Introduction
Whereas FastAPI is nice for implementing RESTful APIs, it wasn’t particularly designed to deal with the advanced necessities of serving machine studying fashions. FastAPI’s help for asynchronous calls is primarily on the net stage and doesn’t prolong deeply into the mannequin prediction layer. This limitation poses challenges as a result of AI mannequin predictions are resource-intensive operations that must be configured to optimize efficiency, particularly when coping with trendy giant language fashions (LLMs).
Deploying and serving machine studying fashions at scale might be as difficult as even constructing the fashions themselves. That is the place LitServe, an open-source, versatile serving engine constructed on prime of FastAPI, comes into play. LitServe simplifies the method of serving AI fashions by offering highly effective options like batching, streaming, GPU acceleration, and autoscaling. On this article, we are going to introduce LitServe, delve into its functionalities, and the way it may be used to construct scalable, high-performance AI servers.
Studying Goals
- Perceive the right way to simply arrange and serve AI fashions utilizing LitServe.
- Learn to use batching, streaming, and GPU acceleration to raised AI mannequin efficiency.
- Achieve hands-on expertise with a toy instance, constructing a easy server to serve AI fashions.
- Discover options to optimize mannequin serving for top throughput and scalability.

This text was printed as part of the Knowledge Science Blogathon.
What’s Mannequin Serving?
In machine studying, deploying and serving fashions successfully helps to make predictions in real-time functions when deployed to manufacturing. Mannequin serving refers back to the technique of taking a educated machine-learning mannequin and making it accessible to be used in manufacturing environments. This may contain exposing the mannequin by means of APIs in order that customers or functions could make inference and obtain predictions.
The significance of mannequin serving impacts the responsiveness and scalability of machine studying functions. A number of challenges come up throughout the deployment, like with giant language fashions (LLMs) that demand excessive computational sources. These challenges embody latency in response instances, the necessity for environment friendly useful resource administration, and making certain that fashions can deal with various masses with out degradation in efficiency. Builders want sturdy options that simplify the serving course of whereas maximizing effectivity. That is the place specialised instruments like LitServe are available in with options designed to streamline mannequin serving and efficiency.
What’s LitServe?
LitServe is an open-source mannequin server designed to supply a quick, versatile, and scalable serving of AI fashions. By dealing with advanced engineering duties like scaling, batching, and streaming, eliminates the necessity to rebuild FastAPI servers for every mannequin. You should utilize LitServe to deploy fashions on native machines, cloud environments, or high-performance computing with a number of GPUs.
Key Options of LitServe
Allow us to discover key options of LitServe:
Sooner Mannequin Serving: LitServe is optimized for efficiency, making certain fashions serve higher than conventional strategies and even higher.
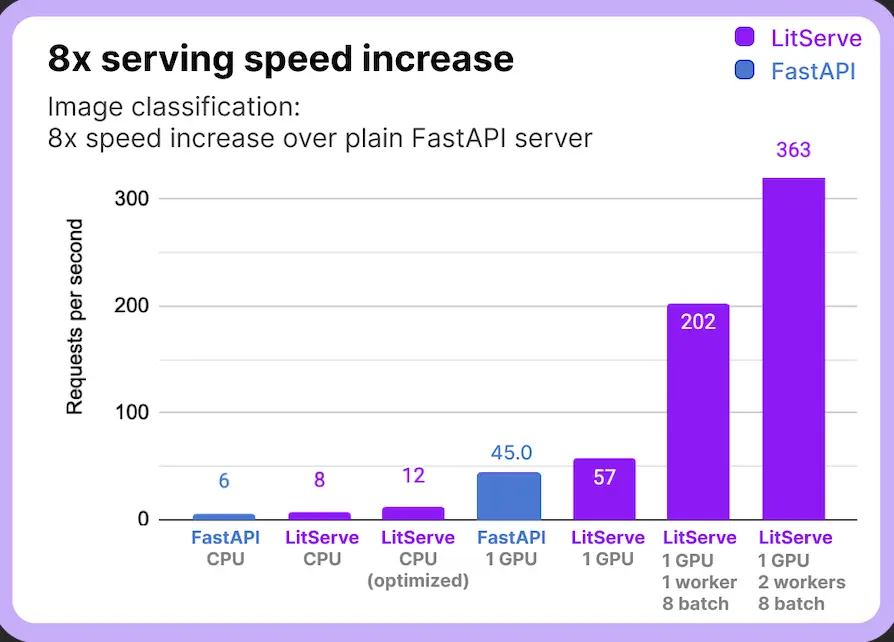
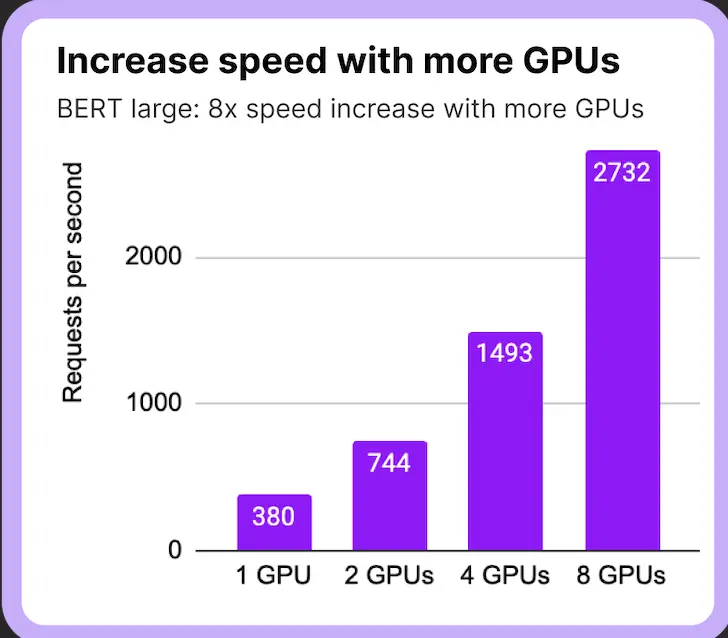
Multi-GPU Help: In instances the place the server has a number of GPUS, It leverages the facility of a number of GPUs to parallelize mannequin serving, lowering latency.
Batching and Streaming: LitServe can serve a number of calls concurrently utilizing batching strategies or streaming the response with out overloading the server.
LitServe brags about a number of options from authentication to OpenAI specs with options to cater to advanced AI workloads.
Getting Began with LitServe
For example how LitServe works, we’ll start with a easy instance after which transfer on to deploying a extra sensible AI server for picture captioning utilizing fashions from Hugging Face. Step one is to put in LitServe:
pip set up litserveDefining a Easy API with LitServe
LitServe simplifies the method of defining how your mannequin interacts with exterior calls. The LitAPI class handles incoming calls and returns mannequin predictions. Right here’s how one can arrange a easy API:
import litserve as ls
class SimpleLitAPI(ls.LitAPI):
def setup(self, system):
self.model1 = lambda x: x**2
self.model2 = lambda x: x**3
def decode_request(self, request):
return request["input"]
def predict(self, x):
squared = self.model1(x)
cubed = self.model2(x)
output = squared + cubed
return {"output": output}
def encode_response(self, output):
return {"output": output}Let’s break down the category:
- setup: Initializes the fashions or sources your server wants. On this instance, we outline two easy capabilities that simulate fashions.
- decode_request: Converts incoming calls right into a format that the mannequin can course of. It extracts the enter from the request payload.
- predict: Runs the mannequin(s) to make predictions. Right here, it calculates the sq. and dice of the enter and sums them.
- encode_response: Converts the mannequin’s output right into a response format that may be despatched again to the consumer.
After defining your API, you possibly can run the server by instantiating your API class and passing it to LitServer:
if __name__ == "__main__":
api = SimpleLitAPI()
server = ls.LitServer(api, accelerator="gpu") # accelerator may also be 'auto'
server.run(port=8000)This command will launch the server to deal with inferences with GPU acceleration.
Serving a Imaginative and prescient Mannequin with LitServe
To showcase LitServe’s full potential, let’s deploy a practical AI server that performs picture captioning utilizing a mannequin from Hugging Face. This instance will present the best way LitServe handles extra advanced duties and options like GPU acceleration.
Implementing the Picture Captioning Server
First, import the required libraries and outline helper capabilities:
import requests
import torch
from PIL import Picture
from transformers import VisionEncoderDecoderModel, ViTImageProcessor, GPT2TokenizerFast
from tqdm import tqdm
import urllib.parse as parse
import os
# LitServe API Integration
import litserve as ls
# Confirm URL perform
def check_url(string):
attempt:
consequence = parse.urlparse(string)
return all([result.scheme, result.netloc, result.path])
besides:
return False
# Load a picture from a URL or native path
def load_image(image_path):
if check_url(image_path):
return Picture.open(requests.get(image_path, stream=True).uncooked)
elif os.path.exists(image_path):
return Picture.open(image_path)Subsequent, outline the LitAPI class for picture captioning:
# HuggingFace API class for picture captioning
class ImageCaptioningLitAPI(ls.LitAPI):
def setup(self, system):
# Assign accessible GPU or CPU
self.system = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# Load the ViT Encoder-Decoder Mannequin
model_name = "nlpconnect/vit-gpt2-image-captioning"
self.mannequin = VisionEncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained(model_name).to(self.system)
self.tokenizer = GPT2TokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.image_processor = ViTImageProcessor.from_pretrained(model_name)
# Decode payload to extract picture URL or path
def decode_request(self, request):
return request["image_path"]
# Generate picture caption
def predict(self, image_path):
picture = load_image(image_path)
# Preprocessing the Picture
img = self.image_processor(picture, return_tensors="pt").to(self.system)
# Producing captions
output = self.mannequin.generate(**img)
# Decode the output to generate the caption
caption = self.tokenizer.batch_decode(output, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
return caption
# Encode the response again to the consumer
def encode_response(self, output):
return {"caption": output}For this very use case:
- setup: Masses the pre-trained picture captioning mannequin and related tokenizer and processor, shifting them to the system (CPU or GPU).
- decode_request: Extracts the picture path from the incoming name.
- predict: Processes the picture, generates a caption utilizing the mannequin, and decodes it.
- encode_response: Codecs the caption right into a JSON response.
# Operating the LitServer
if __name__ == "__main__":
api = ImageCaptioningLitAPI()
server = ls.LitServer(api, accelerator="auto", units=1, workers_per_device=1)
server.run(port=8000)This command will launch the server, robotically detecting accessible accelerators and configuring units. Discover the complete code right here.
Testing the Server
With the server working, you possibly can take a look at it by sending POST requests with an image_path (both a URL or a neighborhood file path) within the payload. The server will return a generated caption for the picture.
Instance: 1
Picture:

Generated Caption: “a view from a ship of a seashore with a big physique of water”
Instance 2:
Picture:

Generated Caption: “a person in a go well with and tie holding a crimson and white flag”
You should utilize the Colab pocket book supplied on GitHub to check the server straight. You may discover as the chances are limitless.
Enhancing Efficiency with Superior Options
LitServe lets you optimize your server’s efficiency by using its superior options:
- Batching: Embody max_batch_size=2 in LitServer to course of a number of calls concurrently, bettering throughput.
- Streaming: Set stream as True to deal with giant inputs effectively with out overloading the server.
- System Administration: Specify GPU IDs in units for management over {hardware}, particularly helpful in multi-GPU setups.
For an in depth listing of options and configurations, examine the official documentation: LitServe Options
Why Select LitServe?
LitServe successfully tackles the distinctive challenges of deploying giant language fashions. Not like conventional mannequin serving strategies, it’s constructed for high-performance inference, enabling builders to serve fashions with minimal latency and most throughput. Right here’s why you need to take into account LitServe on your mannequin serving wants:
- Scalability: LitServe is constructed to scale seamlessly along with your utility. It may well deal with a number of calls collectively, effectively distributing computational sources primarily based on demand.
- Optimized Efficiency: It gives options like batching, which permits for processing calls on the identical time, lowering the common response time. That is helpful when serving giant language fashions that want sources.
- Ease of Use: LitServe simplifies the deployment of machine studying fashions with the setup. Builders can rapidly transition from mannequin coaching to manufacturing with sooner iterations and deployments.
- Help for Superior Options: LitServe consists of help for GPU acceleration and streaming, permitting for environment friendly dealing with of real-time information and sophisticated mannequin architectures. This ensures that your functions can keep excessive efficiency, even underneath heavy masses.
Conclusion
LitServe offers a strong, versatile, and environment friendly means for serving AI fashions. By abstracting away the complexities of scaling, batching, and {hardware}, it permits builders to give attention to constructing high-quality AI options with out worrying concerning the intricacies of deployment. Whether or not you’re deploying easy fashions or advanced, multimodal AI techniques, LitServe’s sturdy options and ease of use make it a good selection for each rookies and skilled practitioners.
Key Takeaways
- LitServe streamlines the method of serving AI fashions, eliminating the necessity to rebuild servers for every mannequin.
- Options like batching, streaming, and multi-GPU help enhances mannequin serving efficiency.
- LitServe adapts to environments, from native machines to multi-GPU servers, making it appropriate for tasks of all sizes.
- LitServe handles advanced AI workloads by supporting authentication, compliance requirements, and extra.
References and Hyperlinks
Continuously Requested Questions
A. Whereas FastAPI is nice for REST APIs, it isn’t optimized particularly for resource-heavy AI mannequin serving. LitServe, constructed on prime of FastAPI, enhances mannequin serving by including options like batching, streaming, GPU acceleration, and autoscaling, that are essential for giant AI fashions, particularly for dealing with real-time predictions with excessive throughput.
A. Sure, LitServe helps each CPU and GPU acceleration. You may configure it to robotically detect and use accessible GPUs or give which GPUs to make use of. This makes it good for scaling throughout {hardware}.
A. Batching permits LitServe to group a number of incoming calls collectively, course of them in a single go, and ship the outcomes again. This reduces overhead and will increase the effectivity of mannequin inference, particularly for workloads requiring parallel processing on GPUs.
A. LitServe can serve all kinds of fashions, together with machine studying fashions, deep studying fashions, and huge language fashions (LLMs). It helps integration with PyTorch, TensorFlow, and Hugging Face Transformers, making it appropriate for serving imaginative and prescient, language, and multimodal fashions.
A. Sure, LitServe is simple to combine with present machine studying pipelines. It makes use of a well-recognized API primarily based on FastAPI, and with its customizable LitAPI class, you possibly can rapidly adapt your mannequin inference logic, making it seamless to serve fashions with out an excessive amount of refactoring your pipeline.
The media proven on this article is just not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used on the Creator’s discretion.



