Introduction
The log-normal distribution is an enchanting statistical idea generally used to mannequin information that exhibit right-skewed habits. This distribution has wide-ranging functions in varied fields, corresponding to biology, finance, and engineering. On this article, we are going to delve into the log-normal distribution, its key parameters, and easy methods to interpret them, in addition to discover some sensible examples to reinforce understanding.
Overview
- A log-normal distribution fashions information the place the pure logarithm of a variable follows a standard distribution, exhibiting constructive skewness.
- Perceive the form (σ), scale (m or eμ), and site (μ) parameters to interpret and apply the log-normal distribution.
- The log-normal distribution is linked to the conventional distribution; if X is log-normal, ln(X) is normally distributed, and vice versa.
- Estimate parameters μ σ from information utilizing strategies like Most Probability Estimation, which includes log transformation and calculating the imply and commonplace deviation.
- The log-normal distribution is extensively utilized in biology, finance, reliability engineering, and environmental science to mannequin right-skewed information corresponding to development charges, inventory costs, and time to failure.
What’s a Log-normal Distribution?
A log-normal distribution describes the likelihood distribution of a random variable when its logarithm follows a standard distribution. In less complicated phrases, if the pure logarithm of a variable X follows a standard distribution, then X follows a log-normal distribution. This distribution stays steady and options constructive skewness, that means it has an extended proper tail.
Key Parameters
There are primarily three parameters as follows:
- Form Parameter (σ): This parameter impacts the overall form of the distribution. Additionally it is the usual deviation of the log-transformed variable.
- Scale Parameter (m or eμ): This parameter stretches or shrinks the distribution’s graph. On this distribution, the size parameter is usually referred to as the median.
- Location Parameter (μ): This parameter determines the place on the x-axis the graph is positioned. It’s the imply of the log-transformed variable.
These parameters are crucial in understanding how this distribution behaves and the way it may be utilized to real-world information.
Additionally Learn: What’s Regular Distribution : An Final Information
Chance Density Operate
The likelihood density operate (PDF) of a log-normal distribution is given by:
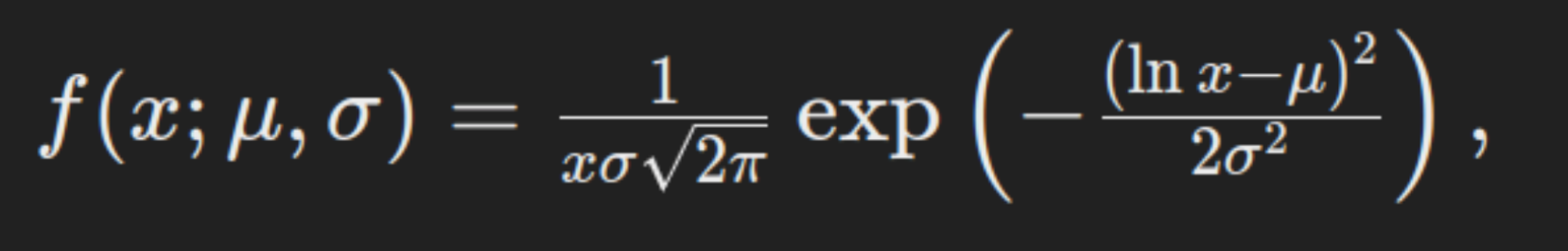
the place x>0, μ is the imply of the variable’s logarithm, and σ is the usual deviation of the variable’s logarithm. This components reveals that the log-normal distribution is outlined for constructive values solely, because the logarithm isn’t outlined for non-positive values.
Relationship with the Regular Distribution
One of the crucial attention-grabbing facets of its relationship with the conventional distribution. If X follows a log-normal distribution, Y = ln(X) follows a standard distribution. Conversely, if Y follows a standard distribution, X = eY follows a log-normal distribution. This relationship permits us to make use of well-established strategies for regular distributions to investigate log-normal information by remodeling the information utilizing logarithms.
Calculating Parameters from Knowledge
We frequently use strategies corresponding to Most Probability Estimation (MLE) to estimate the parameters of this type of distribution from information. Right here’s a simplified strategy to estimate μ and σ:
- Log-transform the information: Take the pure logarithm of all information factors.
- Calculate the log-transformed information’s pattern imply and commonplace deviation: These statistics would be the estimates for μ and σ.
For instance, think about a dataset of log-normally distributed incomes. By taking the pure logarithm of every earnings, we are able to compute the imply and commonplace deviation of those log-transformed values to estimate μ and σ.
Sensible Purposes
This distribution is extensively utilized in varied fields as a consequence of its capability to mannequin skewed information. Listed below are some examples:
- Biology: In organic research, organisms’ development charges typically observe a log-normal distribution as a result of development charges are multiplicative moderately than additive.
- Finance: Inventory costs are generally modeled utilizing log-normal distributions as a result of the proportion change in costs is generally distributed.
- Reliability Engineering: The time to failure of sure merchandise could be modeled utilizing a log-normal distribution, particularly when the failure course of is multiplicative.
- Environmental Science: The distribution of particle sizes in aerosols or the quantity of rainfall in a given interval.
Instance Calculation
Let’s think about a sensible instance to calculate the parameters of a log-normal distribution. Assume we have now the next earnings information (in 1000’s): 20, 22, 25, 27, 30.
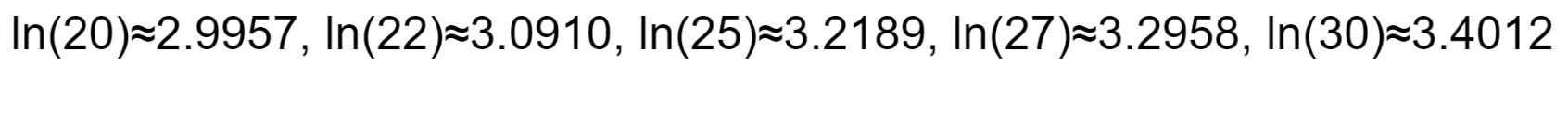
- Calculate the pattern imply μ:
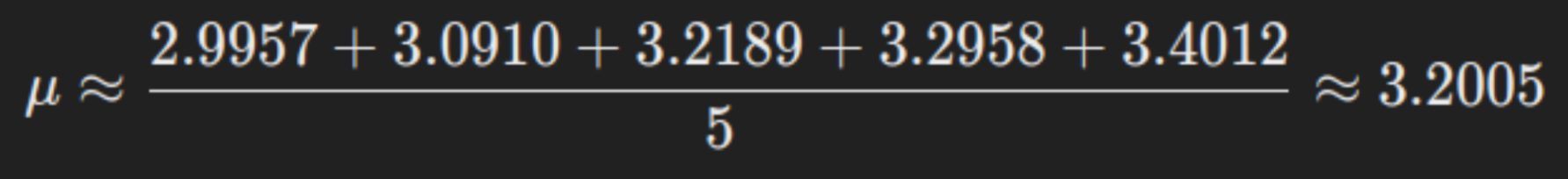
- Calculate the pattern commonplace deviation (σ):
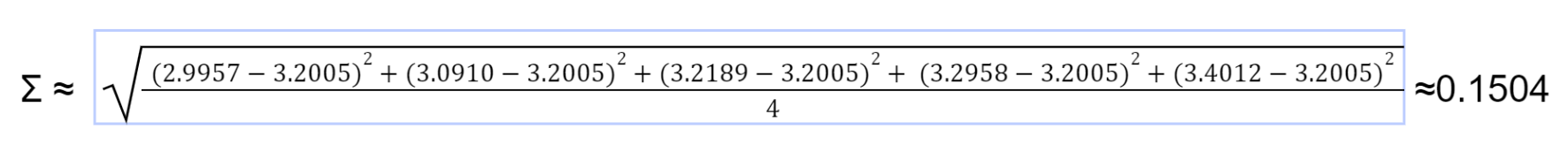
Thus, the estimated parameters for the log-normal distribution are μ approx 3.2005 and σ approx 0.1504.
Decoding the Parameters
- μ: That is the imply of the log-transformed information. In our instance, a μ of three.2005 signifies that the common of the pure logarithms of the incomes is round this worth.
- σ: That is the usual deviation of the log-transformed information. A σ of 0.1504 means that the log-transformed incomes are comparatively near the imply on a logarithmic scale.
Conclusion
The log-normal distribution is a robust software for modeling right-skewed information. We are able to successfully analyze and interpret information in varied fields by understanding its key parameters and their relationship with the conventional distribution. Whether or not coping with monetary information, organic development charges, or reliability metrics, it gives a strong framework for understanding and predicting habits.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
A. A lognormal distribution describes a variable whose logarithm is generally distributed, that means the unique variable is positively skewed and multiplicative elements trigger its variation.
A. The log of a standard distribution curve converts a lognormal distribution into a standard distribution, that means if 𝑋, is lognormally distributed, ln(𝑋), is generally distributed.
A. The log-normal distribution is vital as a result of it fashions many pure phenomena and monetary variables the place values are positively skewed, and it helps in understanding and predicting multiplicative processes.



