Trendy server processors function a trusted execution setting (TEE) for dealing with particularly delicate data. There are numerous TEE implementations, however two are most related to this dialogue: Intel Software program Guard eXtensions (SGX), and AMD Safe Encrypted Virtualization (SEV). Virtually concurrently, two separate groups of researchers — one within the U.S. and one in Europe — independently found very related (although distinct) strategies for exploiting these two implementations. Their aim was to achieve entry to encrypted information held in random entry reminiscence. The scientific papers detailing these outcomes have been printed simply days aside:
- WireTap: Breaking Server SGX through DRAM Bus Interposition is the hassle of U.S. researchers, which particulars a profitable hack of the Intel Software program Guard eXtensions (SGX) system. They achieved this by intercepting the information alternate between the processor and the DDR4 RAM module.
- In Battering RAM, scientists from each Belgium and the UK additionally efficiently compromise Intel SGX, in addition to AMD’s comparable safety system, SEV-SNP, by manipulating the data-transfer course of between the processor and the DDR4 RAM module.
Hacking a TEE
Each the applied sciences talked about — Intel SGX and AMD SEV — are designed to guard information even when the system processing it’s fully compromised. Subsequently, the researchers started with the premise that the attacker would have full freedom of motion: full entry to each the server’s software program and {hardware}, and the confidential information they search residing, for example, on a digital machine working on that server.
In that situation, sure limitations of each Intel SGX and AMD SEV develop into vital. One instance is the usage of deterministic encryption: an algorithm the place a particular sequence of enter information at all times produces the very same sequence of encrypted output information. Because the attacker has full entry to the software program, they’ll enter arbitrary information into the TEE. If the attacker additionally had entry to the ensuing encrypted data, evaluating these two information units would permit them to calculate the non-public key used. This, in flip, would allow them to decrypt different information encrypted by the identical mechanism.
The problem, nonetheless, is how one can learn the encrypted information. It resides in RAM, and solely the processor has direct entry to it. The theoretical malware solely sees the unique data earlier than it will get encrypted in reminiscence. That is the primary problem, which the researchers approached in several methods. One simple, head-on answer is hardware-level interception of the information being transmitted from the processor to the RAM module.
How does this work? The reminiscence module is eliminated after which reinserted utilizing an interposer, which can be linked to a specialised gadget: a logic analyzer. The logic analyzer intercepts the information streams touring throughout all the information and tackle strains to the reminiscence module. That is fairly advanced. A server usually has many reminiscence modules, so the attacker should discover a technique to power the processor to put in writing the goal data particularly to the specified vary. Subsequent, the uncooked information captured by the logic analyzer should be reconstructed and analyzed.
However the issues don’t finish there. Trendy reminiscence modules alternate information with the processor at super speeds, performing billions of operations per second. Intercepting such a high-speed information movement requires high-end tools. The {hardware} that was used to show the feasibility of this sort of assault in 2021 value a whole bunch of 1000’s of {dollars}.
The options of WireTap
The U.S. researchers behind WireTap managed to slash the price of their hack to only below a thousand {dollars}. Their setup for intercepting information from the DDR4 reminiscence module regarded like this:
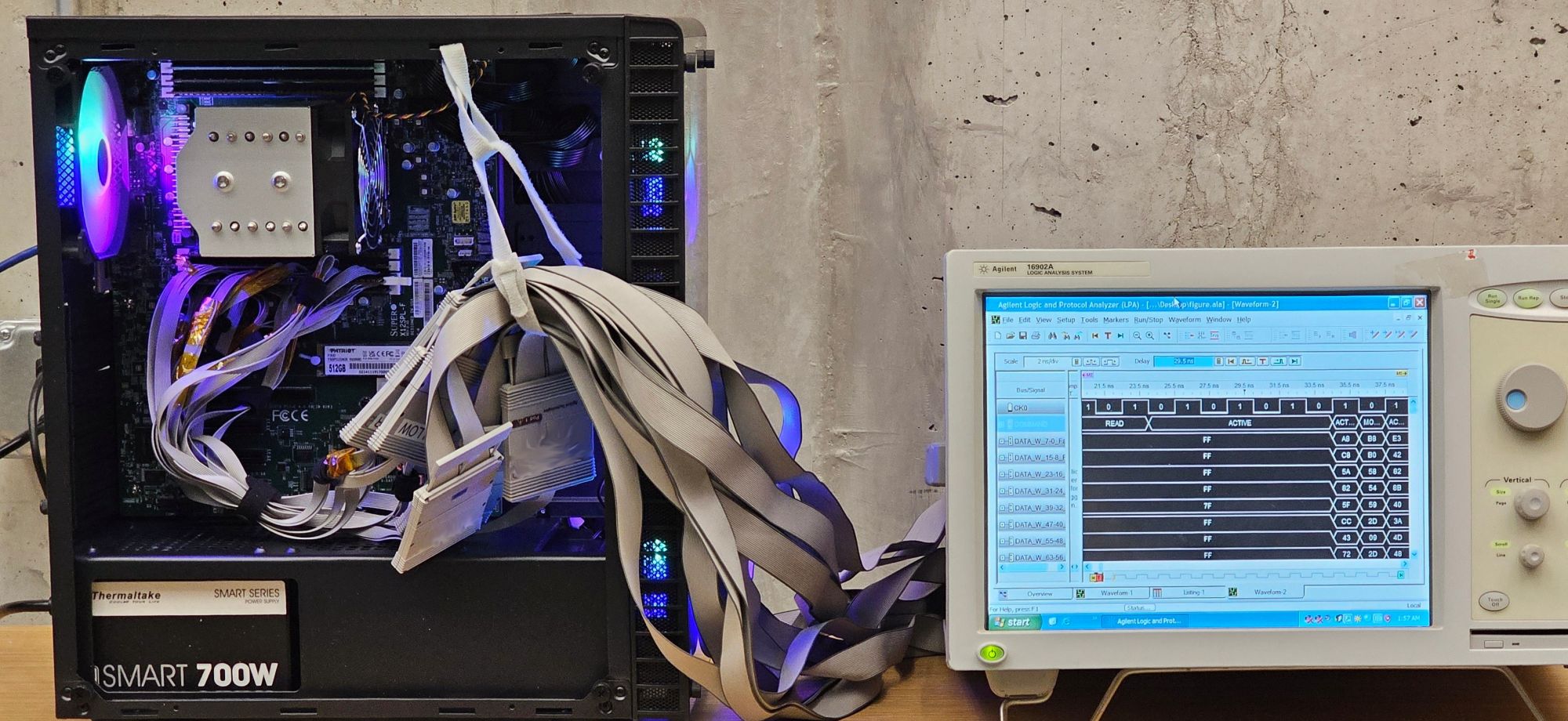

Take a look at system for intercepting the information alternate between the processor and the reminiscence module Supply
They spent half of the funds on an historic, quarter-century-old logic analyzer, which they acquired by means of a web-based public sale. The rest lined the mandatory connectors, and the interposer (the adapter into which the goal reminiscence module was inserted) was custom-soldered by the authors themselves. An out of date setup like this might not probably seize the information stream at its regular pace. Nevertheless, the researchers made a key discovery: they may decelerate the reminiscence module’s operation. As a substitute of the usual DDR4 efficient speeds of 1600–3200 megahertz, they managed to throttle the pace right down to 1333 megahertz.
From there, the steps are… effectively, probably not easy, however clear:
- Make sure that the information from the goal course of was written to the hacked reminiscence module after which intercept it, nonetheless encrypted at this stage.
- Enter a {custom} information set into Intel SGX for encryption.
- Intercept the encrypted model of the identified information, examine the identified plaintext with the ensuing ciphertext, and compute the encryption key.
- Decrypt the beforehand captured information belonging to the goal course of.
In abstract, WireTap work doesn’t essentially change our understanding of the inherent limitations of Intel SGX. It does nonetheless exhibit that the assault will be made drastically cheaper.
The options of Battering RAM
As a substitute of the simple data-interception method, the researchers from Belgium’s KU Leuven college and their UK colleagues sought a extra delicate and chic methodology to entry encrypted data. However earlier than we dive into the main points, let’s have a look at the {hardware} element and examine it to the American group’s work:
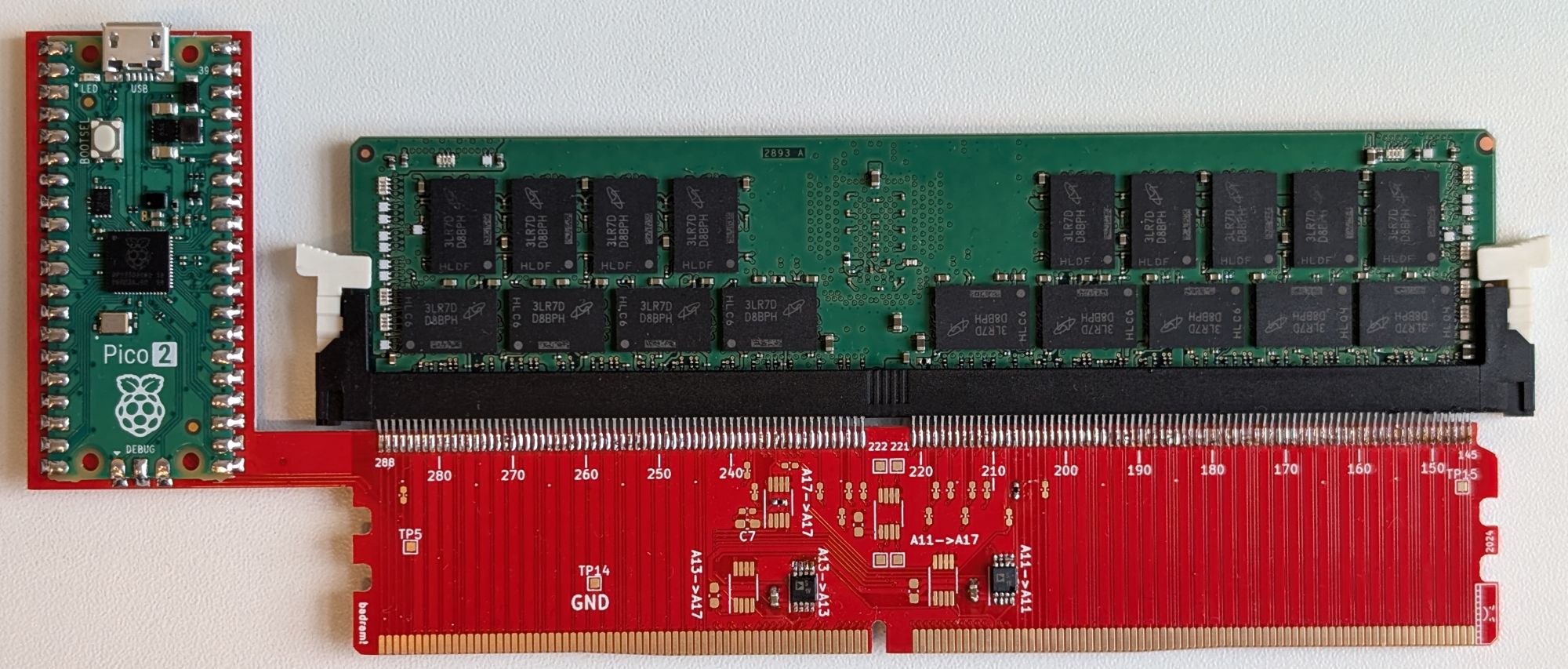
The reminiscence module interposer utilized in Battering RAMSupply
Instead of a tangle of wires and a cumbersome information analyzer, this setup incorporates a easy board designed from scratch, into which the goal reminiscence module is inserted. The board is managed by an affordable Raspberry Pi Pico microcomputer. The {hardware} funds is negligible: simply 50 euros! Furthermore, not like the WireTap assault, Battering RAM will be performed covertly; steady bodily entry to the server isn’t wanted. As soon as the modified reminiscence module is put in, the required information will be stolen remotely.
What precisely does this board do? The researchers found that by grounding simply two tackle strains (which dictate the place data is written or learn) on the proper second, they may create a knowledge mirroring scenario. This causes data to be written to reminiscence cells that the attacker can entry. The interposer board acts as a pair of easy switches managed by the Raspberry Pi microcomputer. Whereas manipulating contacts on reside {hardware} usually results in a system freeze or information corruption, the researchers achieved steady operation by disconnecting and reconnecting the tackle strains solely on the exact moments required.
This methodology gave the authors the flexibility to pick the place their information was recorded. Crucially, this implies they didn’t even must compute the encryption key! They first captured the encrypted data from the goal course of. Subsequent, they ran their very own program throughout the similar reminiscence vary and requested the TEE system to decrypt the beforehand captured data. This method allowed them to hack not solely Intel SGX but additionally AMD SEV. Moreover, this management over information writing helped them circumvent AMD’s safety extension referred to as SEV-SNP. This extension, utilizing Safe Nested Paging, was designed to guard the digital machine from compromise by stopping information modification in reminiscence. Circumventing SEV-SNP theoretically permits attackers not solely to learn encrypted information but additionally to inject malicious code right into a compromised digital machine.
The relevance of bodily assaults on server infrastructure
It’s clear that whereas the sensible software of such assaults is feasible, they’re unlikely to be performed within the wild. The worth of the stolen information would have to be extraordinarily excessive to justify hardware-level tampering. Not less than, that is the stance taken by each Intel and AMD concerning their safety options: each chipmakers responded to the researchers by stating that bodily assaults fall outdoors their safety mannequin. Nevertheless, each the American and European analysis groups demonstrated that the price of these assaults isn’t almost as excessive as beforehand believed. This probably expands the checklist of menace actors prepared to make the most of such advanced vulnerabilities.
The proposed assaults do include their very own restrictions. As we already talked about, the knowledge theft was performed on programs outfitted with DDR4 commonplace reminiscence modules. The newer DDR5 commonplace, finalized in 2020, has not but been compromised, even for analysis functions. That is due each to the revised structure of the reminiscence modules and their elevated working speeds. However, it’s extremely seemingly that researchers will ultimately discover vulnerabilities in DDR5 as effectively. And that’s a great factor: the declared safety of TEE programs should be repeatedly subjected to unbiased audits. In any other case, it might prove sooner or later {that a} supposedly trusted safety system unexpectedly turns into fully ineffective.



