Introduction
Tableau is a robust and superior visualization device. It covers the entire visible improvement lifecycle. Beginning with Tableau Prep Builder, you possibly can successfully clear, rework, and supply knowledge below one roof. Tableau Desktop then presents this knowledge to inform a narrative, whereas Tableau Server means that you can share these visuals with the supposed viewers. On this entire course of, the interpretation of the dashboard requires a handbook effort. From the creator’s perspective, the dashboard presents an ideal pattern such that it grasps all of the eyeballs however from a viewer’s perspective, it’d take a while to grasp the dashboard. The viewer would require a walkthrough of the charts, and figures after which draw some conclusions. To streamline this course of, integrating Google Gemini into Tableau can improve dashboard comprehension by leveraging AI-driven insights, lowering the time required to interpret knowledge.
What if the viewer will get an AI helper to determine the charts and figures themselves? Introducing LLMs. For the reason that introduction of GPTs and massive language fashions (LLMs), many handbook workflows, similar to chatbots, translations, and analysis, have shifted to AI brokers. Information Evaluation is one such sector that’s progressively sliding to AI brokers. These brokers can take up automated knowledge wrangling, anomaly detection, function choice, or predictive analytics. On this information, we are going to discover how you can combine Google Gemini into Tableau dashboards. Ask it to offer knowledge summaries, predictions, conclusions, and extra.
Studying Aims
- Uncover how you can broaden your dashboard performance with Dashboard Extensions.
- Perceive the toolkit for organising Gemini in Tableau Dashboards.
- Discover how you can leverage Python to work together with the Tableau Dashboard and ship info to and from the dashboards.
- Discover ways to allow customers to ask questions on graphs and figures and get responses in the identical window.
- Acknowledge the potential safety dangers of sending delicate info to LLMs.
This text was revealed as part of the Information Science Blogathon.
What are Dashboard Extensions?
Including an exterior service to an already fully-fledged utility is a tough job. Tableau is a reasonably large utility and it’s almost not possible to code out a brand new function with out getting access to all of the codebase and the dependencies. Subsequently we have now Tableau Dashboard Extensions. Dashboard Extensions are net apps that may be included right into a dashboard like different dashboard parts. These net apps work together with Tableau internals utilizing Tableau Extensions API. On a excessive degree, these apps will be divided into two sorts:
- Community-enabled: These apps run on servers situated outdoors the Tableau atmosphere. The app will be hosted on any platform and the client-side code is embedded immediately into Tableau by way of the extension file (trex).
- Sandboxed: The sandboxed apps run in a protected atmosphere with restricted or no entry to sources or net providers. Normally developed by the Tableau crew, they’ve restricted capabilities but are highly effective in enhancing dashboard interactivity.
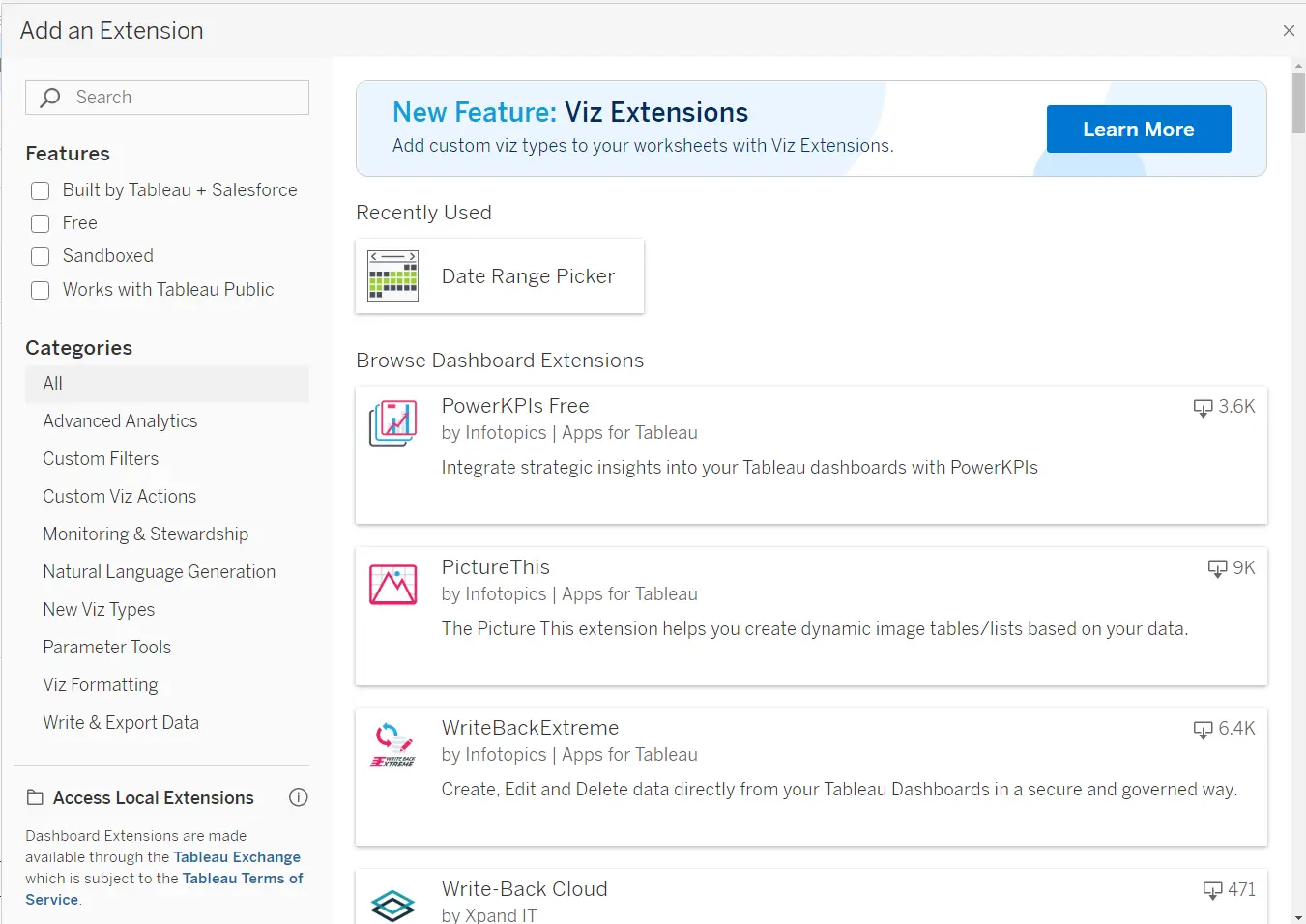
There’s a entire library of Dashboard Extensions accessible on the Tableau Change. Some are formally developed by the Tableau and Salesforce groups and extra by well-known companies. The extensions are an effective way to increase the performance of a base dashboard and make it extra interactive. There are extensions to export knowledge from the charts, add new info to the dashboards, or edit the prevailing knowledge!
For our use case, we are going to construct a Dashboard extension the place a consumer selects knowledge factors on the dashboard, submits a query, sends all this info to Gemini for evaluation, and shows the ends in the identical window.
Dashboard Extensions makes use of the underlying Tableau Extensions API to work together with the Tableau dashboard’s inner objects. This JavaScript library API can restrict the Python developer’s abilities. To beat this, we are going to use Anvil. Anvil is a platform for constructing full-stack net purposes in Python. It has an open-source library known as trexjacket that permits builders to work together with the dashboard internals utilizing Python. The Anvil sits as an interface between Tableau JavaScript APIs and the Python code from the consumer facet. The trexjacket supplies the Tableau dashboard entry by way of Python and the workflow continues.
For our Dashboard Extension that works with Google Gemini, we’d like the next:
- Gemini API Entry
- Anvil challenge preconfigured with trexjacket
- Tableau Utility and a Dashboard
Gemini API Entry
Google has launched API entry to Gemini, beforehand referred to as Bard below a sub-vertical known as “Google AI for builders”. One can discover Gemini API, Google AI Studio, Gemma fashions, and Google AI Edge. The API entry continues to be offered by way of the Google Cloud Venture (GCP). Head to Gemini and click on the “Get API key in Google Studio” possibility. Clicking “Create API key” will immediate two choices, create a brand new challenge or add API entry to an present challenge.
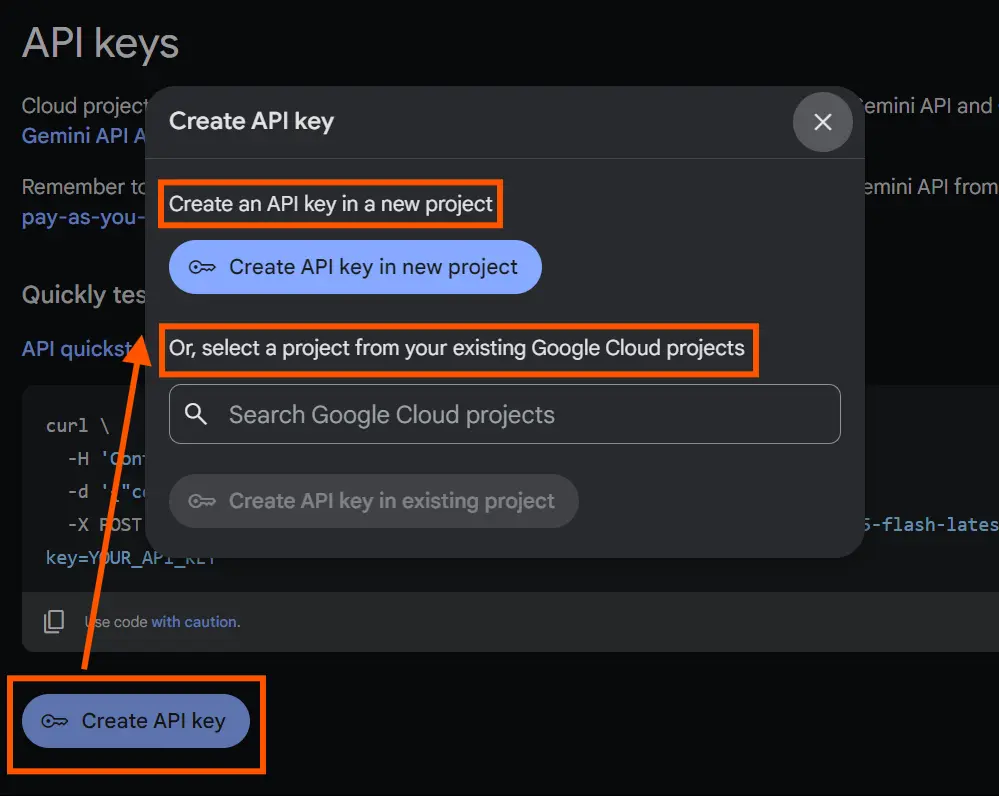
Select any possibility and hold the API key in a protected place.
Anvil Venture with Trexjacket
Anvil is a powerpack platform providing full-stack net improvement in Python. The primary differentiator is constructing the frontend in Python and successfully stitching it to the backend server code. The design organizes the entire utility in an object-oriented programming paradigm, facilitating simpler entry and administration of various parts within the net app. It additionally permits modifying the underlying make-up information, HTML, CSS, and JS for extra granular management over the consumer interface.
Anvil has constructed a template challenge preconfigured with trexjacket that fast-tracks the Dashboard extension improvement below Anvil X. This template has the configuration set for trexjacket as a dependency for the Anvil app. To arrange a challenge with trexjacket as a dependency, join an account on anvil.works, choose “Create a brand new app” and choose “Tableau Extension”.
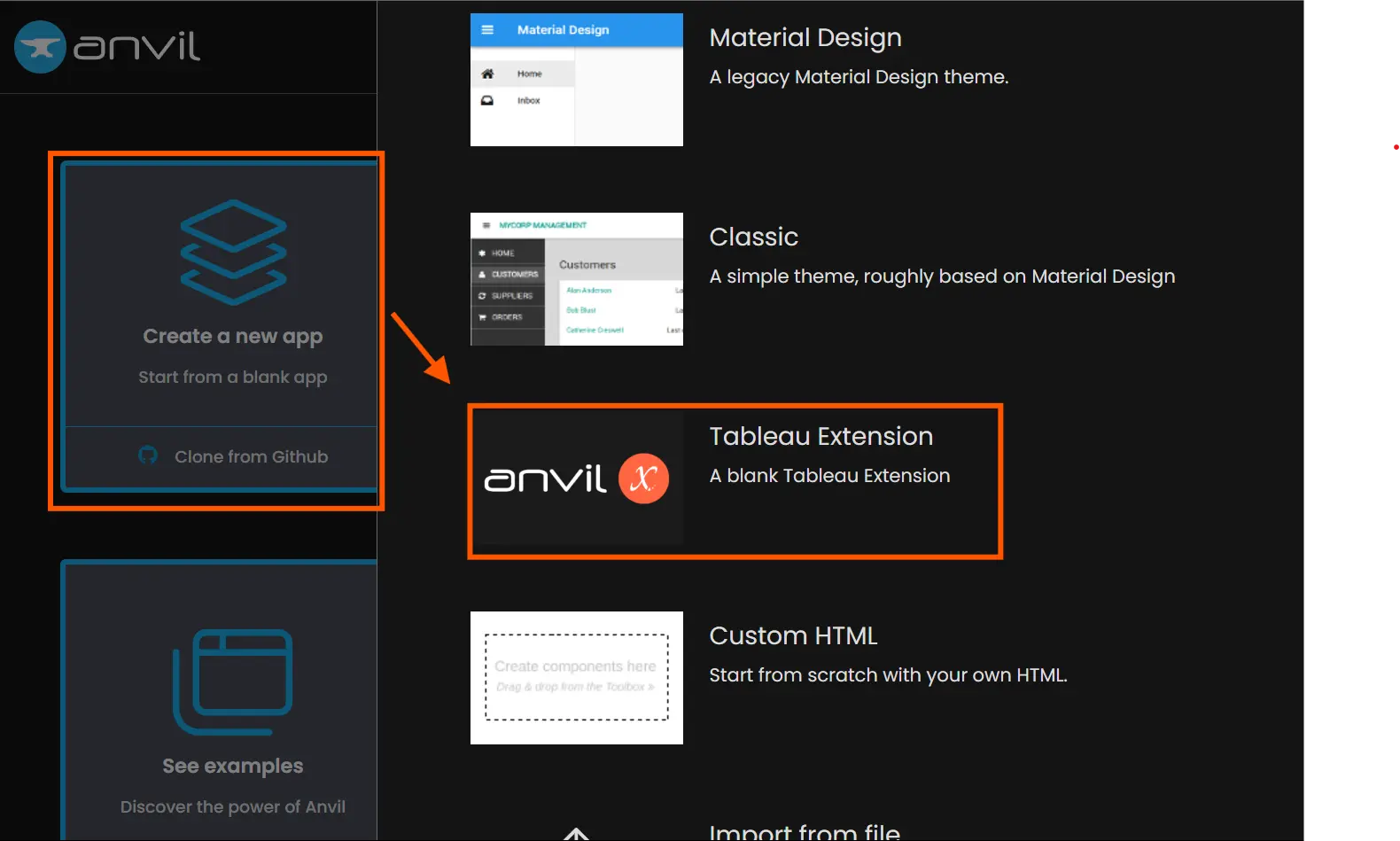
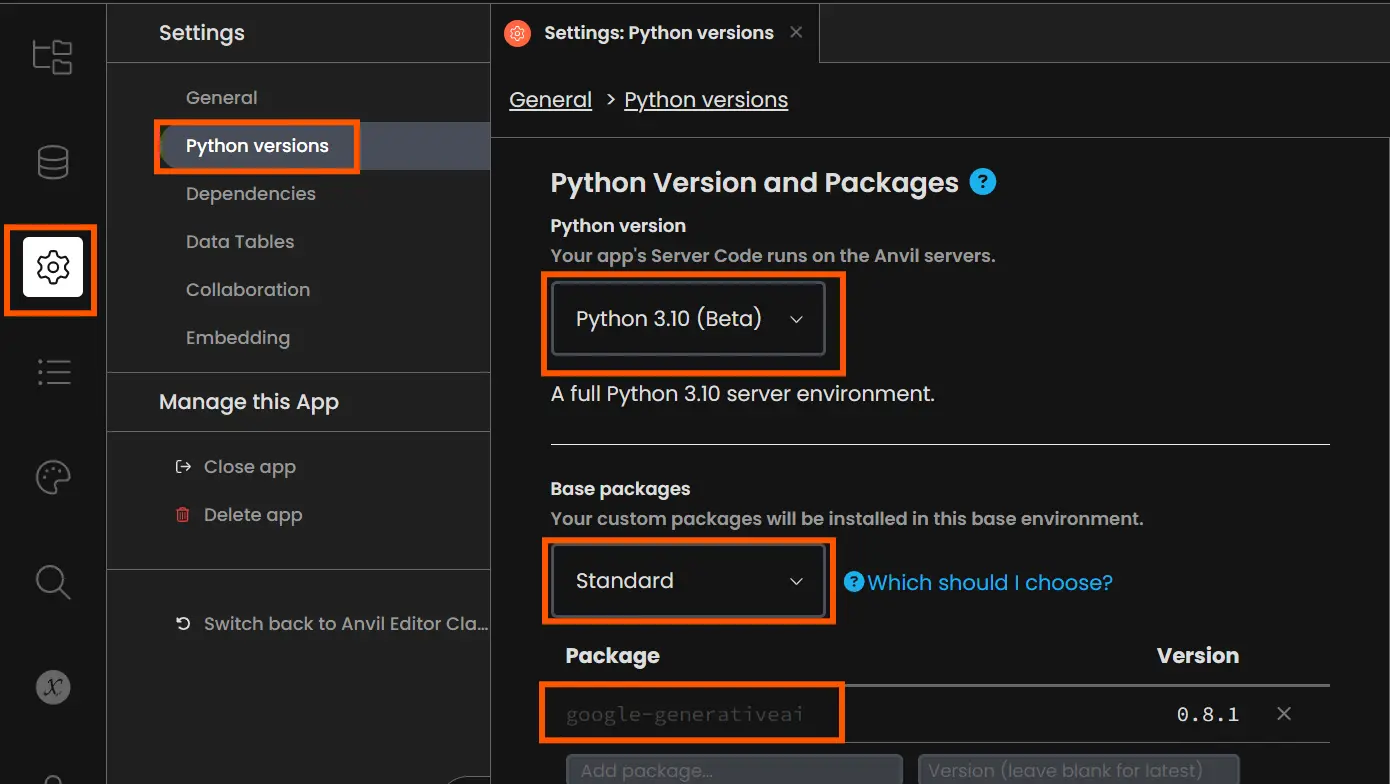
Within the template app, you possibly can delete the configure settings, and startup module and clear up the design web page of the app as these will not be wanted for our use case. Subsequent, we have to add the Google Generative AI Python library within the Anvil atmosphere. For that, go to settings from the left, choose Python variations, change to Python beta, choose the bottom package deal as normal, and add the package deal identify as “google-generativeai”
For the scope of this information, we is not going to discover Anvil fundamentals and canopy solely the required sections of Anvil. If you wish to deep-dive into Anvil as a device, take a look at my different article Frontend, Backend & Database Utilizing Python: Anvil.
Tableau
Tableau Dashboard extensions help each desktop and server/cloud situations, in addition to Tableau Desktop Public and full-suite purposes. We’ll use Tableau Desktop Public to check the extension in our use case. The following factor we require is a working dashboard. You’ll be able to decide any dashboard of your selection for testing functions. I’m utilizing a dashboard revealed on Tableau Public in regards to the Paris Olympics 2024.
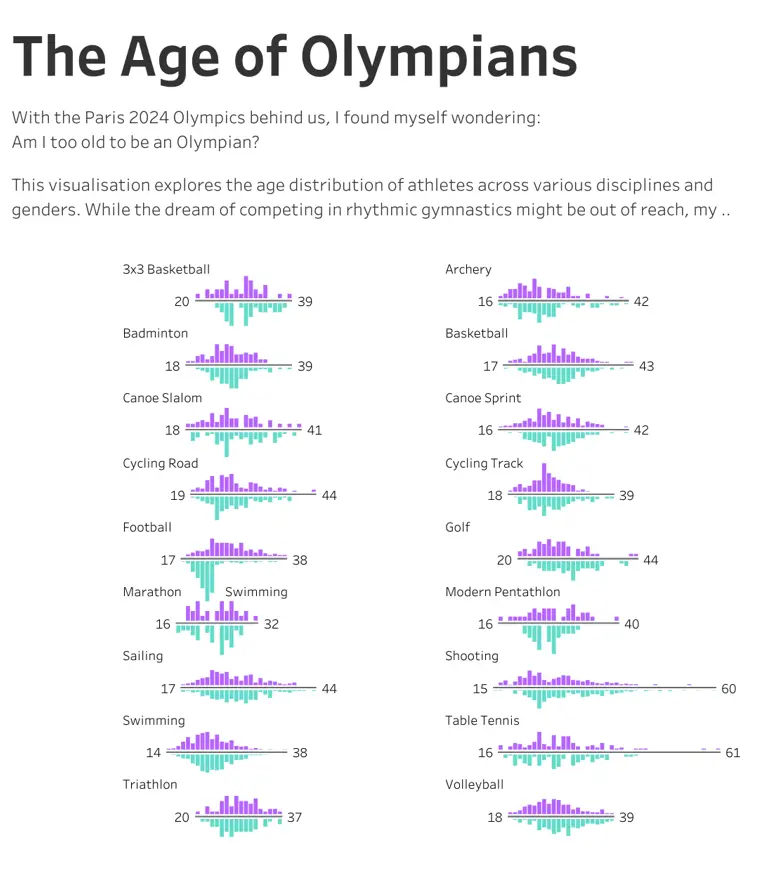
Notice: The writer of this dashboard mentions the dataset is from the Paris 2024 Olympic Video games Dataset in Kaggle.
Tableau Dashboard and Anvil Connection Setup
Let’s create a dummy extension to ascertain the connection between the Tableau Dashboard and the Anvil. Within the Anvil app, drag a label from the add element choice to show some textual content. Upon clicking this label, we will change the label show textual content and tweak different properties similar to font, colour, and measurement.
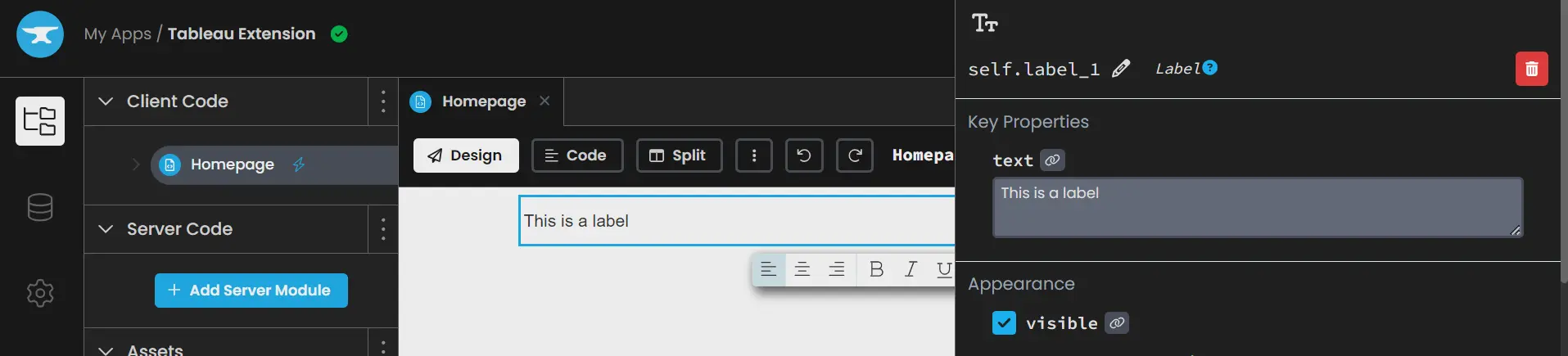
Subsequent, from the highest of the app, click on “Check in Tableau” and obtain the manifest file. This file has the “trex” extension and will be loaded as a neighborhood extension within the Tableau Dashboard. You’ll be able to select to maintain the dashboard in Tableau Desktop for now and later publish it on the server. The server configuration for that can be talked about within the popup.
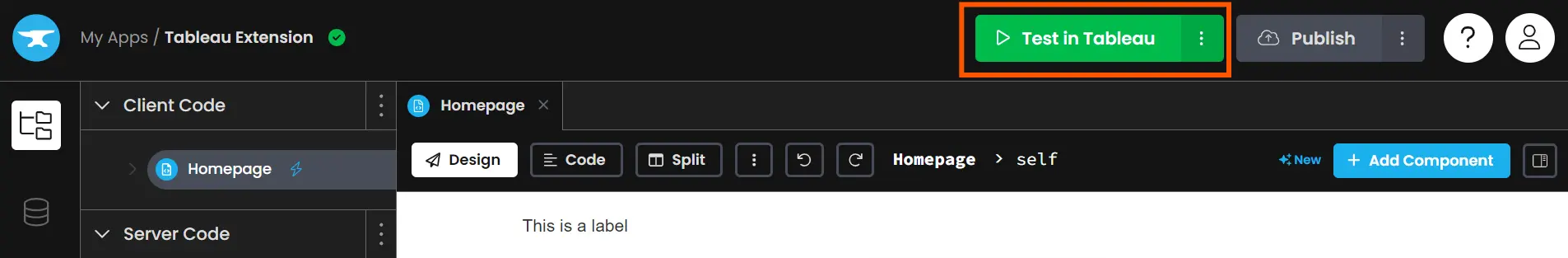
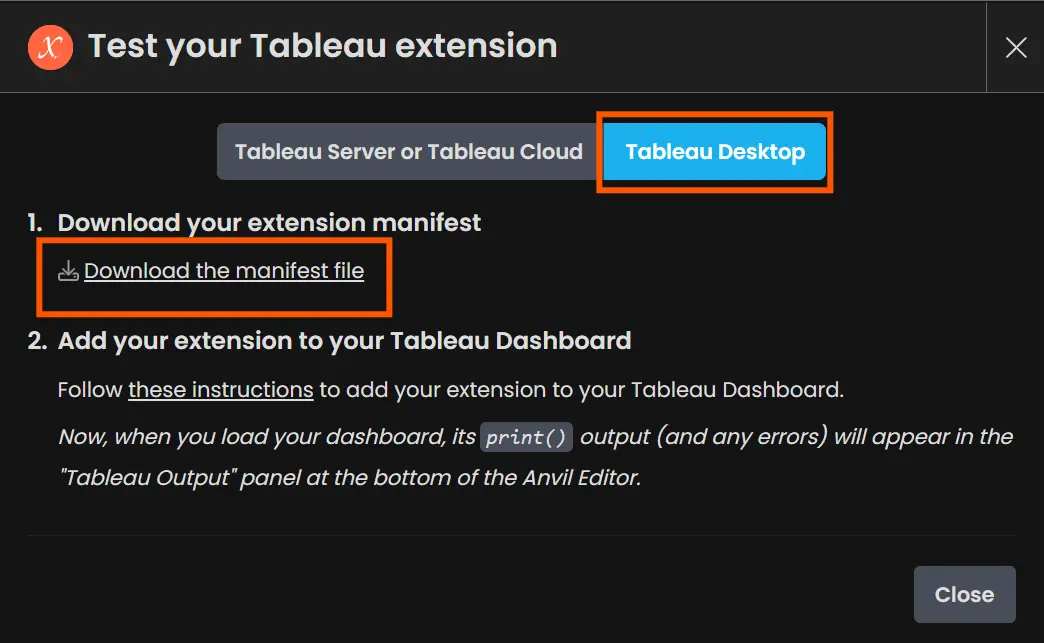
Now drag an extension object into the Tableau dashboard and click on “Entry Native Extensions”. Right here choose the manifest file generated by Anvil.
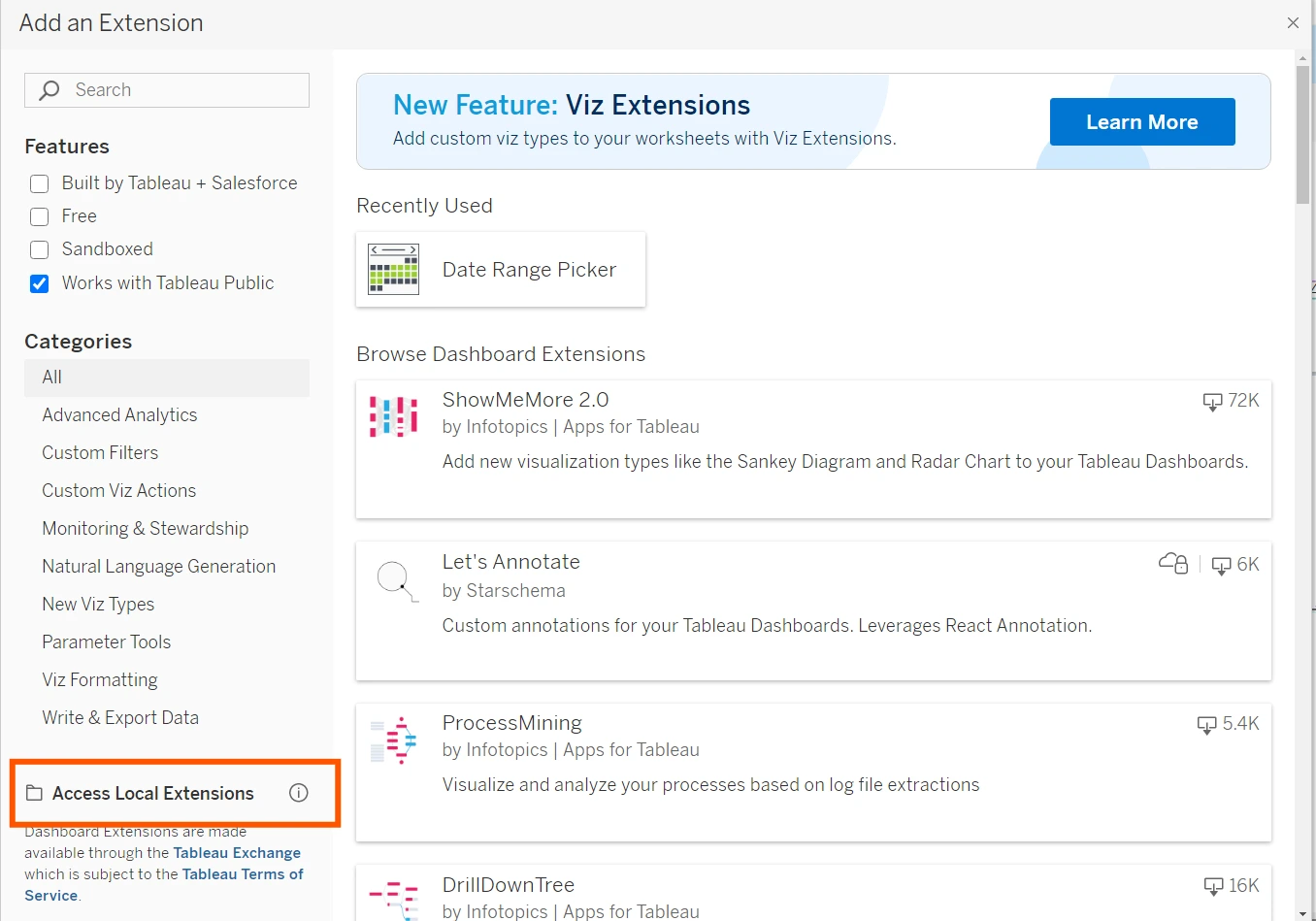
This extension will work together with Anvil to course of the info we ship from the Tableau dashboard and subsequently falls below the network-enabled class of Dashboard extensions. Choose “Okay” when prompted to permit entry to the extension. The Anvil App will load within the window, establishing our connection between the Tableau Dashboard and the Anvil server! We will begin including parts to this app and sew the Gemini API.
Constructing the Extension UI
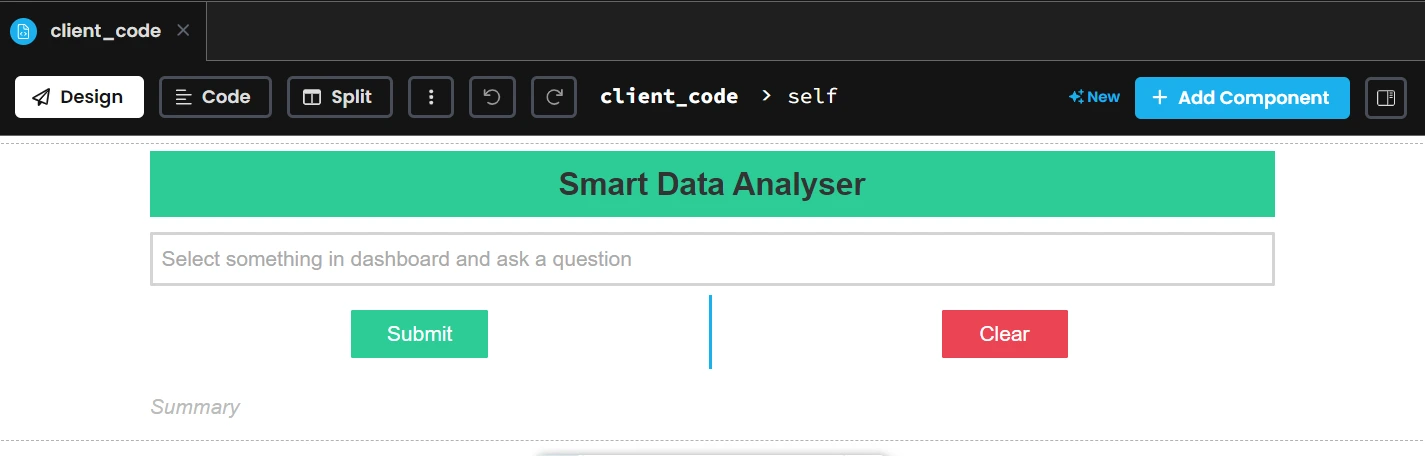
Anvil supplies drag-and-drop performance for designing the consumer interface of the appliance. There are numerous parts accessible within the library to select from. For our use case, the design breakdown seems to be like this:
- Enter field (TextBox) for taking the consumer query
- Submit button for sending the info to Anvil and Clear button to clear the query and the evaluation textual content
- A abstract label placeholder will show textual content that the Gemini API replaces with the outcomes.
- A title, colours for submit and clear button, and textual content colours to enhance consumer expertise
- You’ll be able to add the placeholder texts and show names by clicking on the element, opening the properties panel, and modifying the required attributes.
Under is the design we can be utilizing for this extension:
One of the best half about network-enabled extensions is the flexibility to ship modifications to the top consumer with none reinstallation. We will see the up to date UI immediately within the dashboard with out regenerating the manifest file. Click on on the extension object, choose the dropdown, and click on “Reload”. This may replace the extension in real-time.
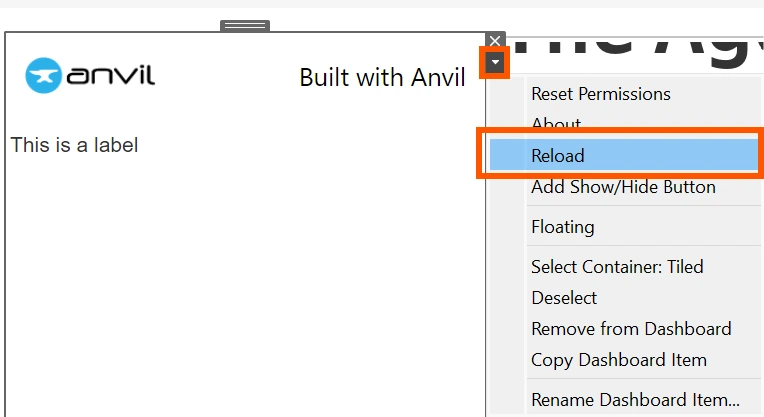
We have to present object names to those UI parts to sew them collectively, change their state within the coding half, and make them practical. To try this, open the element properties panel and add the identify within the “self”. As you possibly can guess, these parts can be accessible as objects on our major display screen. The names offered for this extension are:
- TextBox: user_question
- Submit Button: btn_submit
- Clear Button: btn_clear
- Abstract Label: abstract
Coding the Logics for Extension
In Anvil, client-side coding manages the consumer interface and handles all UI interactions, whereas holding much less safe coding components. For the reason that shopper code runs within the net browser, it has restricted capabilities for processes on the browser degree. Then again, server-side coding manages duties like authentication, password checks, and sustaining database connections.
In our case, the shopper code can deal with all of the dashboard interactions and go this knowledge to the server code to arrange and ship to the Gemini. The Gemini API must be accessed securely and would require server-side coding there. Let’s begin organising the client-side coding after which transfer to the server facet.
Accessing Dashboard and Stitching UI
To modify to the coding a part of the UI, choose the “Code” tab from the highest. The system populates it with some boilerplate code to get issues began. You’ll be able to take away issues like registering occasion handlers and the config web page at startup for now. Use the code under as a place to begin to observe alongside.
from ._anvil_designer import client_codeTemplate
from anvil import *
import anvil.server
from trexjacket.api import get_dashboard
dashboard = get_dashboard()
class client_code(client_codeTemplate):
def __init__(self, **properties):
self.init_components(**properties)
The system robotically imports and initializes the trexjacket as a dashboard object named “dashboard,” which serves because the entry level to entry all of the dashboard interactions. We will register 3 varieties of interactions from the dashboard: choice, filter & parameter change. To register an occasion kind, we have to use the register_event_handler perform of the dashboard object. It takes the occasion kind and the handler perform because the arguments. The handler perform takes care of the half when the occasion is triggered. This perform can entry the occasion metadata, worksheet, and underlying knowledge.
In our case, the choices carried out within the dashboard have to stream by means of our extension. Subsequent, to get the chosen knowledge level values, we will use the handler perform’s occasion worksheet object to name the get_selected_marks perform and retailer it to go the info to the backend. For demonstration, let’s change the show worth of the abstract element to indicate the chosen values. To try this, we will modify the textual content property of the element to take the worth as the choice.
Code Implementation
Right here is the code implementation:
class client_code(client_codeTemplate):
def __init__(self, **properties):
self.init_components(**properties)
dashboard.register_event_handler('selection_changed', self.selection_changed_event_handler)
def selection_changed_event_handler(self, occasion):
user_selections = occasion.worksheet.get_selected_marks()
if len(user_selections) != 0:
self._data = user_selections
self.abstract.textual content = user_selections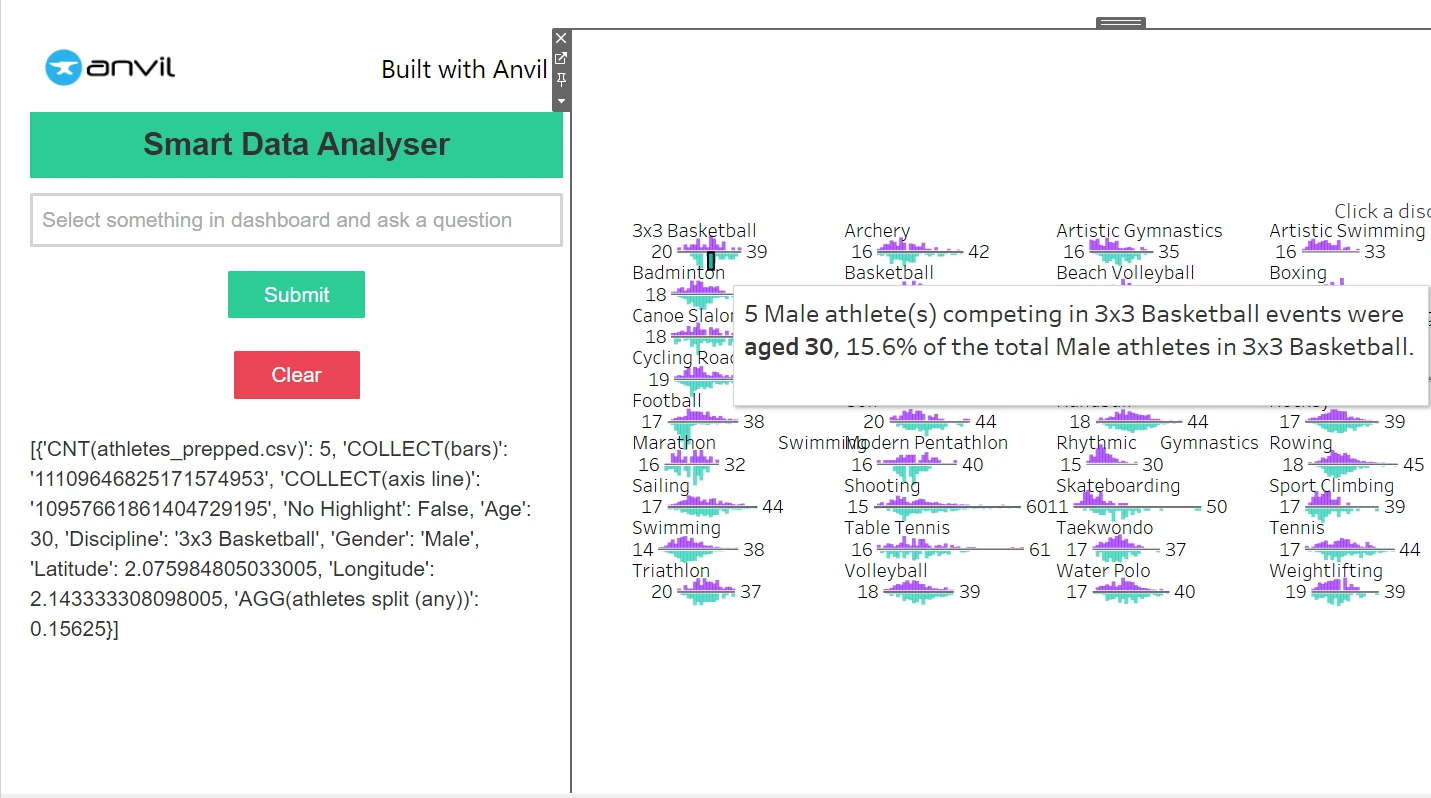
Subsequent, we’d like the Submit and Clear buttons practical. You’ll be able to view the kind of occasions supported for any element by choosing the element and switching to the properties panel. The occasions part will record all of the occasions together with their perform mappings. For buttons, we have to map the press occasion to do some operations.
- Clear button: We have to clear the query field, abstract part, and the info saved for beforehand chosen marks
- Submit button: The textual content within the query field must be despatched to the Gemini API.
The supposed work of the submit button can be mentioned within the subsequent part. For now, let’s change the abstract textual content with the query textual content upon clicking the submit button.
Code Implementation
The code implementation is as:
class client_code(client_codeTemplate):
def __init__(self, **properties):
self.init_components(**properties)
self.abstract.seen = False
dashboard.register_event_handler('selection_changed', self.selection_changed_event_handler)
def selection_changed_event_handler(self, occasion):
user_selections = occasion.worksheet.get_selected_marks()
if len(user_selections) != 0:
self._data = user_selections
def btn_submit_click(self, **event_args):
"""This methodology is named when the button is clicked"""
self.abstract.seen = True
self.abstract.textual content = self.user_question.textual content
def btn_clear_click(self, **event_args):
"""This methodology is named when the button is clicked"""
self.abstract.textual content=""
self.user_question.textual content=""
self._data=""
self.abstract.seen = False
Including Gemini API Backend
Our UI is able to settle for the consumer inputs and the parts are stitched collectively. Now we will add the mind of our utility, the Gemini API entry to course of these consumer inputs. The following tips describe our subsequent steps:
- Server module: So as to add server-side coding to the appliance, click on on 3-dots within the server code part on the left and choose “add server module”.
- Secrets and techniques: We should always retailer the Gemini API entry key in a safe place to forestall unauthorized requests. Anvil Secrets and techniques is a secret supervisor the place we will add keys, passwords, or credentials and entry them in our code utilizing the Anvil secret module.
- Pre-configure Gemini API: Though Gemini like another LLM can course of any info, we will present pre-context to Gemini. This context will assist us get extra refined responses and deal with our use case. We will go these directions whereas initializing our mannequin object.
The code half for the above clarification goes like this:
import anvil.secrets and techniques
import google.generativeai as genai
GOOGLE_API_KEY = anvil.secrets and techniques.get_secret("GEMINI_API")
genai.configure(api_key=GOOGLE_API_KEY)
mannequin = genai.GenerativeModel(model_name="gemini-1.5-flash", system_instruction=[
"You are an expert analyst and know everything about data analysis",
"You can interpret data in any form whether it's a single data point or a list of data with keys"
"You are on a mission to provide the best data analysis report when asked",
"You are capable of answering the question without report as well on topics that require you to answer between a finite set of possibilities",
],)Subsequent, we have to create a perform that accepts the query and the info from the shopper, processes the data, and returns the resultant values. We expose this perform to the client-side code to permit it to make calls. We use the Anvil callable decorator to wrap these capabilities and make them callable from the client-side code.
Ultimate Operate in Server Module
Right here is our last perform within the server module:
@anvil.server.callable
def generateDataSummary(immediate, knowledge):
revised_prompt = f'''
{immediate} + "nn" + {knowledge}
'''
response = mannequin.generate_content(revised_prompt)
return response.textual contentThe final step in constructing our dashboard extension is to name this perform, present the consumer inputs, and show the outcomes returned by Gemini API when the consumer selects some knowledge factors and clicks on the submit button. To realize this, we have to use the anvil server module name perform.This perform takes the perform identify uncovered as callable within the server module and accepts the parameters as key phrase arguments. Moreover, we will add a notification for consumer acknowledgment utilizing the Notification module. This implementation is finished as:
class client_code(client_codeTemplate):
.
.
def btn_submit_click(self, **event_args):
"""This methodology is named when the button is clicked"""
msg = "Wait"
Notification(msg).present()
self.abstract.textual content=""
dataSummary = anvil.server.name('generateDataSummary', immediate=self.user_question.textual content, knowledge=self._data)
self.abstract.seen = True
self.abstract.textual content = dataSummary
self._data=""Testing out the Extension
Our extension is able to take inputs from dashboards, course of them in Gemini, and return ends in the identical window! Reload the extension within the dashboard, choose some knowledge factors, enter some questions, and hit undergo see the outcomes.
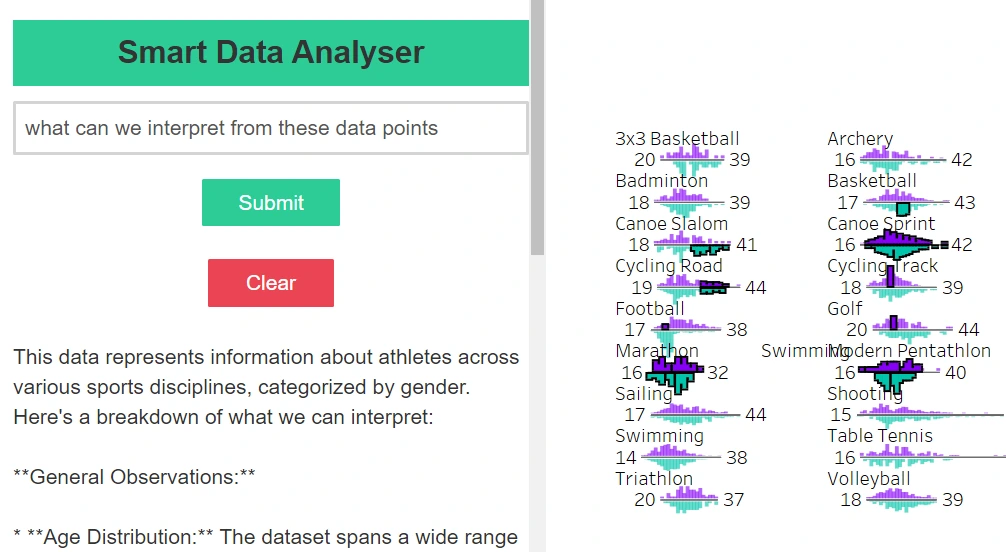
Try this demo video to see issues in motion:
Potential Safety Dangers
We’ve got efficiently created a Tableau Dashboard extension that seamlessly integrates into the dashboard. This extension will be added to any dashboard with none points. The one concern with utilizing an LLM could possibly be the sensitivity of knowledge. Datasets similar to monetary, private well being, confidential, or proprietary info may require extra safety measures and knowledge anonymization/redaction strategies to make sure privateness and compliance. Though LLM supplier firms similar to OpenAI present some flexibility to not permit the info coaching of the mannequin. It would change relying in your agency and one ought to seek the advice of the infosec crew earlier than implementing such options.
Conclusion
On this information, we noticed how you can combine Google Gemini into Tableau Dashboards on a deeper degree. The response high quality depends upon how the query (immediate) is offered. Many enhancements will be made to the extension similar to including a configuration web page to supply choices for choosing the mannequin for use, updating system directions, preprocessing the info to be despatched, and far more.
On the trexjacket facet, you possibly can discover different functionalities similar to accessing the filters and parameters or immediately accessing the underlying knowledge for a worksheet. The documentation is the perfect place to test these capabilities. One can develop extensions natively in JavaScript as nicely however it’s a studying curve for the Python neighborhood, subsequently, leveraging Anvil.
Key Takeaways
- Tableau Extension is an effective way to take advantage of your dashboards. There are tons of extensions for quite a lot of use instances similar to visualization extensions for including Sankey stream charts which aren’t natively supported on the time of writing.
- One can use Gemini, an LLM, to demo the dashboard extension, but it surely’s additionally potential to make use of any LLM, a fine-tuned model, or a knowledge specialist LLM for sensible functions.
- Integrating an LLM in your dashboards can free an analyst from answering among the repetitive queries and focus extra on taking motion.
- One must also pay attention to the potential knowledge leakage and use such programs sparsely by avoiding passing on delicate info.
Incessantly Requested Questions
A. Tableau Extension is a method so as to add functionalities to a dashboard that isn’t natively shipped in Tableau software program. There are extensions to export knowledge from a dashboard, add checkboxes in parameters, superior date pickers, and far more.
A. Anvil supplies the platform to construct full-stack net purposes solely utilizing Python. This permits us to create the Tableau Extension UI with out pondering of dealing with the JavaScript. Trexjacket supplies an abstraction over dashboard components and methods to entry them programmatically.
A. Within the dashboard objects, drag the Extension object within the dashboard sheet and it’ll open a popup. Right here you possibly can select from already revealed extensions or load your custom-build extension.
A. Choice, filters, and parameters interactions will be captured utilizing trexjacket
A. Sure, so long as you expose the LLM as an API endpoint, you possibly can select any LLM and combine it into your Tableau Dashboards.
A. You’ll be able to combine Google Gemini into Tableau through the use of API endpoints to boost dashboards with AI-driven insights and occasion administration.
The media proven on this article just isn’t owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used on the Writer’s discretion.



