Introduction
Google Sheets is among the hottest and broadly used options to Excel. Its collaborative surroundings gives options akin to real-time modifying, and model management, and its tight integration with Google Suite which lets you name Google Sheets in Google Docs, helps to convey one of the best of the Google workspace. You’ll be able to simply load and work with Excel recordsdata programmatically utilizing Pandas, one of the vital standard knowledge science libraries. Equally, you’ll be able to replicate this setup with Google Sheets.
As Google Sheets is a SaaS providing, one must entry Google Sheets knowledge utilizing its API. You’ll be able to entry the API utilizing varied programming languages, together with Java, JavaScript, Node.js, PHP, Ruby, Python, and Google’s personal AppScript. For this text, we are going to concentrate on utilizing Python. By leveraging Python, we will effectively load Google Sheets knowledge into Pandas knowledge frames, a robust software for knowledge manipulation. This enables us to carry out transformations and analyses rapidly. As soon as our adjustments are full, we will push them again to Google Sheets utilizing the gspread Python library, which gives a handy interface for connecting to and interacting with the Google Sheets API.
Studying Targets
- Perceive methods to arrange a Google Cloud undertaking and create a service account for Google Sheets API entry.
- Discover ways to use the gspread library to work together with Google Sheets Automation utilizing Python.
- Grasp the methods for creating, sharing, and managing Google Sheets and worksheets through Python scripts.
- Uncover strategies for inserting, updating, and deleting rows, columns, and cells in Google Sheets utilizing Python.
- Discover methods to fetch and manipulate cell values and ranges from Google Sheets Programmatically.
This text was printed as part of the Knowledge Science Blogathon.
Setting-up your Google Cloud Venture
As talked about earlier, Google Sheets is a SaaS providing, so you must put together additional steps for automation. Google Cloud Platform (GCP), a preferred cloud computing platform, gives quite a lot of companies that assist to work together with Google merchandise together with the deployment of your customized tasks.
Broadly, we have to observe these 3 steps to get began with Google Sheets automation.
Creating and Configuring a Google Cloud Venture
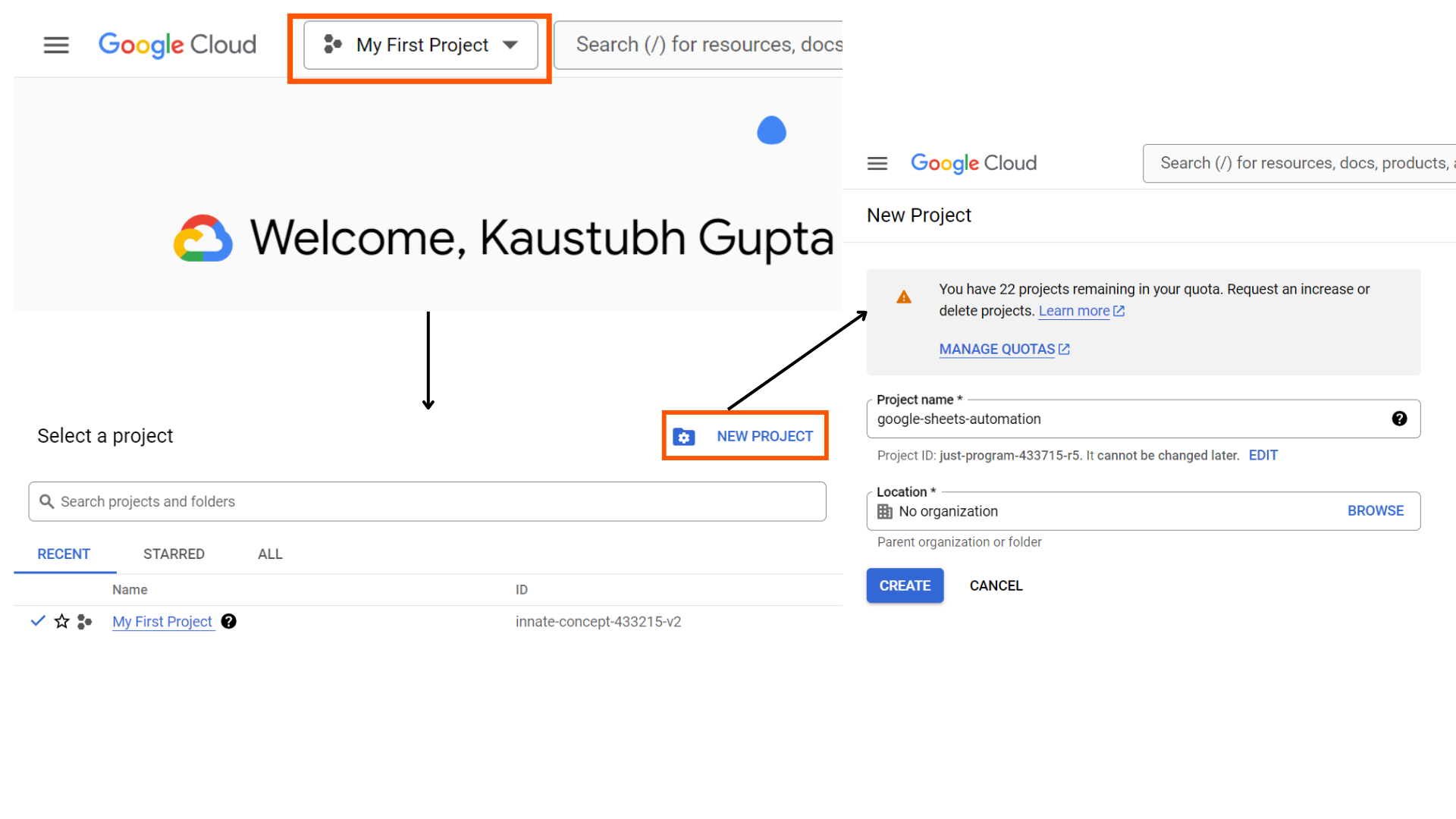
Head over to https://console.cloud.google.com/ and join a free account. Subsequent from the highest left, click on on the undertaking choice menu and choose new undertaking. Present a undertaking identify, leaving the group as “No group”, hit create and your GCP undertaking is about now.
Producing and Securing API Credentials
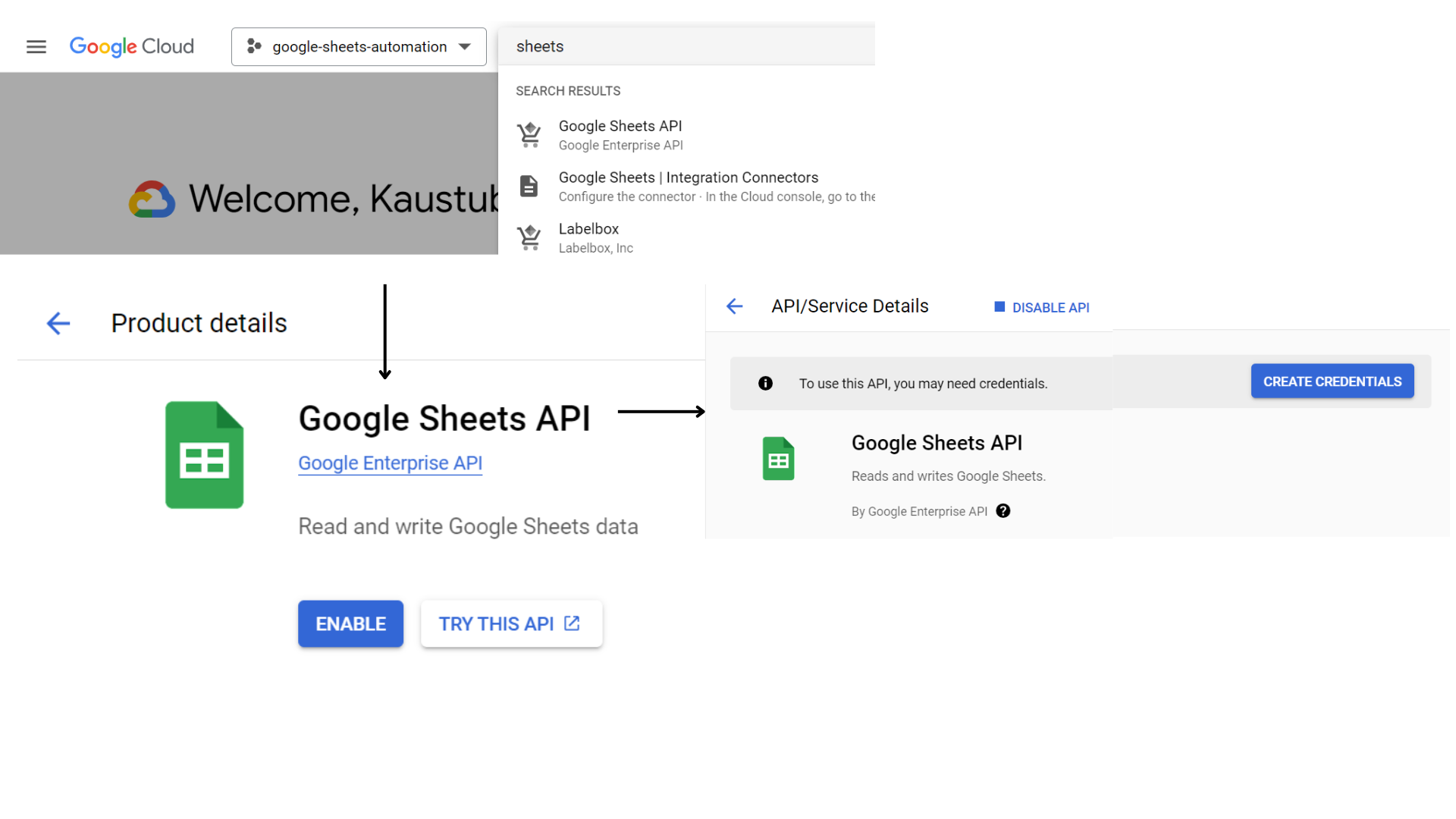
We have to allow the Google Sheets and Google Drive API and create a service account. This particular sort of account permits us to entry and handle Google Cloud sources with out requiring human interplay. To allow the Google Sheets API, seek for sheets within the high search bar and choose “Google Sheets API”. Click on permit and it’ll redirect us to the API particulars web page. Right here click on on “Create Credentials” and it’ll open up the credentials creation type.
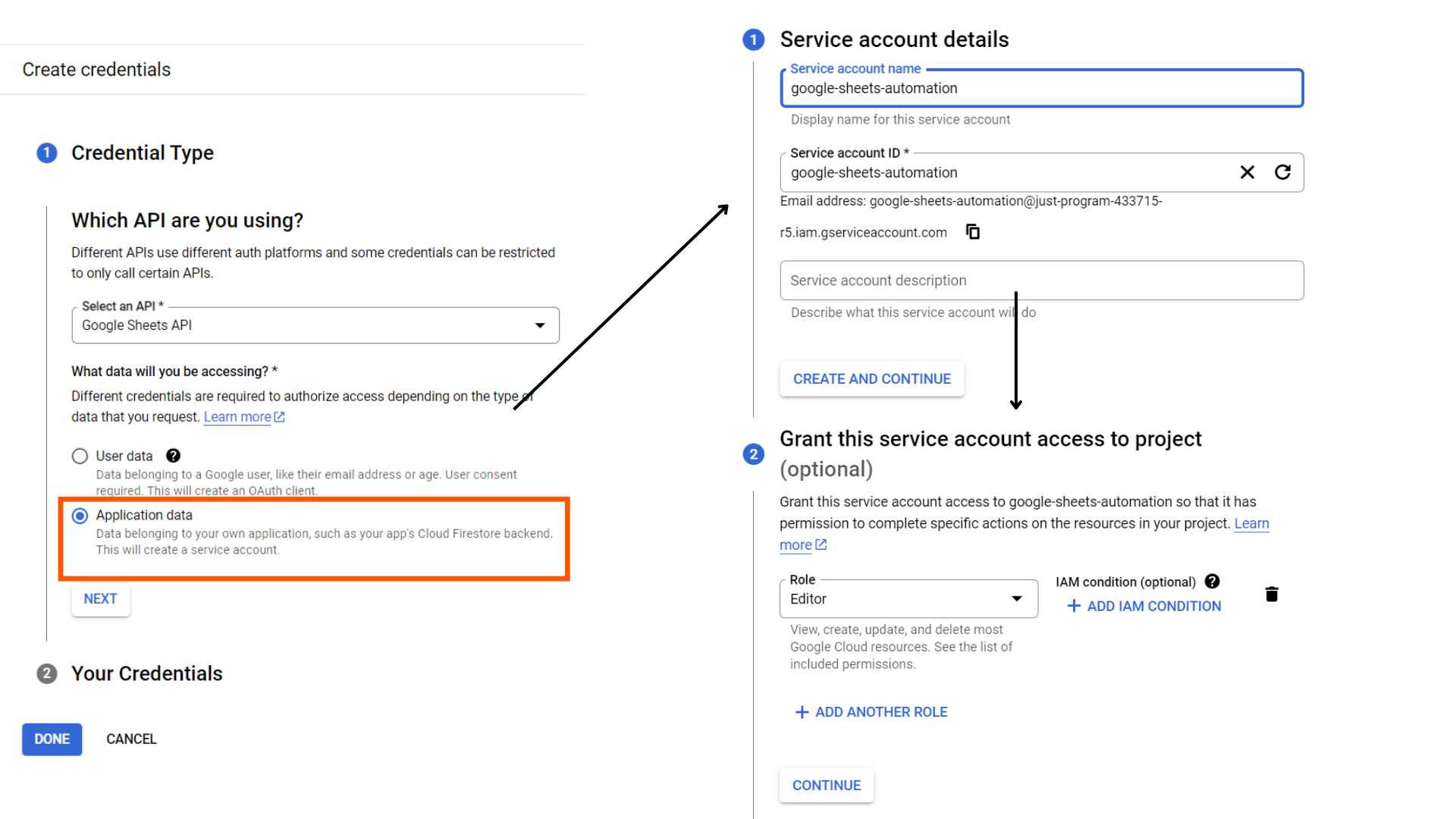
Choose “Utility Knowledge” from the choice field and click on Subsequent. On the following display, present a significant identify for the service account, as you’ll use it in later steps. Then, choose the “Editor” position. Lastly, click on Accomplished on the backside.
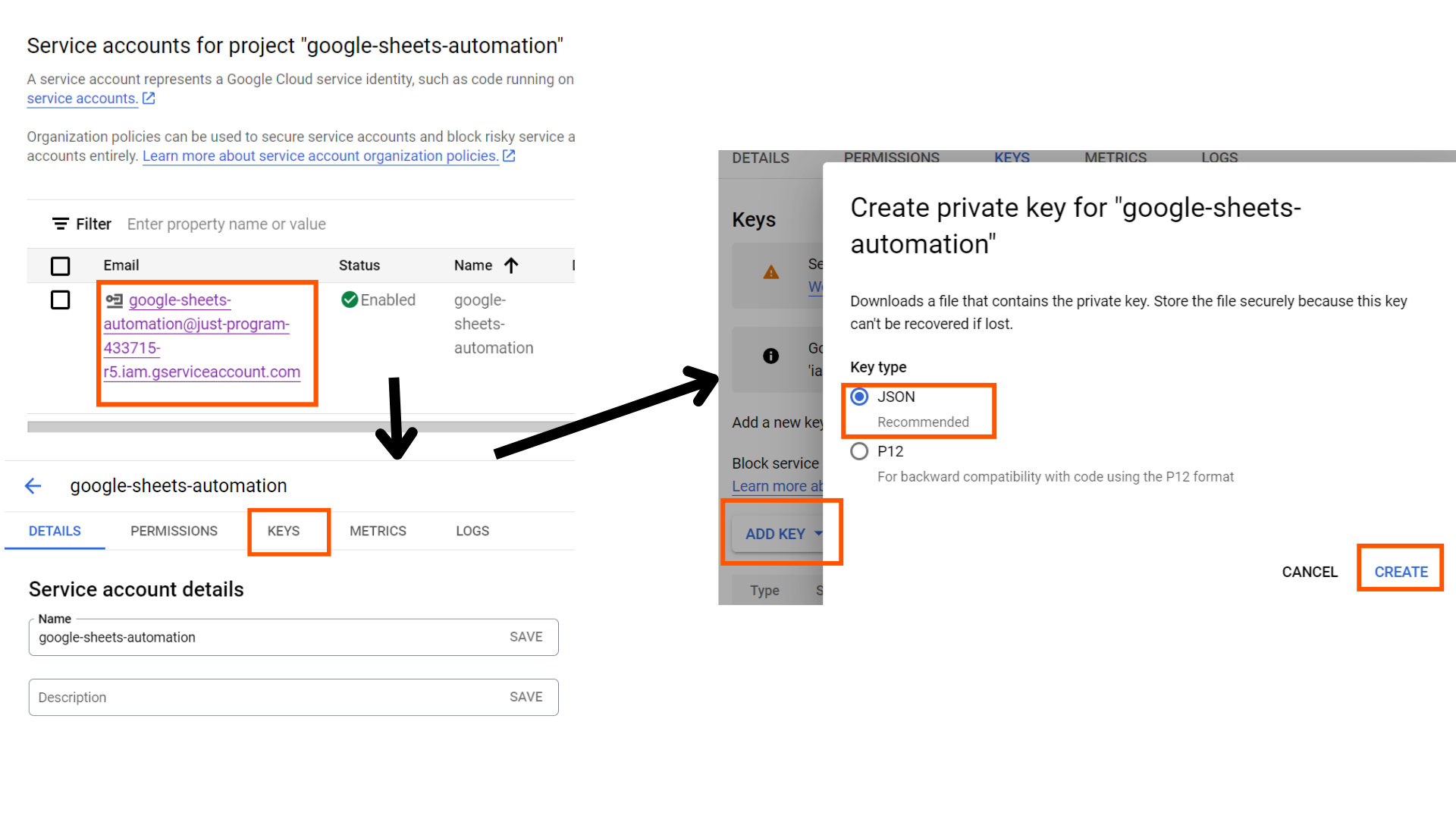
Equally, the Google Drive API might be enabled. Please word that we don’t have to create one other service account for this API. The prevailing service account will have the ability to entry each APIs. Now, we have to obtain the credentials JSON, which our Python script will devour to entry Google Sheets. Click on on the newly generated service account electronic mail, change to the keys tab, click on on the add key button to pick the create new key possibility, choose JSON, after which create.
Granting Entry to Google Sheets
Our Python script will use the generated credentials to entry Google Sheets. Nevertheless, we have to manually grant entry to the recordsdata that our script will use. To do that, copy the e-mail generated for the service account (discovered within the particulars tab of the service account) and add that electronic mail as an Editor to the specified recordsdata.
Understanding gspread
gspread is a Python API wrapper for Google Sheets. It encapsulates numerous functionalities supplied by the Google Sheets API underneath separate courses and entry strategies. It makes interplay with sheets API straightforward to navigate and one can rapidly choose it up.
To arrange the library within the native surroundings, one can use a easy pip command, as with every different Python bundle. Set up the library in a separate surroundings as a finest follow to keep away from any dependency conflicts.
pip set up gspreadA fast word on cell references
The cell addresses in Google Sheets might be referenced utilizing two standard notations:
- A1 notation: This cell reference consists of the sheet identify, row quantity, and column letter.This reference works with out mentioning the sheet identify and lets you discuss with a single cell, a variety of cells, or a whole column.
- Named vary: This can be a outlined vary of cells having a customized identify for simple identification and simplified reference throughout the Google Sheet.
Establishing Connection and Opening Spreadsheet
Now that we have now arrange the mandatory entry and libraries, let’s check our code. Within the spreadsheet containing the service account electronic mail, enter some random textual content within the first cell. We’ll try and retrieve this worth utilizing our Python script.
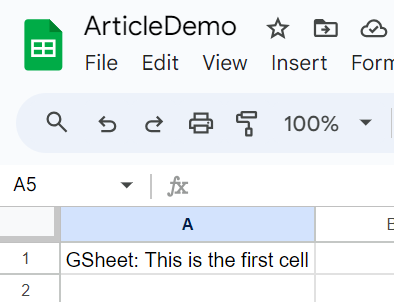
We’ll use the JSON module to load our credentials and cross it to the gspread’s “service_account_from_dict()” perform. This may return a Google Sheets consumer object and this object can be utilized to open any Google Sheet utilizing the “open()” perform. See the code beneath.
import gspread
import json
with open('creds.json') as f:
credentials = json.load(f)
gc = gspread.service_account_from_dict(credentials)
sh = gc.open("ArticleDemo")
There are two other ways to open a Google Sheet as an alternative of a title identify. These other ways get rid of the title identify dependency as in Google Workspace, a number of recordsdata can have the identical title. Within the case of spreadsheets, if there are two recordsdata with the identical title, then the most recent file can be accessed by the API. We are able to entry the spreadsheets utilizing the file URL or the spreadsheet’s distinctive ID which proceeds the next hyperlink: “https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/<unique_id>/edit”. Under is the code to entry the spreadsheet through URL or distinctive ID.
## Entry through distinctive ID
sh = gc.open_by_key("1R97twcM0FfFNSsrh_0FjDDg-HcQF5PLHbhRxu9pTV_Q")
## Entry through URL
sh = gc.open_by_url("https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1R97twcM0FfFNSsrh_0FjDDg-HcQF5PLHbhRxu9pTV_Q/edit?gid=0#gid=0")The next code will learn the worth entered earlier within the sheet. The code working can be defined within the later sections of the article.
print(sh.sheet1.acell('A1').worth)This may return the worth current within the A1 cell within the sheet, which in our case is “GSheet: That is the primary cell”. Now we’re all set to deep dive into the gspread library and discover all of the out there choices.
Notice: The sh variable holds the spreadsheet object and it will likely be referred to all through the information
Creating and Managing Google Sheets
There may very well be many use circumstances the place a spreadsheet is created programmatically. One may very well be constructing an answer to publish knowledge and insights for his or her customers. Together with this, they could wish to share this sheet instantly with the consumer.
- To create a brand new spreadsheet, use the
create()perform of the gspread consumer. Go the title of the brand new spreadsheet as a parameter, and if you wish to specify the situation, use thefolder_idparameter. - The brand new spreadsheet created is barely accessible by the service account consumer. It implies that the spreadsheet is not going to be seen even to the consumer who created the service account. For this goal, we will use the “share()” perform of the spreadsheet object. This perform requires 3 necessary parameters: “email_address” (electronic mail tackle), “perm_type” (permission sort), and “position”. The permission sort can take the next values: consumer, group, area, or anybody. For a lot of the use circumstances, the consumer worth will work. The perm_type additionally has a hard and fast variety of acceptable values: ‘reader’, ‘commenter’, ‘author’, ‘fileOrganizer’, ‘organizer’, and ‘proprietor’. There are some further elective parameters as nicely, providing a granular degree of data.
- “notify”: Boolean worth to regulate if the consumer ought to get a notification of the file shared.
- “email_message”: String worth for the message to be despatched together with the notification electronic mail.
sh = gc.create('ArticleDemoTest') ## Creating a brand new spreadsheet
sh.share(email_address="[email protected]", perm_type="consumer", position="author", notify=True, email_message="This can be a check file")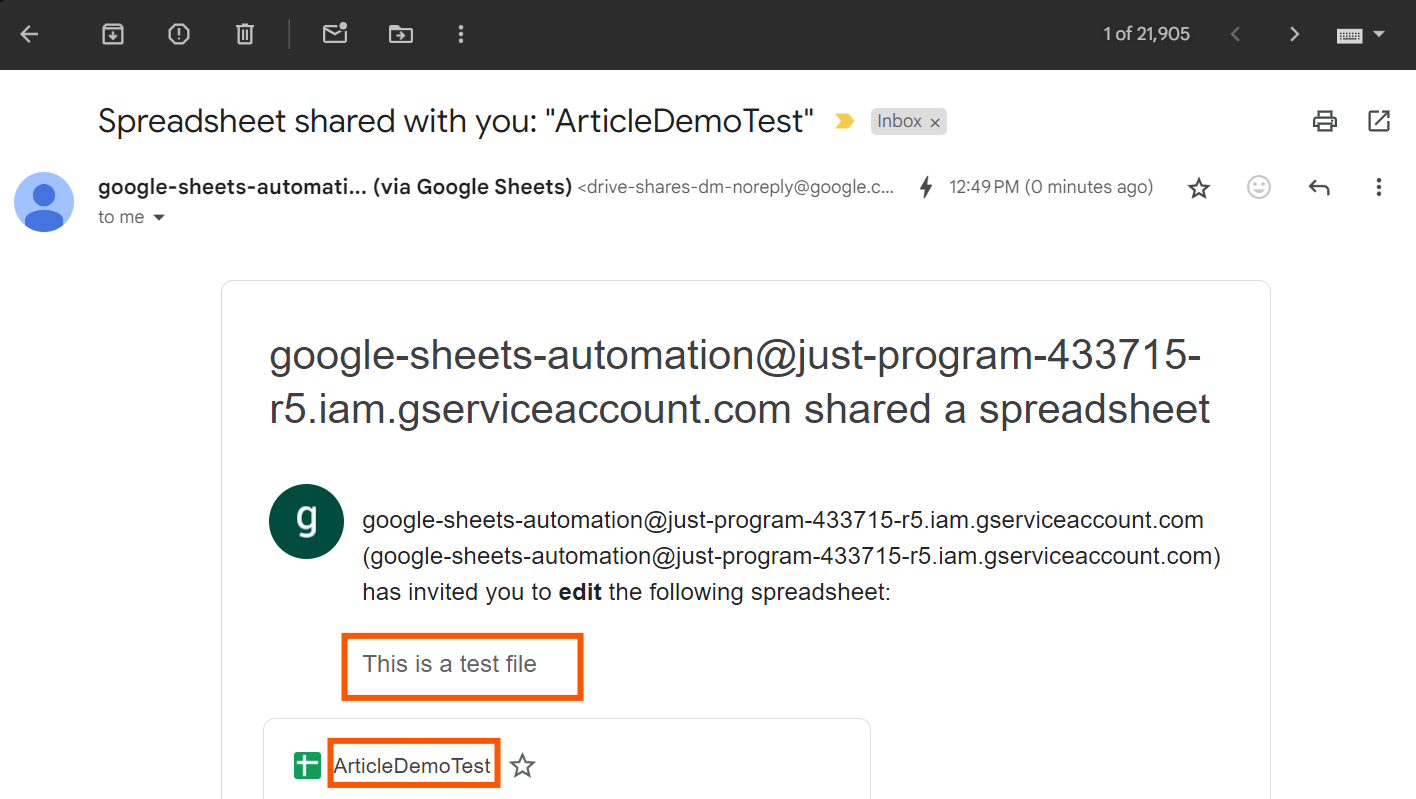
Managing Worksheets
Each spreadsheet is a set of worksheets. A easy analogy to that is how a ebook has a number of pages. Utilizing gspread, customers can entry, modify, delete, or create new worksheets. Let’s check out every of those capabilities.
Worksheet Choice
The worksheet(s) of a spreadsheet object might be accessed utilizing the next strategies of the worksheet object:
- Entry by index: The “get_worksheet()” perform takes within the index of the worksheet that must be accessed.
- Entry by title: The “worksheet()” perform takes within the title of the worksheet. Do word that the worksheet titles are distinctive by nature and due to this fact, no two worksheets can have the identical title.
- Entry by dot notation shortcut: The dot notation shortcut permits accessing the primary worksheet of the spreadsheet with out giving out a title, index, or ID.
- Entry all: The “worksheets()” perform returns all of the worksheets of the spreadsheet. It returns them as gspread worksheet objects. The “title” and “id” are a couple of essential properties of this class that assist in accessing desired worksheets in a bulk method.
- Entry by ID: Whereas growing automation scripts, there may be some use circumstances the place we’re coping with worksheet ID as an alternative of titles. In such eventualities, the “get_worksheet_by_id()” perform can be utilized.
Right here is the pattern code for all of the listed strategies.
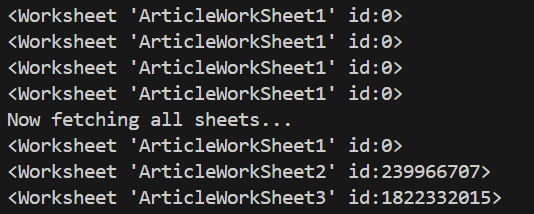
print(sh.get_worksheet(0))
print(sh.worksheet("ArticleWorkSheet1"))
print(sh.sheet1)
print(sh.get_worksheet_by_id(0))
print("Now fetching all sheets...")
## Returning all worksheets
for ws in sh.worksheets():
print(ws)All of those print statements return the worksheet object
Making a New Worksheet
Other than present worksheets within the spreadsheet, we will programmatically create new worksheets in the identical spreadsheet. This strategy might be helpful when processing knowledge from an present worksheet and publishing the leads to a separate worksheet.
To create a brand new worksheet, we have to use the “add_worksheet()” perform of the worksheet object. It takes the next parameters.
- title: The title of the worksheet
- rows, columns, index (elective): We have to outline the variety of rows and columns for the newly created worksheet. The “index” parameter is elective and it controls the ordering of the worksheet.
The beneath code will create a worksheet with 100 rows and 20 columns and place the worksheet within the second place.
sh.add_worksheet('ArticleWorkSheet1.5', rows=100, cols=20, index=1)
And it did place it within the second place (index + 1)

Renaming a Worksheet
You’ll be able to rename worksheet titles utilizing the update_title() perform of the worksheet object, which accepts the brand new title as a parameter.
print(sh.worksheet("ArticleWorkSheet3").update_title("ArticleWorkSheet2.5"))
Deleting a Worksheet
A worksheet might be deleted from a spreadsheet utilizing the next perform of the worksheet object:
- Delete a worksheet utilizing the worksheet object: “del_worksheet()” perform takes the worksheet object as a parameter and deletes the worksheet from the spreadsheet.
- Delete a worksheet utilizing the worksheet ID: “del_worksheet_by_id()” perform takes the worksheet ID as enter for deleting the worksheet.
The collection of which perform to make use of depends upon the use case the script is made. Under is the code pattern demonstrating the utilization of each capabilities.
sh.del_worksheet(sh.worksheet("ArticleWorkSheet2.5"))
sh.del_worksheet_by_id('602396579')Cell Properties
We’re slowly narrowing down from high to backside and reaching the smallest (and most essential) unit of our worksheet, a cell. A cell is an intersection of a row and a column. For gspread library, it holds the next properties:
- row: Row quantity for the cell
- col: Column quantity for the cell
- worth: The worth of the cell
- tackle: The tackle of the cell within the A1 notation
The beneath pattern code accesses all of the properties of a cell. The actual cell for inspection is returned utilizing the cell perform of the worksheet.
sampleCell = sh.worksheet("ArticleWorkSheet1").cell(row=1, col=1)
print('Row: {}nColumn: {}nValue: {}nAddress: {}'.format(sampleCell.row, sampleCell.col, sampleCell.worth, sampleCell.tackle))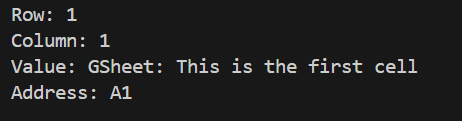
All these accessors will come into play as soon as we’re coping with higher-order capabilities of the library.
Including New Rows and Columns
Let’s start including new rows and columns to our present pattern worksheet to have some knowledge to work on for the later sections of this information. The insertion as an operation is supported in two methods by the gspread library.
Insertion at a selected place
You’ll be able to insert a row or column at a particular place utilizing the insert_row(), insert_rows(), and insert_cols() capabilities of the worksheet object. These capabilities permit us so as to add the row(s) or columns at a selected location in a worksheet. The perform specifics are as beneath:
- insert_row: The perform requires the “values” parameter as a listing of values to insert. The order of values within the checklist determines the order of the inserted rows. The “index” parameter, which defaults to 1, specifies the place for row insertion. Non-obligatory parameters like “value_input_option” and “inherit_from_before” management how the perform interprets the enter knowledge and rows, and whether or not it ought to push the info instantly or parse it as if the consumer is typing within the UI.
- insert_rows: It takes the checklist of lists within the “values” parameter for inserting a number of rows. Every checklist acts as a single row. Internally, that is the precise implementation of how the rows are inserted into the worksheet through gspread. “The insert_row()” perform calls the “insert_rows()” perform and due to this fact, all of the parameters described for the “insert_row()” perform stand true for “insert_rows()” besides one parameter. Within the
insert_row()perform, you establish the offset utilizing theindexparameter, whereas within theinsert_rows()perform, you specify it with therowparameter. - insert_cols: This perform is a duplicate of the “insert_rows()” perform with a modified parameter identify for offset from “row” to “col”. The remainder of the elective parameter functioning stays the identical.
Insertion after a desk vary
This insertion is barely relevant to rows. It permits us to insert rows after a selected desk vary, the place the place is unknown. Once more, the insertion might be performed in a single or multi-row method.
- append_row: It takes within the row values as a listing through the “values” parameter. The “table_range” parameter helps outline the desk vary after which the row insertion ought to occur. The vary is given in A1 notation.
- append_rows: Likewise the “insert_rows()”, the “append_rows()” is the precise implementation of rows insertion after a desk vary. All of the parameters for each capabilities stay the identical with the distinction that “append_rows()” takes a listing of lists within the “values” parameter.
Right here is the pattern code that:
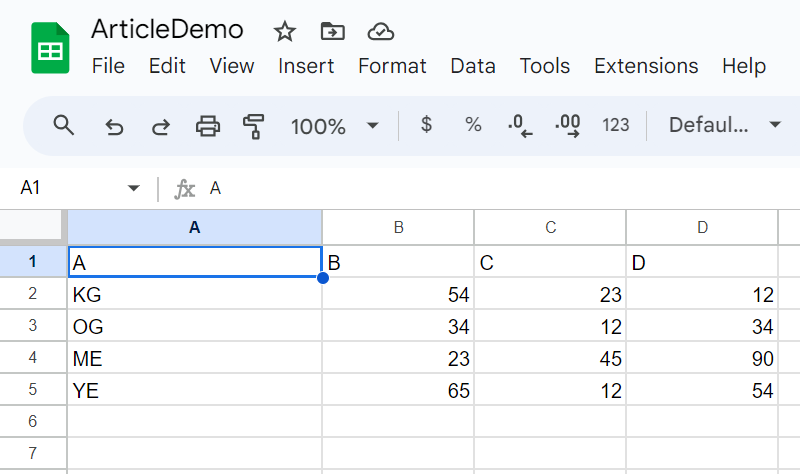
- Provides a row for columns: A, B, C, and D
- Provides 4 rows underneath these columns
sampleWorksheet.insert_row(
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']
)
sampleWorksheet.insert_rows(
[
['KG', 54, 23, 12],
['OG', 34, 12, 34],
['ME', 23, 45, 90],
['YE', 65, 12, 54]
], row=2
)
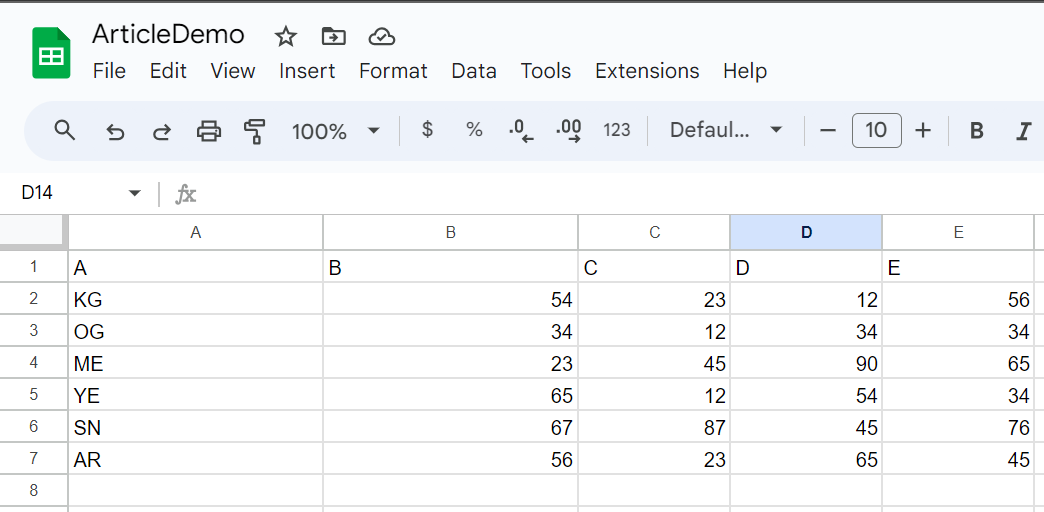
Now, let’s do the next steps on high of this:
- Append 2 rows to proceed on this desk vary
- Add one other column E
sampleWorksheet.append_rows(
[
['SN', 67, 87, 45],
['AR', 56, 23, 65]
],
table_range="A1:D5"
)
sampleWorksheet.insert_cols(
[
['E', 56, 34, 65, 34, 76, 45]
],
col=5
)
Notice: The sampleWorksheet variable holds the worksheet object and it will likely be referred to all through the information.
Fetching Cells and Ranges Values
Within the final sections, we have now ready our knowledge programmatically utilizing varied insertion operations. Now, we will fetch the info inserted utilizing varied learn capabilities. We’ll see methods to fetch cells after which transfer to fetch values from a variety of cells and your complete worksheet.
Fetching Single Cell
Probably the most fundamental learn operation on a worksheet entails getting the worth or every other cell property as described within the earlier sections. To fetch a single cell, there are two capabilities:
- acell: This takes the cell tackle within the A1 notation and returns a cell object.
- cell: This takes the cell coordinates within the order of (row, column).
Each these capabilities return a cell object and we have now already seen methods to get the worth from these objects. The acell perform was used within the part the place we established a reference to the Google Sheets API.
print(sampleWorksheet.acell('A1').row)
print(sampleWorksheet.cell(1, 1).worth)Fetching all Cells of the Worksheet or Vary
- We are able to get all of the cells of the worksheet in a listing of cell objects utilizing the “get_all_cells()” perform of the worksheet object. There isn’t any parameter for this perform and it may be instantly known as on a worksheet object.
- To fetch cell objects for a particular vary, use the
vary()perform of the worksheet object. This perform accepts varied enter kinds, akin to A1 notation, numeric boundaries, or named ranges. If used with out enter, it returns all cells within the worksheet in a single API name. To be used circumstances involving cell properties, this perform helps filter out the specified cells and carry out additional actions.
print(sampleWorksheet.get_all_cells())
print(sampleWorksheet.vary('B4:E5'))Fetching Values of Vary of Cells
Customers normally create a number of miniature tables in the identical worksheet for higher accessibility. In such circumstances, we have to refine our fetching vary to the precise addresses of those desk ranges. To fetch such desk ranges, we will use the next two capabilities of the worksheet object:
- get: The “get()” perform takes the desk vary in A1 notation or a named vary and returns the checklist of lists of values.
- batch_get: The “get()” perform can solely take one vary, but when we’re coping with a number of ranges, we will use batch_get. This perform makes one API name, saving up price.
print('Get Vary: {}'.format(sampleWorksheet.get("A1:D4")))
print('Batch Get Vary: {}'.format(sampleWorksheet.batch_get([
"A1:D4",
"B4:E3"
]))
Fetching all Values from a Row or Column
We are able to fetch all of the values of a row or column utilizing the “row_values()” and “col_values()” capabilities of the worksheet object. Each capabilities take the place (numbering from 1) of a row or column and return the values in a listing.
print(sampleWorksheet.row_values(1))
print(sampleWorksheet.col_values(4))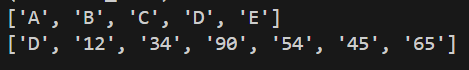
Fetching Total Worksheet Values
Among the finest use circumstances of fetching a whole worksheet could be to load this knowledge instantly right into a pandas knowledge body after which do the post-processing or evaluation as per the requirement. The complete knowledge might be returned utilizing following capabilities of the worksheet object:
- Listing of Lists: The “get_all_values()” perform returns each row as a listing after which all rows lists in a single checklist. This perform is an alias to the “get_values()” perform however curiously, the “get_values()” perform is carried out utilizing the “get()” perform. The “get()” perform with none inputs returns the checklist of lists. Subsequently all 3 capabilities are the identical.
- Listing of Dictionaries: The “get_all_records()” perform returns a listing of dictionaries. Every dictionary is a key-value mapping the place the keys are the first-row values and the values because the next-row values. Each row will get its dictionary. By default, it assumes that the primary row is the important thing however we will make it conscious of a unique row as a key utilizing the “header” parameter. There are some further parameters as nicely that may assist in dealing with empty cells, and anticipated headers.
You’ll be able to instantly cross the outputs of each capabilities to the Pandas DataFrame perform to acquire the worksheet desk as a Pandas DataFrame.
import pandas as pd
print(pd.DataFrame(sampleWorksheet.get_all_records()))
print(pd.DataFrame(sampleWorksheet.get_all_values()))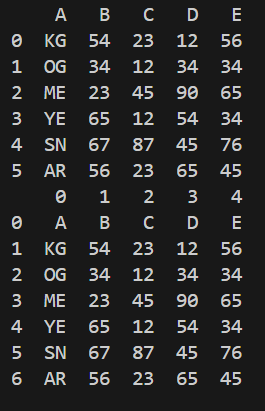
Updating Cells and Ranges
Updating the present knowledge of the spreadsheet is essentially the most essential perform that may be carried out simply utilizing gspread library capabilities. There are a number of methods to replace the cells of a spreadsheet, single cell updation to a number of cells of a variety after which to a number of ranges with a single API name.
Updating a Single Cell
A single cell of a worksheet might be up to date utilizing the next capabilities of the worksheet object.
- update_acell: This perform takes two parameters, the cell tackle within the A1 notation and the worth to be up to date
- update_cell: This perform takes the coordinates of the cell within the row-column order and the worth for updation
- replace: Though this perform has an even bigger scope for updating a number of cells, it will also be used to replace a single cell. The enter parameters order is totally different from the above two capabilities. The “replace()” perform takes a listing of lists as the primary worth after which the cell tackle.
print(sampleWorksheet.update_acell('A2', 'Kaustubh'))
print(sampleWorksheet.update_acell('A3', 'Oggy'))
print(sampleWorksheet.replace([['Hello']], 'A4'))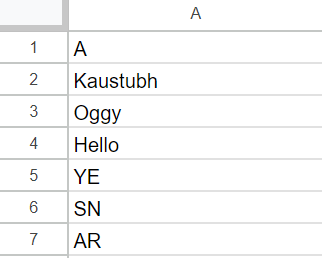
Updating a Vary of Cells
You’ll be able to replace a variety of cells in a worksheet utilizing the next two capabilities from the worksheet object.
- update_cells: This perform works finest together with the “vary()” perform. The “update_cells()” perform takes enter because the checklist of cells. This checklist of cells can have their values modified by looping over the cell objects returned from the vary perform and accessing their worth property.
- replace: As beforehand seen in single-cell updates, you need to use this perform to replace a named vary or an A1-notated vary.
rangeOfCells = sampleWorksheet.vary('B2:B7')
for cell in rangeOfCells:
newValue = int(cell.worth) + 10
cell.worth = newValue
print(sampleWorksheet.update_cells(rangeOfCells))The above code fetches a variety of cells, provides 10 to their worth, and updates them in a single API name.
Updating A number of Vary of Cells
Within the above part, we had been capable of replace a number of cells in a variety with a single API name. This conduct might be prolonged to a number of ranges as nicely. It means we will replace a number of teams of cells with one name. The “batch_update()” perform takes a listing of dictionaries with keys as vary and values. The vary key worth must be the A1 notation vary or a named vary and the values key worth because the checklist of checklist of values.
range1 = 'C2:C7'
range2 = 'E2:E7'
bothRangeValues = sampleWorksheet.batch_get([
range1,
range2
])
range1Values, range2Values = bothRangeValues
range1UpdatedValues = [[int(x[0]) + 10] for x in range1Values]
range2UpdatedValues = [[int(x[0]) + 20] for x in range2Values]
print(sampleWorksheet.batch_update([
{
'range': range1,
'values': range1UpdatedValues
},
{
'range': range2,
'values': range2UpdatedValues
}
]))The above code fetches two ranges utilizing the “batch_get()” perform, then updates their values regionally, after which makes use of the “batch_update()” perform to push again the up to date values to the Google Sheets. The output of this replace appears like this:

Deleting Rows and Columns
Until this level, we have now inserted, learn, and up to date the info within the worksheet. We are able to carry out delete operations to take away redundant or pointless knowledge from the worksheet. The “delete_rows()” and “delete_colums()” perform takes the “start_index” to be deleted. If “end_index” is specified, then it deletes all of the columns within the index vary of begin and finish.
print(sampleWorksheet.delete_columns(4))
print(sampleWorksheet.delete_rows(6))Looking Cells
The Google Sheets API lets you seek for cells by matching a string or an everyday expression. You’ll be able to carry out case-sensitive or case-insensitive searches and slim the search to particular rows or columns if desired. Use these two worksheet capabilities to seek out matching cells:
- discover: The “discover()” perform returns the primary incidence of the match. This takes within the search string or a regex, “in_row” or “in_column” parameters to slim down the search and the “case_sensitive” flag to regulate the search sort. The “in” parameters take the row or column positions (index + 1)
- findall: The “findall()” is the superior stage of the “discover()” perform the place it returns all of the matches of the search.
import re
print(sampleWorksheet.discover('64', in_column=2))
searchRe = re.compile(r'(a|A)')
print(sampleWorksheet.findall(searchRe))
Formatting Cells
In Excel, you’ll be able to format worksheets in varied methods, together with textual content highlights, formatting, borders, alignment, and quite a few capabilities. The Google Sheets additionally gives quite a lot of formatting choices for cells. The entire checklist of fields is on the market in Google Sheets Cells documentation.
You should utilize the format() perform of the gspread worksheet object to specify the cell or vary the place you wish to apply formatting. Present the format as a JSON dictionary, which incorporates all of the formatting key fields and their values.
The beneath code will apply borders to all of the cells of the desk.
borderFormatting = {
"fashion": "SOLID",
"colorStyle": {"rgbColor": {"purple": 0, "inexperienced": 0, "blue": 0, "alpha": 1}},
}
print(
sampleWorksheet.format(
"A1:D6",
format={
"borders": {
"high": borderFormatting,
"backside": borderFormatting,
"left": borderFormatting,
"proper": borderFormatting,
},
},
)
)We are able to additionally apply batch formatting to format a number of ranges on the similar time. This protects numerous time writing totally different format calls for each new change. The “batch_format()” perform takes the checklist of dictionaries containing two essential keys. The primary secret is the vary key which defines the cell’s scope and the format key which accommodates the formatting dictionary.
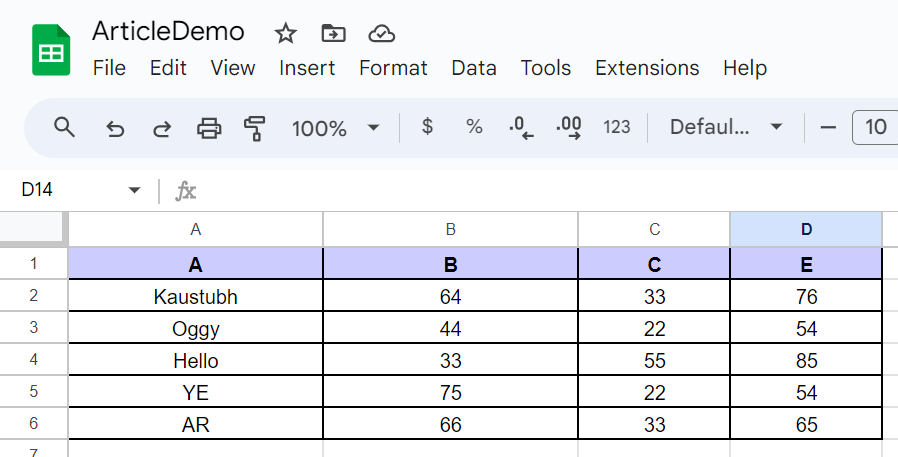
Let’s do the next on our pattern desk utilizing the “batch_format()” perform:
- Apply borders to all of the cells of the desk.
- Daring the textual content of the primary row, indicating that these are the columns of our desk.
- Align all the info within the heart.
- Add a light-weight blue shade for the columns (the primary row).
borderFormatting = {
"fashion": "SOLID",
"colorStyle": {"rgbColor": {"purple": 0, "inexperienced": 0, "blue": 0, "alpha": 1}},
}
codecs = [
{
"range": "A1:D6",
"format": {
"borders": {
"top": borderFormatting,
"bottom": borderFormatting,
"left": borderFormatting,
"right": borderFormatting,
},
"horizontalAlignment": "CENTER",
},
},
{
"range": "A1:D1",
"format": {
"textFormat": {
"bold": True,
},
"backgroundColorStyle": {
"rgbColor": {"red": 0.8, "green": 0.8, "blue": 1, "alpha": 0.8}
},
},
},
]
print(sampleWorksheet.batch_format(codecs))
And that is the ultimate state of our desk.
Clear Vary of Cells and Worksheet
It may be potential that we wish to clear the vary earlier than finishing up the operations. For clearing the cell ranges, the “batch_clear()” perform of the worksheet object can be utilized. This takes the checklist of ranges that must be cleared. Let’s clear column C from our pattern desk.
print(sampleWorksheet.batch_clear(["C1:C6"]))
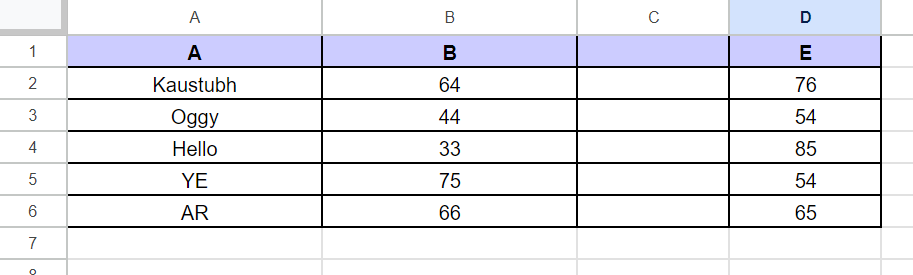
Notice: Clear perform solely clears the values and never the formatting utilized.
The complete worksheet might be cleared utilizing the “clear()” perform of the worksheet object.
print(sampleWorksheet.clear())Limitations of Google API
We have now performed numerous operations on Google Sheets utilizing the gspread library. This library is only a wrapper that prepares the user-passed knowledge into the format that’s acceptable and makes the API calls to Google tasks related to the sheets.It really works in order that the developer doesn’t want to know the underlying API calls, payloads, and responses. The developer interacts solely with the abstracted capabilities.
Whereas that is good for builders who’re simply taking part in round, for manufacturing and important duties, a developer wants to know how the API calls are consuming the quota. Whereas the utilization of Google Sheets API is free, there are some restrictions to what number of API calls might be made.
As a consequence of such limitations, numerous customers encounter the well-known 429 error that reads as “Too many requests”. For instance, the present quota is 300 requests per minute per undertaking. For some purpose, in case your script is sending greater than 300 requests, then the extra requests is not going to be processed. Exponential backoff is one such methodology that implements a retry mechanism based mostly on producing random wait occasions. Such mechanisms might be deployed to deal with these limitations.
Conclusion
On this information we created a Google Service account to carry out all of the operations one would carry out on the Google Sheets UI. We explored numerous capabilities akin to including, updating, and deleting knowledge. We additionally explored methods to format sheets and Google Sheets Automation utilizing Python.
The Google Sheets API gives much more functionalities akin to merging cells, making protected ranges, hiding cells, including notes, copy ranges, and even including filters, all operations programmatically! Whereas the documentation for the gspread library lacks these explanations, one can go forward to discover the Google Sheets official documentation and likewise examine the API reference part of the gspread documentation that offers high-level details about all of the capabilities carried out within the library.
Key Takeaways
- Google Sheets automation requires organising a Google Cloud Venture, which incurs no price. Nevertheless, when you don’t optimize the code, you would possibly exhaust the quota, resulting in errors later within the code. Purpose to make use of the batch perform wherever potential.
- There are various prospects of what might be achieved utilizing Google Sheets API and the gspread library is simply a place to begin. One ought to discover the official documentation to implement the functionalities lacking within the library (and perhaps contribute again)
- You should utilize Google Sheets automation setups to construct sourcing pipelines that preserve a grasp document and push it to a extra superior database, like an OLAP database. Join these databases to BI software program, akin to Tableau, to finish an end-to-end undertaking.
- Google Sheets automations may also help you get rid of guide knowledge entry by organising workflows that mechanically replace, import, or arrange knowledge, considerably enhancing effectivity.
- Utilizing Google Sheets automations, you’ll be able to schedule recurring duties akin to sending studies, performing calculations, or updating cells, lowering the necessity for repetitive guide actions.
If you wish to learn/discover each article of mine, then head over to my grasp article checklist.
I hope you appreciated my article. For any doubts, queries, or potential alternatives, you’ll be able to attain out to me through LinkedIn — in/kaustubh-gupta
Regularly Requested Questions
A. A retry mechanism must be carried out that tries to make the requests once more in a while. One such instance is the exponential backoff algorithm
A. batch_get, batch_update, batch_format, and batch_clear are a number of the generally used batch capabilities.
A. You should utilize the format() and batch_format() capabilities to cross the vary of cells and the formatting to be utilized in a dictionary. The dictionary accommodates varied fields you can format.
A. You’ll be able to arrange Google Sheets automations utilizing built-in instruments like Macros and Google Apps Script. Macros permit you to document actions and replay them, whereas Google Apps Script allows you to create customized automations utilizing JavaScript. These automations can streamline repetitive duties akin to knowledge entry, formatting, or working particular capabilities mechanically in Google Sheets.
A. In style Google Sheets automations for knowledge evaluation embrace automated knowledge import from exterior sources, scheduled studies utilizing Google Apps Script, and conditional formatting to spotlight tendencies. These automations assist optimize the info evaluation course of, making Google Sheets a robust software for managing and deciphering giant datasets effectively.
The media proven on this article is just not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used on the Creator’s discretion.



