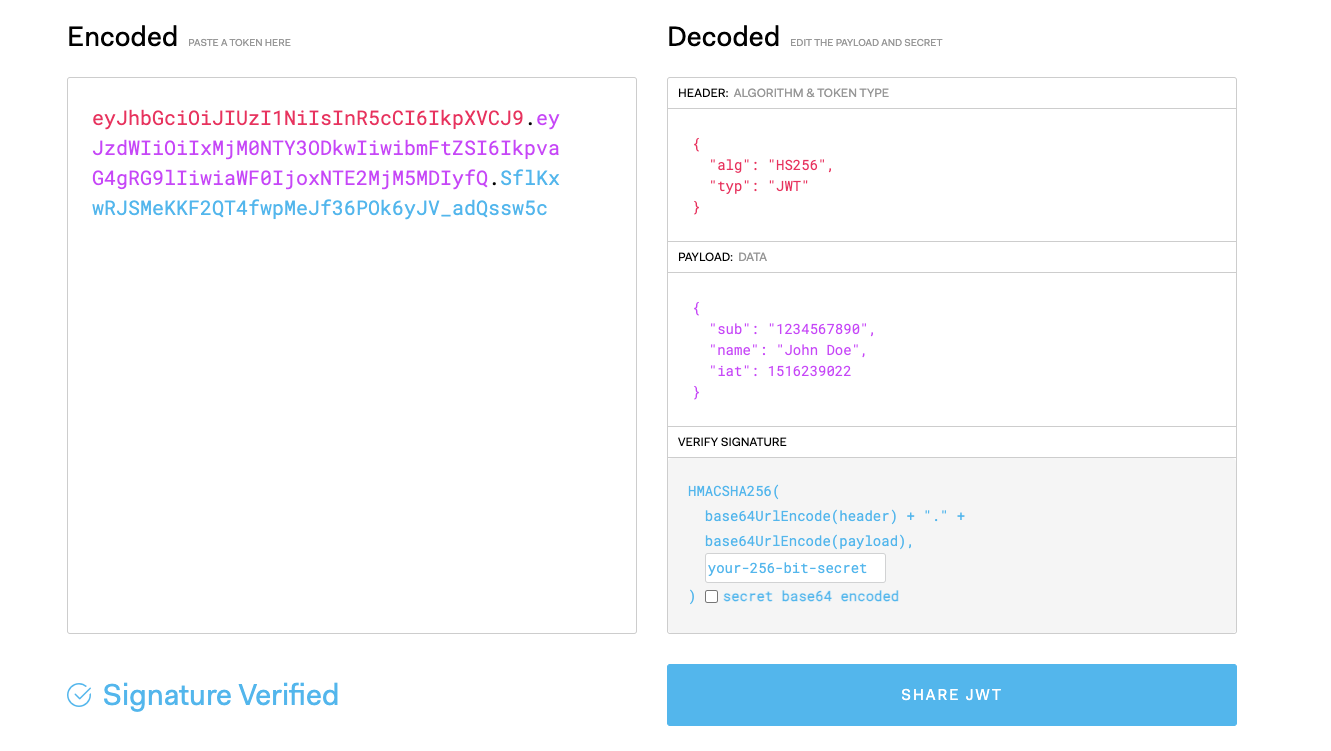
As you may see, the header, payload and signature are decoded and proven above.
Course of Stream of a JWT
Now, once you’re constructing an API with JWT it is advisable think about the next:
- logging in
- token era
- token validation
This may look one thing like what’s pictured under.
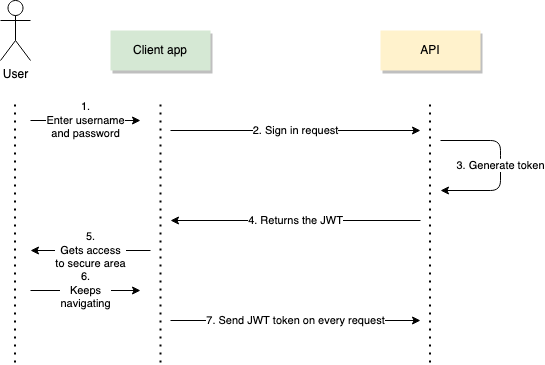
The cycle begins when a person first submits a request to log in to the API. They supply a username and a password. Your API verifies whether or not the credentials are legitimate and, in that case, generates a JWT token for the person.
Subsequent, your person would come with this token within the Request Header — Authorization — as a Bearer token, in each request they execute. Your API must have a look at the request header for all requests and decode and validate the token to authorize the request.
It’s important to comply with this course of when working with JWT. The API will reject the request in case your header is lacking the JWT Token.
Constructing a REST API with JWT
Constructing an API with JWT authentication is less complicated than it appears. There are lot of libraries obtainable that deal with the method of token era and validation by easy API strategies.
So, let’s construct a easy REST API with JWT Authentication.
To take action, let’s first bootstrap a venture utilizing the command:
npm initNotice: ensure to proceed with the default configurations.
Subsequent, let’s set up the JWT Library that we’re working with. Let’s use the jsonwebtoken library to create and handle JWT tokens.
Notice: I’ve chosen this library as it’s incessantly maintained on GitHub and it has over 14 million downloads per week.
So, set up the library utilizing the command:
npm i jsonwebtokenSubsequent, let’s set up Specific to construct the API. To take action, run the command:
// categorical - to construct the api
// cors - to allow cross origin requests
// body-parser - to parse the physique as JSON
npm i categorical cors body-parserSubsequent, let’s create a database.js file. Since we’re focusing strictly on JWTs right here, I received’t spin up a database, however quite preserve an in-code database of customers. So, open up your database.js file and embody the next code:
const customers = [
{ id: '1', name: 'Lakindu', username: 'lak', password: '1234', role: 'customer' },
{ id: '2', name: 'David', username: 'david', password: '1234', role: 'customer' },
{ id: '3', name: 'John', username: 'john', password: '1234', role: 'customer' },
{ id: '4', name: 'Nishanthan', username: 'nishanthan', password: '1234', role: 'customer' },
{ id: '5', name: 'Pasindu', username: 'pasindu', password: '1234', role: 'customer' },
{ id: '6', name: 'Sahan', username: 'sahan', password: '1234', role: 'admin' },
]
module.exports = {
customers
}As you may see, we’ve outlined a listing of customers which can be going to have entry to our API.
Notice: in case you had been constructing this on a manufacturing degree, I’d advocate utilizing one thing like Amazon Cognito to handle your customers, or think about hashing to retailer passwords.
Subsequent, create an index.js file to outline the API. Open up the index.js file and embody the next code:
app.submit('/login', (req, res) => {
const { username, password } = req.physique;
const person = customers.discover((person) => person.username === username);
if (!person || person.password !== password) {
res.standing(400);
res.ship({ message: 'Invalid username or password' })
return;
}
if (person.password === password) {
const token = jwt.signal({
function: person.function,
}, tokenSecret, {
algorithm: 'HS256',
expiresIn: '5m',
issuer: 'my-api',
topic: person.id
})
res.ship({ token });
return;
}
});We’ve now applied three API endpoints:
- POST /login. This route makes an attempt to authenticate a person. It expects a username and password to be within the request physique. The handler searches for a person with the matching username within the customers array. If no person is discovered or the password doesn’t match, it responds with a 400 standing code and an error message. If a person is discovered, it responds with a message indicating profitable login.
- GET /customers. This route responds with a JSON string containing all customers.
- GET /customers/:userId. This retrieves a
userIdfrom the trail parameters and makes use of it to discover a person within the customers array.
Now, in our case, we will leverage JWT for a number of circumstances:
- When logging in, generate a JWT token and return it to the person.
- When making requests for the customers API, they’ll embody the token for authorization. For instance, solely an admin ought to have the ability to fetch a person by ID, and get all customers. Prospects shouldn’t be ready to do that.
So, let’s replace the login endpoint to generate a token:
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
app.submit('/login', (req, res) => {
const { username, password } = req.physique;
const person = customers.discover((person) => person.username === username);
if (!person || person.password !== password) {
res.standing(400);
res.ship({ message: 'Invalid username or password' })
return;
}
if (person.password === password) {
const token = jwt.signal({
function: person.function,
}, tokenSecret, {
algorithm: 'HS256',
expiresIn: '5m',
issuer: 'my-api',
topic: person.id
})
res.ship({ token });
return;
}
});As you may see, we’ve up to date the login endpoint to leverage the jsonwebtoken library to create a signed token. The token makes use of the HMAC SHA-256 algorithm, and can expire in 5 minutes and is issued to the topic with the userId. Because of this the token is supposed for use for a selected person.
Moreover, we’ve additionally handed a tokenSecret. This can be a secret key that’s used to decode the token for all future requests. This additionally provides a layer of safety to your token, through which all tokens that may’t be decoded by your secret key might be deemed as tampered.
So, once you execute your login endpoint, it’s best to get a token as your output, as pictured under.
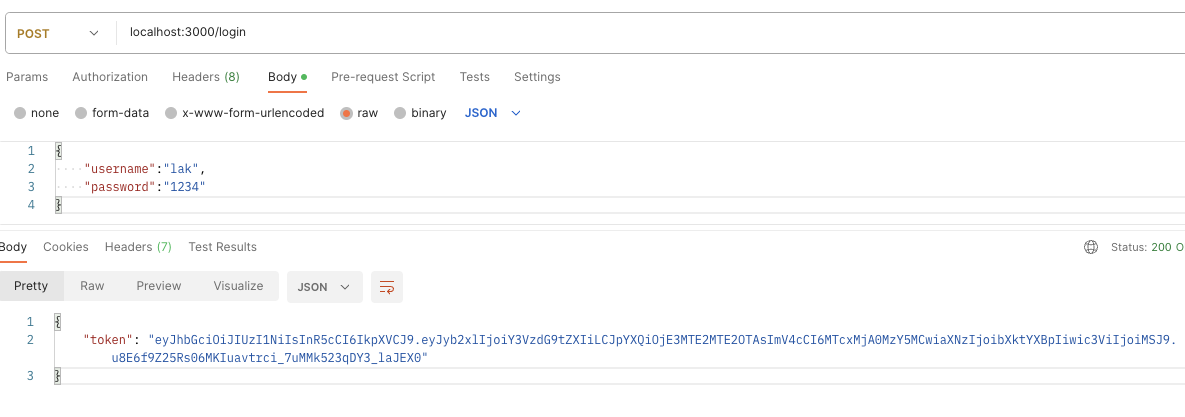
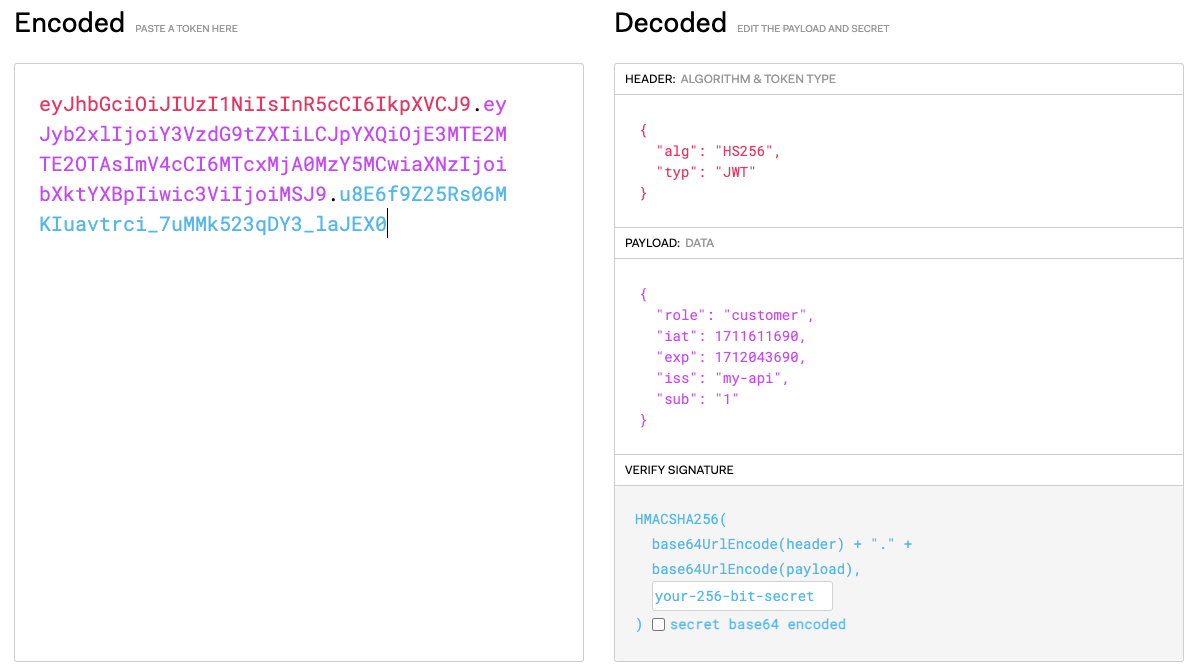
When you paste the token on jwt.io‘s on-line debugger, you may see the properties pictured under.
Now, let’s replace the Consumer API to validate the token. To take action, let’s create a role-based entry management (RBAC) operate:
const validateRequest = (requiredRole) => {
return (req, res, subsequent) => {
const { authorization } = req.headers
const token = authorization.substring('Bearer '.size);
strive {
const { exp, iss, function } = jwt.confirm(token, tokenSecret);
if (iss === 'my-api' && exp < Date.now() && function === requiredRole) {
subsequent();
return;
}
} catch (err) {
res.sendStatus(403);
return;
}
}
}Over right here, we’ve created a higher-order operate that takes a requiredRole parameter and returns a middleware operate. This design permits us to create middleware tailor-made to the function required for accessing particular routes. In consequence, the returned operate is middleware appropriate with Specific. It takes the usual req (request), res (response), and subsequent (operate to name the following middleware) parameters.
This returned operate validates the JWT token by doing the next:
- Extracting the token. It begins by extracting the JWT from the Authorization header of the incoming request. The anticipated format of the header is Bearer [token], so it removes the
'Bearer 'prefix to isolate the token. - Decoding the token. The token is then decoded utilizing
jwt.decode(token), which parses the JWT and extracts its payload with out verifying the signature. The payload is anticipated to include no less than three claims:exp(expiration time),iss(issuer), andfunction(person function). - Validation checks. The middleware performs the next checks on the decoded token:
- Issuer. Verifies that the
iss(issuer) declare matches'my-api', indicating that the token was issued by the anticipated authority. - Expiration. Checks if
exp(expiration time) is lower than the present time (Date.now()), which might imply the token is expired. - Position. Compares the function declare within the token to the
requiredRoleparameter handed tovalidateRequest. This ensures the person has the suitable function for the request.
- Issuer. Verifies that the
Notice: if all checks cross (issuer is right, token has not expired, and person has the required function), it calls subsequent() to proceed to the following middleware or route handler. If any examine fails, it sends a 403 Forbidden standing code because the response, indicating that the request is unauthorized.
Subsequent, you may add the middleware operate to your routes and specify the function required to entry the route:
app.get('/customers', validateRequest('admin'), (req, res) => {
res.ship(JSON.stringify({ customers }))
});
app.get('/customers/:userId', validateRequest('admin'), (req, res) => {
const { params } = req;
const { userId } = params;
console.log({ userId });
const person = customers.discover((person) => person.id === userId);
if (!person) {
res.sendStatus(404)
return;
}
res.ship({ person })
});As proven above, each routes are protected in order that solely the administrator can entry it. Now, in case you try to entry the route as a buyer or with an invalid token, it’s best to see the output pictured under.
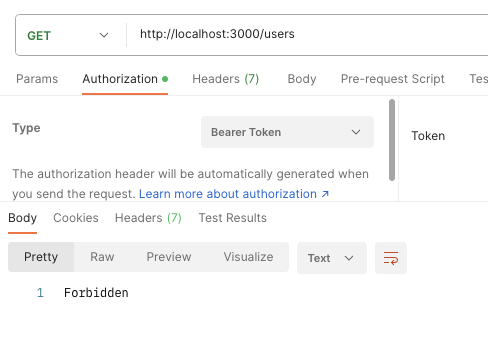
However, in case your token is legitimate, it’s best to see the output pictured under.
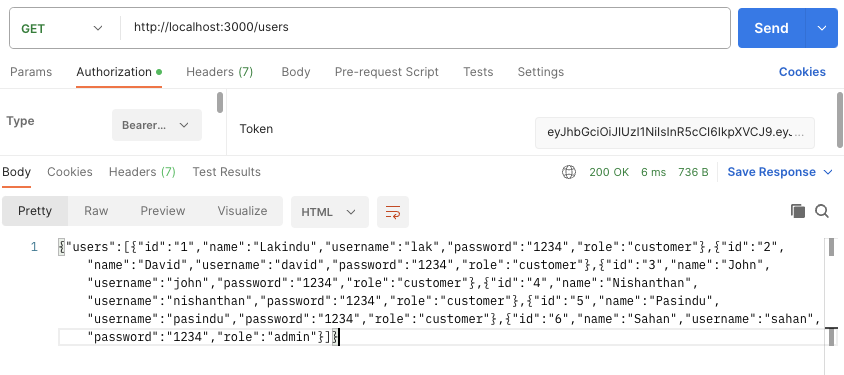
Wrapping Up
And that’s just about it for this text. You’ve efficiently constructed a REST API utilizing JWT primarily based authentication/authorization.
Subsequent, you may make the most of this token in your client-side apps like Angular or React and cross the token in all API requests to make sure that your frontend is ready to talk with the API efficiently.
When you want to take a look at the code, be happy to go to my GitHub repo, or this CodeSandbox demo.
Thanks for studying.
Regularly Requested Questions (FAQs) about Utilizing JSON Internet Tokens in Node.js
A JSON Internet Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe technique of representing claims to be transferred between two events. JWTs are used to securely transmit info between a consumer and a server as a JSON object, which might be verified and trusted as a result of it’s digitally signed.
How do I deal with JWT expiration?
JWTs have an expiration discipline (exp) that determines when the token is not legitimate. To deal with expiration in Node.js, you should use a technique supplied by the token era library that you’ve got used.
Ought to I retailer JWTs in cookies or native storage?
The selection between storing JWTs in cookies or native storage is determined by the particular wants and safety issues of your software.
Cookies are usually safer when correctly configured (e.g., HttpOnly, Safe, SameSite), as they’re much less vulnerable to XSS assaults than native storage. Nevertheless, cookies might be weak to CSRF assaults. Utilizing native storage makes your token vulnerable to XSS assaults however not CSRF assaults.
Subsequently, it’s important to weigh these issues and apply extra safety measures accordingly, whatever the approach you undertake.
Sure, JWTs might be refreshed by issuing a brand new token to the consumer earlier than the previous token expires. This usually entails having a separate refresh token that’s used solely to acquire new entry tokens.
The refresh token is saved securely on the server and is distributed to the consumer alongside the entry token. When the entry token is about to run out, the consumer can request a brand new one utilizing the refresh token.
How do I ship a JSON Internet Token to the consumer?
After producing a token, you may ship it to the consumer within the response to a profitable login request. The consumer ought to then retailer the token and embody it within the Authorization header of subsequent requests.
How do I shield routes with JSON Internet Tokens in Node.js?
To guard routes, you may create a middleware operate that verifies the token included within the request’s Authorization header. If the token is legitimate, the middleware operate ought to name subsequent to permit the request to proceed. If the token is invalid, the middleware operate ought to ship a response with an error standing code.
How do I deal with errors when verifying a token?
When verifying a token, the confirm technique calls the callback operate with an error if the token is invalid. You possibly can deal with this error to ship a response with an acceptable standing code and message. For instance, if the error is as a result of the token has expired, you would possibly ship a 401 Unauthorized standing code with a message saying “Session expired. Please log in once more.”



