Introduction
Within the fast-paced software program growth business, mastering sturdy software administration and easy deployment is essential. Docker, a game-changing know-how, has revolutionized software program distribution, operating, and bundles by separating functions from infrastructure, enabling fast software program supply. It improves portability, scalability, and workflow optimization, making it a typical element in present growth practices. This text goals to elucidate the complexities of Docker and reveal its software by Flask software dockerization.
Docker is a software program platform that revolutionizes the best way we encapsulate and deploy software program. Its core idea is containerization, which gives a manageable, unbiased setting for executing functions. This standardization standardizes the packaging of every part from code to dependencies, permitting builders to construct, ship, and run functions throughout numerous environments.
What’s Docker?
Docker is a platform for creating, delivery, and operating functions utilizing containerization know-how. It allows builders to bundle functions and their dependencies into light-weight containers, which might run persistently throughout completely different environments. This facilitates simpler deployment, scaling, and administration of functions.
Parts of Docker
- Docker Picture: Docker photographs are the inspiration of containers, a light-weight, executable bundle containing libraries, configuration recordsdata, and dependencies. They’re immutable and can’t be modified as soon as fashioned.
- Docker Containers: Docker containers are host machine situations of Docker photographs, encapsulating software code, runtime, system instruments, libraries, and settings. They supply consistency, portability, and ease of development, begin, cease, or termination.
- Information Quantity: Docker volumes retailer and share information between containers and host techniques, preserving database recordsdata, configuration recordsdata, logs, and different information past a container’s lifecycle. They provide efficiency, dependability, and suppleness in containerised settings.
- DockerFile: Dockerfiles are textual content recordsdata with directions for creating Docker photographs, together with set up, copying, setting setting variables, configuring, and operating. They allow automated, reproducible picture builds, permitting builders to create customized photographs for distinctive functions.
- Docker Engine: The Docker Engine, the core element of the Docker platform, manages volumes, networks, photographs, and containers. It includes subcomponents just like the Docker shopper and Docker daemon, and extra parts just like the Docker API and plugins.
These parts type the inspiration of the Docker platform, enabling builders and operators to construct, ship, and run functions effectively and reliably in any setting.
What’s Containerization?
A container is a typical software program unit that encapsulates code along with all of its dependencies to allow fast and reliable software execution throughout numerous computing environments. Code, runtime, system instruments, system libraries, and settings are all included in a small, standalone, executable software program bundle often known as a Docker container picture.
Within the case of Docker containers, photographs grow to be containers throughout Docker Engine operation. Container photographs grow to be containers throughout runtime. Containerised software program is accessible for each Home windows and Linux-based apps, and it’ll all the time operate the identical means whatever the infrastructure. Containers enable software program to be remoted from its environment and assure constant operation even in instances of variations, akin to between growth and staging environments.
How is Containerization Totally different From Digital Machine?
What differentiates Docker from different choices for containerisation? Its adaptability, effectivity, and ease of use are its main parts. Docker containers share the host OS kernel, that means they function higher and use fewer assets than digital machines, which want separate working techniques and lots of overhead. The utilisation of a light-weight approach not solely quickens deployment occasions but additionally facilitates swift scaling and efficient useful resource administration, that are essential traits within the present dynamic computing setting.
Whereas digital machines (VMs) additionally allow operating a number of functions on a single bodily machine, they function on the {hardware} degree, requiring a separate working system (OS) for every VM. In distinction, Docker containers share the host OS kernel, leading to considerably decrease overhead and sooner startup occasions. Docker containers are additionally extra light-weight and moveable in comparison with VMs, making them very best for microservice architectures and cloud-native functions.
Understanding Docker Instructions
Earlier than Beginning with dockerization of our flask app, lets perceive the essential docker instructions.
docker run command
The docker run command is used to create and begin a brand new Docker container based mostly on a specified picture. It lets you specify numerous choices and parameters to customise the container’s habits. For instance:
docker run <img>docker ps command
The docker ps command is used to record all operating Docker containers. It supplies info such because the container ID, picture used, command being executed, creation time, standing, and ports mapping. If you wish to see all containers, together with these which are stopped, you need to use the -a flag.
docker ps -adocker rm command
The docker rm command is used to take away a number of Docker containers. It’s essential specify the container ID or identify of the container(s) you wish to take away. You may take away picture with rmi.
docker rm <name_container/id_container>
docker rmi <image_name/id>There are instructions that are much like these in git instructions and works in an analogous means like dock pull dock push.
Learn how to Dockerize a Flask Utility?
Now, let’s stroll by way of the steps to dockerize a Flask software. we’ll carry out the dockerisation on Ubuntu EC2, Merely create EC2 occasion with microservices and Enable inbound guidelines which units the port to be open at 5000 and in addition enable all site visitors. After connecting your EC2 occasion with ssh. Run the instructions to replace and improve first earlier than putting in docker on it.
Allow us to look into the steps of how you can dockerize a flask software:


flask_app/
├── app.py
├── necessities.txt
├── templates/
│ ├── index.html
│ └── nextpage.html
├── static/
│ ├── css/
│ │ ├── types.css
│ │ └── styles2.css
└── Dockerfile
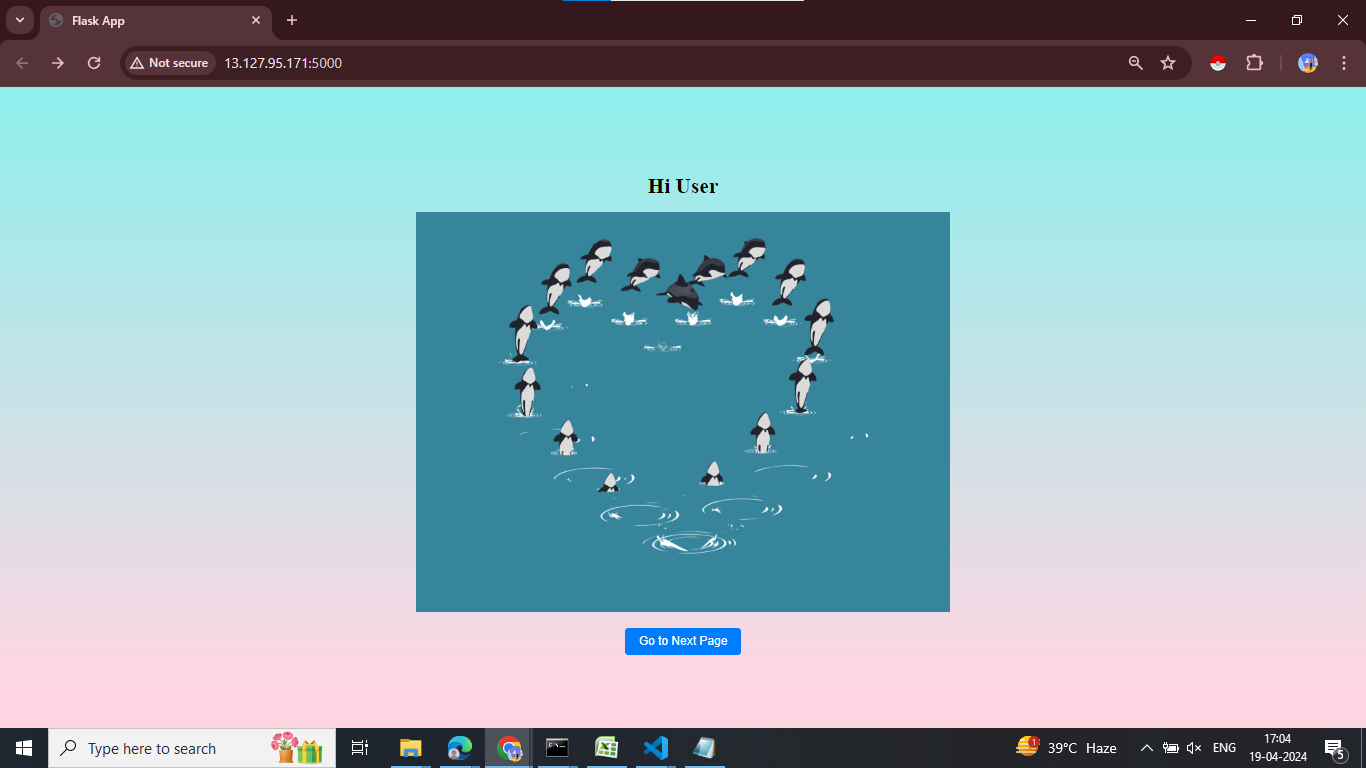
After operating app.py, we’ll get an output like this :
You may create your flask software in your native (pc) and ship it to ec2 utilizing the under instructions.
scp -r /path/to/native/listing username@ec2-instance-ip:/path/to/vacation spot/listing- scp: Stands for “safe copy”, used to repeat recordsdata securely between hosts on a community.
- -r: Recursively copy total directories.
- /path/to/native/listing: Exchange this with the trail to the listing in your native Ubuntu laptop computer that you simply wish to ship.
- username: Exchange this with the username of your EC2 occasion.
- ec2-instance-ip: Exchange this with the general public IP tackle or hostname of your EC2 occasion.
- /path/to/vacation spot/listing: Exchange this with the trail to the listing in your EC2 occasion the place you wish to copy the recordsdata.
Step4: Creating Dockerfile
Create a dockerfile with named “Dockerfile” within the listing to create a docker picture.
FROM python:3.8-slim
# Set setting variables
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE 1
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1
# Set the working listing within the container
WORKDIR /app
# Copy the necessities file into the container at /app
COPY necessities.txt /app/
# Set up any dependencies laid out in necessities.txt
RUN pip set up --no-cache-dir -r necessities.txt
# Copy the present listing contents into the container at /app
COPY . /app/
# Expose port 5000 to the surface world
EXPOSE 5000
# Command to run the Flask software
CMD ["python", "app.py"]Understanding Every Part
It is a Dockerfile used to containerize a Flask software. Allow us to perceive every part:
- FROM python:3.8-slim: This line specifies the bottom picture to make use of for the container. On this case, we’re utilizing the official Python 3.8 slim picture as the bottom picture right here.
- ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE 1 and ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1: These strains set setting variables within the container to optimize Python operating in a Docker container. PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE prevents Python from writing bytecode (.pyc) recordsdata to disk, and PYTHONUNBUFFERED ensures that Python outputs are despatched straight to stdout and stderr with out buffering.
- WORKDIR /app: This units the working listing contained in the container to /app, that means that each one subsequent instructions shall be executed from this listing.
- COPY necessities.txt /app/: This copies the necessities.txt file from the native recordsdata system into the /app listing throughout the container.
- RUN pip set up –no-cache-dir -r necessities.txt: This command installs the Python dependencies listed in necessities.txt into the container. The –no-cache-dir possibility ensures that pip doesn’t cache downloaded packages.
- COPY . /app/: This copies your complete contents of the present listing (the Flask software code, together with app.py, templates, and static recordsdata) into the /app listing throughout the container.
- EXPOSE 5000: This exposes port 5000 on the container. It doesn’t really publish the port, nevertheless it informs Docker that the container will hear on port 5000 at runtime.
- CMD [“python”, “app.py”]: This specifies the command to run when the container begins. It runs the Flask software by executing python app.py.
Step5: Construct Docker Picture
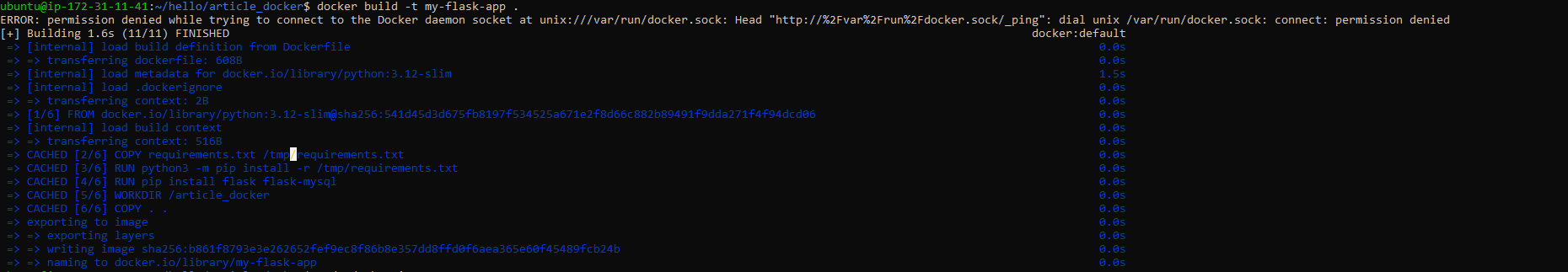
Once you run docker picture construct command, Docker will learn the Dockerfile within the present listing, execute every instruction within the Dockerfile to create layers, after which assemble these layers right into a Docker picture tagged as my-flask-app(identify we selected right here). This picture will comprise every part wanted to run your Flask software, together with Python dependencies, software code, and configuration settings.
docker construct -t my-flask-app .- docker picture construct: That is the Docker command used to construct Docker photographs. It tells Docker to construct a picture based mostly on the directions supplied in a Dockerfile.
- -t my-flask-app: This feature tags the picture with the identify my-flask-app. Tags are used to label Docker photographs with a selected identify and optionally a model. On this case, test_docker is the identify of the picture.
- . (dot): specifies the construct context. It tells Docker to search for the Dockerfile and every other recordsdata wanted for the construct course of within the present listing. The dot (.) represents the present listing.
You will note an output like this,
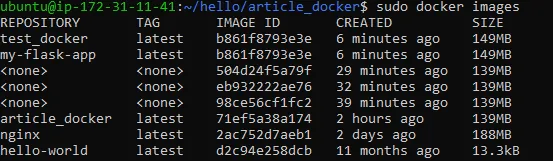
Lets see if the picture is there or not.
sudo docker photographs
Step6: Lets Docker Run the Picture We Created
sudo docker run -p5000:5000 my-flask-appThis command runs a Docker container based mostly on the Docker picture named my-flask-app and maps port 5000 on the host to port 5000 on the container.
You may run it on the Docker public IP, which is 172.17.0.2:5000
The Output seems to be like this:
Moreover, Docker allows collaboration and sharing of functions. After Dockerizing your software, you possibly can push the Docker picture to a public repository utilizing the docker push command along with your username. This makes your software accessible to others, selling collaboration and facilitating deployment throughout groups and environments.
Steps to Push Docker Picture to Docker Hub
To push the Docker picture to Docker Hub for public use, you must observe these steps:
Step1: Log in to Docker Hub
First step is to log in to docker hub utilizing the docker login command and it’s a must to enter your Docker Hub username and password.
sudo docker login Step2: Tag Docker picture
Second step is to tag your docker picture along with your Docker Hub username and the repository identify, user211 is the instance username for docker hub account
sudo docker tag my-flask-app user211/my-flask-appStep3: Push Tagged Picture to Docker Hub
sudo docker push user211/my-flask-appThis command uploads your Docker picture to Docker Hub underneath your account. The picture shall be publicly accessible until you’ve set it to non-public in your Docker Hub settings.
After executing these instructions, your Docker picture shall be accessible on Docker Hub for public use underneath your specified repository identify. Others can pull this picture utilizing docker pull your-docker-hub-username/my-flask-app.
Conclusion
Docker is a transformative know-how that revolutionizes software program distribution, administration, and bundles. It separates functions from infrastructure, permitting builders to ship software program shortly whereas managing infrastructure like functions. Docker enhances portability, scalability, and workflow optimization, making it a vital part of contemporary growth practices. By dockerizing a Flask software, it demonstrates its sensible software in streamlining software deployment and administration, offering a light-weight, unbiased setting for executing functions.
Key Takeaways
- Docker simplifies software administration and deployment by separating functions from infrastructure.
- Docker containers present a light-weight, unbiased setting for executing functions, enhancing portability and scalability.
- Docker’s effectivity and ease of use make it a typical element of contemporary growth practices.
- Containerization streamlines software deployment and administration, eliminating compatibility points and complexities.
- Docker allows collaboration and sharing of functions, facilitating deployment throughout groups and environments.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
A. Docker is a platform that lets you bundle, distribute, and run functions in containers. Containers are light-weight, moveable, and self-sufficient models that encapsulate all the required parts to run an software, together with code, runtime, system instruments, libraries, and settings.
A. Not like digital machines, which require separate working techniques for every VM and eat extra assets, Docker containers share the host OS kernel, leading to decrease overhead and sooner startup occasions. Docker containers are additionally extra light-weight and moveable, making them very best for microservice architectures and cloud-native functions.
A. Dockerization gives a number of advantages, together with enhanced portability, scalability, and workflow optimization. It simplifies software administration and deployment by separating functions from infrastructure and supplies a constant setting for operating functions throughout completely different environments.
A. To Dockerize your software, you must create a Dockerfile that specifies the steps to construct your software’s Docker picture. This contains defining the bottom picture, establishing the setting, putting in dependencies, copying the applying code, and specifying the command to run the applying. After getting a Dockerfile, you possibly can construct the Docker picture utilizing the docker construct command after which run the container utilizing the docker run command.



