Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime surroundings permitting builders to construct server-side purposes exterior a browser. It may be used to construct mission-critical manufacturing purposes that carry out extraordinarily properly. On this sensible information, we’ll take a look at how one can create your net server with Node.js.
Key Takeaways
- Implementing a easy net server with Node.js. This information exhibits methods to arrange and deploy an internet server utilizing Node.js. It walks by every step, together with undertaking initialization, Specific.js integration, and lots of important options, offering a strong basis for anybody new to Node.js.
- Constructing dynamic net purposes. This information covers a big selection of functionalities, equivalent to dealing with varieties, responding to consumer requests, and dynamically serving net pages, that are important to creating your net purposes interactive and interesting.
- Exploring Node.js options. Dive deeper into Node.js’s choices for net improvement, together with methods to work with static information, deal with errors, and implement type submissions. This information offers a sensible strategy to utilizing Node.js to construct feature-rich net purposes.
Half 1: Venture Setup and Set up
Step 1: Set up Node.js and npm
To start out constructing our net utility, guarantee you may have Node.js and npm put in in your system. Node.js offers a JavaScript runtime surroundings, whereas npm is the package deal supervisor for Node.js. You possibly can obtain and set up Node.js from the official web site.
To make sure that Node.js and npm are accurately put in, open your terminal and run the next instructions:
node -v
npm -v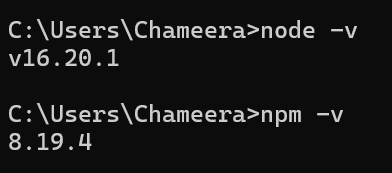
Step 2: Initialize a brand new Node.js Venture
Create a brand new listing on your undertaking and initialize a brand new Node.js undertaking by working the next command in your terminal:
mkdir book-club
cd book-club
npm init -yThis command will create a package deal.json file on your undertaking. It is going to include metadata concerning the undertaking, together with its dependencies:
{
"title": "book-club",
"model": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"fundamental": "index.js",
"scripts": { "check":
"echo "Error: no check specified" && exit 1" },
"key phrases": [],
"creator": "",
"license": "ISC" }Step 3: Set up Specific.js
Specific.js is a well-liked net framework for Node.js, with options for constructing net and cellular purposes. The command beneath installs Specific.js and provides it as a dependency in your package deal.json file:
npm set up specificHalf 2: Setting Up the Specific Server
Step 1: Create a brand new file for the server
Now that the undertaking is about up, create a brand new file named app.js within the undertaking listing. This file will include the code for the Specific server.
Step 2: Import Specific.js
On the high of your app.js file, import the Specific.js module:
const specific = require('specific');Step 3: Create an Specific utility
Subsequent, create an occasion of an Specific utility:
const app = specific();The specific() perform is a top-level perform exported by the Specific module. It creates an Specific utility, which we assign to the app variable.
Step 4: Outline a route
Outline a route for the trail / with a easy message when accessed:
app.get("https://www.sitepoint.com/", (req, res) => {
res.ship('Hey World!');
});Right here, app.get() is a perform that tells the server what to do when a GET request is made to a selected path, on this case, /. This perform takes two arguments: the trail and a callback perform that takes a request and a response.
Step 5: Begin the server
Lastly, let’s begin the server on port 3000:
const port = 3000;
app.hear(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is working at http://localhost:${port}`);
});The app.hear() perform begins the server and makes it hear for requests on the required port.
Half 3: Constructing the Utility Performance
Now that we’ve got the Specific server arrange, let’s begin constructing the applying’s performance by creating just a few totally different routes.
Step 1: Create a brand new file for messages
In your undertaking listing, create a brand new file named messages.js. This file will include the messages that your server will ship as responses:
module.exports = {
dwelling: 'Welcome to our E-book Membership!',
about: 'About Us',
notFound: '404 Not Discovered'
};Step 2: Import messages into your server file
On the high of your app.js file, import the messages:
const messages = require('./messages');Step 3: Use messages in your routes
Now, use these messages within the routes:
app.get("https://www.sitepoint.com/", (req, res) => {
res.ship(messages.dwelling);
});
app.get('/about', (req, res) => {
res.ship(messages.about);
});
app.use((req, res) => {
res.standing(404).ship(messages.notFound);
});
Right here, app.use() is a technique that is named for each request made to the server. We’re utilizing it right here to deal with all routes that aren’t outlined and ship a 404 Not Discovered message.
Half 4: Including Static File Serving
Step 1: Create a brand new listing for static information
Create a brand new listing named public. This listing will include all of your static information:
mkdir publicStep 2: Add some static information
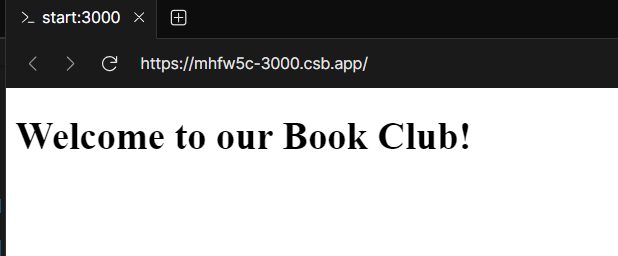
For the aim of this information, let’s add a easy HTML file and a CSS file. In your public listing, create a brand new file named index.html and add the next code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>E-book Membership</title>
<hyperlink rel="stylesheet" kind="textual content/css" href="/kinds.css">
</head>
<physique>
<h1>Welcome to our E-book Membership!>/h1>
</physique>
</html>Additionally, create a brand new file named kinds.css within the public listing and add the next code:
physique {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
Step 3: Use specific.static to serve static information
Add the road beneath to the app.js file, earlier than the route definitions:
app.use(specific.static('public'));The specific.static perform is a built-in middleware perform in Specific.js. It serves static information and takes the listing title from which you need to serve information as an argument.
Half 5: Dealing with POST Requests
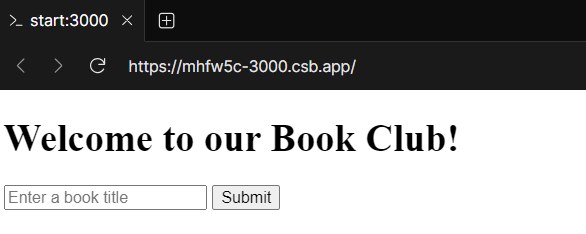
Step 1: Add a type to index.html
In your index.html file, add a type with a single enter discipline and a submit button:
<type motion="/submit" methodology="publish">
<enter kind="textual content" title="e book" placeholder="Enter a e book title">
<button kind="submit">Submit</button>
</type>This type will ship a POST request to the /submit path. The request physique will embrace the enter discipline’s worth.
Step 2: Set up body-parser
It’s worthwhile to set up a middleware known as body-parser to deal with the info despatched within the POST request:
npm set up body-parserStep 3: Import and use body-parser
Import body-parser into the app.js file:
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ prolonged: false }));The bodyParser.urlencoded() perform parses incoming request our bodies out there beneath the req.physique property.
Step 4: Deal with POST requests
Now, create a brand new endpoint to deal with this POST request within the app.js file:
app.publish('/submit', (req, res) => {
const e book = req.physique.e book;
console.log(`E-book submitted: ${e book}`);
res.ship(`E-book submitted: ${e book}`);
});
Half 6: Including a Knowledge Retailer
On this half, we’ll add a easy information retailer to our utility to retailer the books that customers submit. We’ll use an array to retailer the info for simplicity.
Step 1: Create an information retailer
On the high of your app.js file, create an array to retailer the books:
const books = [];Step 2: Replace POST request handler
Replace the handler for POST requests so as to add the submitted e book to the books array:
app.publish('/submit', (req, res) => {
const e book = req.physique.e book;
books.push(e book);
console.log(`E-book submitted: ${e book}`);
res.ship(`E-book submitted: ${e book}`);
});Step 3: Create a path to view all books
Create a brand new route handler that returns all of the submitted books:
app.get('/books', (req, res) => {
res.ship(books.be a part of(', '));
});
Word: in a real-world utility, you’d seemingly retailer your information in a database. Right here, the info within the array will likely be misplaced each time you restart your server.
Half 7: Including Error Dealing with
On this half, we’ll create an error handler. Specific.js offers a built-in error handler. However it’s also possible to create your personal error dealing with middleware.
Step 1: Create an error dealing with middleware
In your app.js file, add the next code on the finish of the file:
app.use((err, req, res, subsequent) => {
console.error(err.stack);
res.standing(500).ship('One thing Went Improper!');
});This middleware perform has 4 arguments as an alternative of the standard three (req, res, subsequent). This perform is named each time there’s an error in your utility.
Step 2: Use the following perform to cross errors
In case you cross an argument to the subsequent() perform, Specific.js will assume it’s an error, skip all subsequent middleware features, and go straight to the error dealing with middleware perform:
app.publish('/submit', (req, res, subsequent) => {
const e book = req.physique.e book;
if (!e book) {
const err = new Error('E-book title is required');
return subsequent(err);
}
books.push(e book);
console.log(`E-book submitted: ${e book}`);
res.ship(`E-book submitted: ${e book}`);
});This handler checks if a e book title was offered within the POST request. If not, it creates a brand new Error object and passes it to the subsequent perform. This can skip all subsequent middleware features and go straight to the error dealing with middleware.
Half 8: Serving HTML Pages
On this half, we’ll modify our utility to serve HTML pages as an alternative of plain textual content. This can can help you create extra complicated consumer interfaces.
Step 1: Set up EJS
EJS (Embedded JavaScript) is a straightforward templating language that permits you to generate HTML markup utilizing plain JavaScript:
npm set up ejsStep 2: Set EJS because the view engine
In your app.js file, set EJS because the view engine on your Specific utility:
app.set('view engine', 'ejs');This tells Specific to make use of EJS because the view engine when rendering views.
Step 3: Create a views listing
By default, Specific will look in a listing named views on your views. Create this listing in your undertaking listing:
mkdir viewsStep 4: Create an EJS view
In your views listing, create a brand new file named index.ejs and add the next code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>E-book Membership</title>
</head>
<physique>
<h1><%= message %></h1>
<type motion="/submit" methodology="publish">
<enter kind="textual content" title="e book" placeholder="Enter a e book title">
<button kind="submit">Submit</button>
</type>
<h2>Submitted Books:</h2>
<ul>
<% books.forEach(perform(e book) { %>
<li><%= e book %></li>
<% }); %>
</ul>
</physique>
</html>The <%= message %> placeholder is used to output the worth of the message variable.
Step 5: Replace POST request handler
Replace the POST /submit route handler so as to add the submitted e book to the books array and redirect the consumer again to the house web page:
app.publish('/submit', (req, res) => {
const e book = req.physique.e book;
books.push(e book);
console.log(`E-book submitted: ${e book}`);
res.redirect("https://www.sitepoint.com/");
});Word: It’s a superb observe to redirect the consumer after a POST request. This is called the Submit/Redirect/Get sample, and it prevents duplicate type submissions.
Step 6: Replace the house route
Replace the GET / route handler to cross the books array to the index.ejs:
app.get("https://www.sitepoint.com/", (req, res) => {
res.render('index', { message: messages.dwelling, books: books });
});Step 7: Replace the house route
Now it’s time to run the applying and see it in motion.
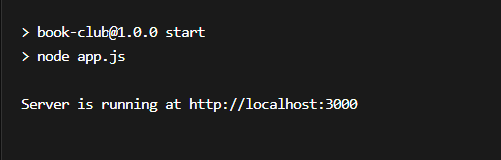
You can begin the server by working the next command in your terminal:
node app.jsYou need to see a message saying Server is working at http://localhost:3000 within the terminal.
Alternatively, you may simplify the beginning course of by including a script to the package deal.json file:
Now, as an alternative of working node app.js , you may name npm begin:
npm begin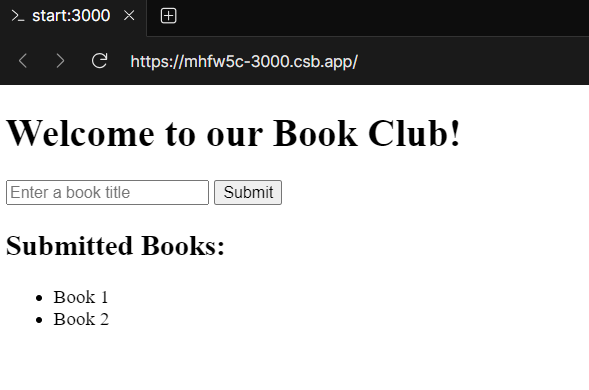
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve constructed an internet utility with Node.js and Specific.js. This utility serves static information, handles totally different routes, makes use of middleware, and extra.
In case you’d like to do this out for your self, or want to discover the code, checkout this CodeSandbox demo.
There’s a lot extra you are able to do with Node.js and Specific.js. You possibly can add extra routes, hook up with totally different databases, construct APIs, create real-time purposes with WebSockets, and rather more. The chances are limitless.
I hope this information has been useful. Glad coding!
Steadily Requested Questions (FAQs)
How can I deal with routing in a Node.js net server?
You should use the http module deal with routes manually by checking the request object URL. Nonetheless, as purposes turn into extra complicated, it is strongly recommended to make use of a framework like Specific.js. It helps you outline routes primarily based on HTTP strategies and URLs in a modular and clear means.
How can I implement real-time communication in a Node.js net server?
Actual-time communication in a Node.js net server will be applied utilizing WebSockets. The socket.io library is well-liked for including WebSocket assist to a Node.js server. It allows real-time, bidirectional, event-based communication between purchasers and the server.
What's one of the simplest ways to handle database operations in Node.js net servers?
One of the simplest ways to handle database operations in Node.js is to make use of ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) or ODM (Object Doc Mapping) instruments. They supply high-level abstraction for database interactions and simplifies connection pooling, question constructing, and schema validation.
For SQL databases: Sequelize, TypeORM
For NoSQL databases: Mongoose, Couchbase
How can I deal with errors globally in an Specific.js utility?
World error dealing with in an Specific.js utility will be applied by defining a particular middleware perform with 4 arguments: (err, req, res, subsequent). This middleware must be added in any case app.use() and route calls. Inside this perform, you may log the error, set the response standing code, and ship again an error message.
How can you make sure that a Node.js net server is scalable?
There are a number of methods to make sure the scalability of a Node.js net server:
Utilizing the cluster module to make the most of multi-core techniques.
Optimizing code and database queries.
Implementing caching methods.
Utilizing load balancers to distribute site visitors throughout a number of app situations.
Moreover, designing the stateless utility permits horizontal scaling by including extra situations as wanted.



