Area title system (DNS) spoofing is a kind of cyberattack that makes use of tampered DNS server information to redirect customers to faux web sites. These malicious websites typically look reliable however are designed to put in malware onto customers’ units, steal delicate information or redirect site visitors.
Think about logging into what you thought was a trusted account on considered one of your favourite websites simply to have your information stolen by a hacker. That is the hazard of area title system (DNS) spoofing and poisoning.
DNS spoofing can result in extreme penalties akin to id theft, fraud, malware distribution and information breaches — making it essential for people and organizations to know and handle this risk. By being conscious of DNS spoofing ways, you may determine indicators of suspicious exercise and take proactive steps to safeguard your information privateness.
Learn on to study the various kinds of DNS spoofing assaults, the best way to determine them and tricks to forestall DNS spoofing and DNS poisoning.
What Is DNS Spoofing?
DNS spoofing is a cyberattack the place a hacker tips a pc or community into believing it’s speaking with a reliable web site or server. In actuality, the pc is interacting with a faux web site or server arrange by the attacker. This deception leads customers to malicious web sites — exposing them to id theft, monetary fraud, malware and different on-line threats.
For instance, think about you’re attempting to entry your Gmail account. Nonetheless, a cyberattacker has manipulated the DNS information so if you kind “www.gmail.com” into your internet browser, you’re directed to a faux web site that appears like Gmail, however the attacker has full management of it. When the faux web site takes you to the login web page, you enter your electronic mail and password. The attacker now has your credentials and may use them to entry your electronic mail.
DNS interprets easy-to-remember web site names into the complicated numerical addresses required for computer systems to speak with one another. Nonetheless, cybercriminals can make use of misleading ways to govern the DNS and lead unsuspecting customers astray. Two such ways are DNS spoofing and DNS poisoning.
DNS Poisoning vs. DNS Spoofing
DNS poisoning is a technique cyberattackers make use of to compromise and substitute reliable DNS information with malicious data, sometimes by injecting false DNS information into DNS caches. This misleading tactic goals to redirect customers to fraudulent web sites or servers, resulting in potential safety breaches, information theft or different cyberthreats.
DNS spoofing — a results of DNS poisoning — happens when customers are redirected to malicious web sites or servers by way of the manipulated DNS cache. In DNS spoofing assaults, hackers exploit the poisoned DNS cache to intercept customers’ requests for reliable web sites and redirect them to fraudulent locations beneath the attackers’ management. This DNS document manipulation can lead customers to unknowingly disclose delicate data, fall sufferer to phishing scams or inadvertently obtain malware.
Regardless of their variations, each ways pose vital cybersecurity dangers, necessitating vigilance and sturdy safety measures to mitigate cybersecurity breaches successfully.
How Does DNS Spoofing Work?
There are a number of strategies attackers can use to execute DNS spoofing assaults, however all of them share the identical purpose: to trick customers and their servers into pondering a fraudulent web site is reliable. To do that, attackers sometimes observe these three steps:

Step 1: Accessing the DNS server
Earlier than a hacker can carry out this assault, they should acquire entry to the DNS server or DNS resolver cache. This course of entails figuring out a DNS server’s software program versioning and MAC handle, scanning for vulnerabilities and figuring out whether or not it makes use of DNSSEC (area title system safety extensions) or DNS encryption. Sadly, most DNS queries and responses are unprotected, making it simple for attackers to realize entry and redirect site visitors to a server they management.
Step 2: Rerouting Connections
As soon as the attacker has entry to a DNS server or resolver, they will substitute saved IP addresses with faux ones. As a result of these methods can’t differentiate between a reliable IP handle and a malicious one, attackers can trick them into storing a spoofed entry that results in a malicious web site. As soon as this course of is full, the spoofed entry stays within the system and directs anybody related to the server to the malicious website as an alternative of the reliable one.
Step 3: Accessing Delicate Information
As soon as a consumer arrives at a malicious web site, it might immediate them to enter their login data like they usually would. As a result of the faux website seems to be precisely just like the reliable one, the sufferer has no concept that they’re dealing with delicate data over to the attacker. Attackers may also use DNS spoofing to put in malware on a consumer’s gadget or redirect site visitors to phishing web sites. That is particularly frequent for on-line purchasing and banking web sites.
Cybersecurity Penalties of DNS Spoofing
DNS spoofing can pose a number of dangers to customers. Among the commonest dangers embrace:
 Information Theft
Information Theft
Attackers often use DNS spoofing to entry delicate consumer information like banking, bank card and private login data. Phishing web sites could be troublesome to detect, so customers could not discover their information was compromised till it’s too late.
Censorship
Censorship is when somebody controls or blocks entry to sure data or web sites. Within the digital world, attackers can use DNS spoofing to censor internet outcomes by tricking your laptop into pondering a web site doesn’t exist. Some governments purposely manipulate DNS caches like web handle books to cease individuals from accessing particular web sites or on-line assets. As an example, China makes use of DNS censorship as a part of its Nice Firewall, which redirects customers away from sure web sites.
Malware An infection
Faux web sites are sometimes stuffed with malicious hyperlinks and downloads that may infect your gadget with malware. If the spoofed website is an web safety supplier, it could possibly not directly expose you to viruses by stopping reliable safety updates. This danger is highest for customers who don’t use antivirus software program.
Kinds of DNS Spoofing Assault Strategies
There are a number of alternative ways attackers can execute a DNS spoofing assault. Among the commonest examples embrace:
DNS Server Compromise
A DNS server compromise is likely one of the commonest strategies for DNS spoofing. On this state of affairs, an attacker features entry to the DNS server and injects a faux DNS entry. As soon as the faux IP handle is within the system, it directs site visitors away from the reliable website to the malicious one.
A well-known instance of one of these assault occurred in 2018, when hackers compromised Amazon’s Route 53 DNS server and public Google DNS servers. After gaining entry, they rerouted roughly 1,300 IP addresses to malicious phishing web sites designed to steal consumer data.
Certainly one of their largest targets was the cryptocurrency web site MyEtherWallet. Attackers despatched customers making an attempt to entry their digital wallets to a phishing website and managed to steal round $152,000 through the two-hour assault window.
Man-in-the-Center (MITM) Assault
A man-in-the-middle (MIM) assault is a kind of cyberattack that hackers use to intercept digital site visitors or information transfers and hijack essential data. To execute this assault, an attacker intercepts a consumer’s DNS request earlier than it reaches a reliable server and reroutes to a faux IP handle. This not solely sends a spoofed end result again to the consumer and infects their gadget however may also poison the DNS server that acquired the preliminary request.
Exploiting Time-to-Reside (TTL)
Time-to-live (TTL) is a setting in DNS information that determines how lengthy the document could be saved (cached) by DNS servers earlier than it must be refreshed. By extending the TTL, attackers be certain that their malicious DNS mappings stay within the cache of DNS servers and customers’ units for an extended interval than supposed.
This tactic prolongs the window of alternative for attackers to redirect customers to malicious web sites or servers, amplifying the affect of DNS spoofing incidents.
Methods to Stop DNS Spoofing and Cache Poisoning
DNS spoofing and cache poisoning could be troublesome to detect since they will have an effect on each consumer units and DNS servers. Nonetheless, people and companies can take steps to cut back their danger of falling sufferer to an assault.
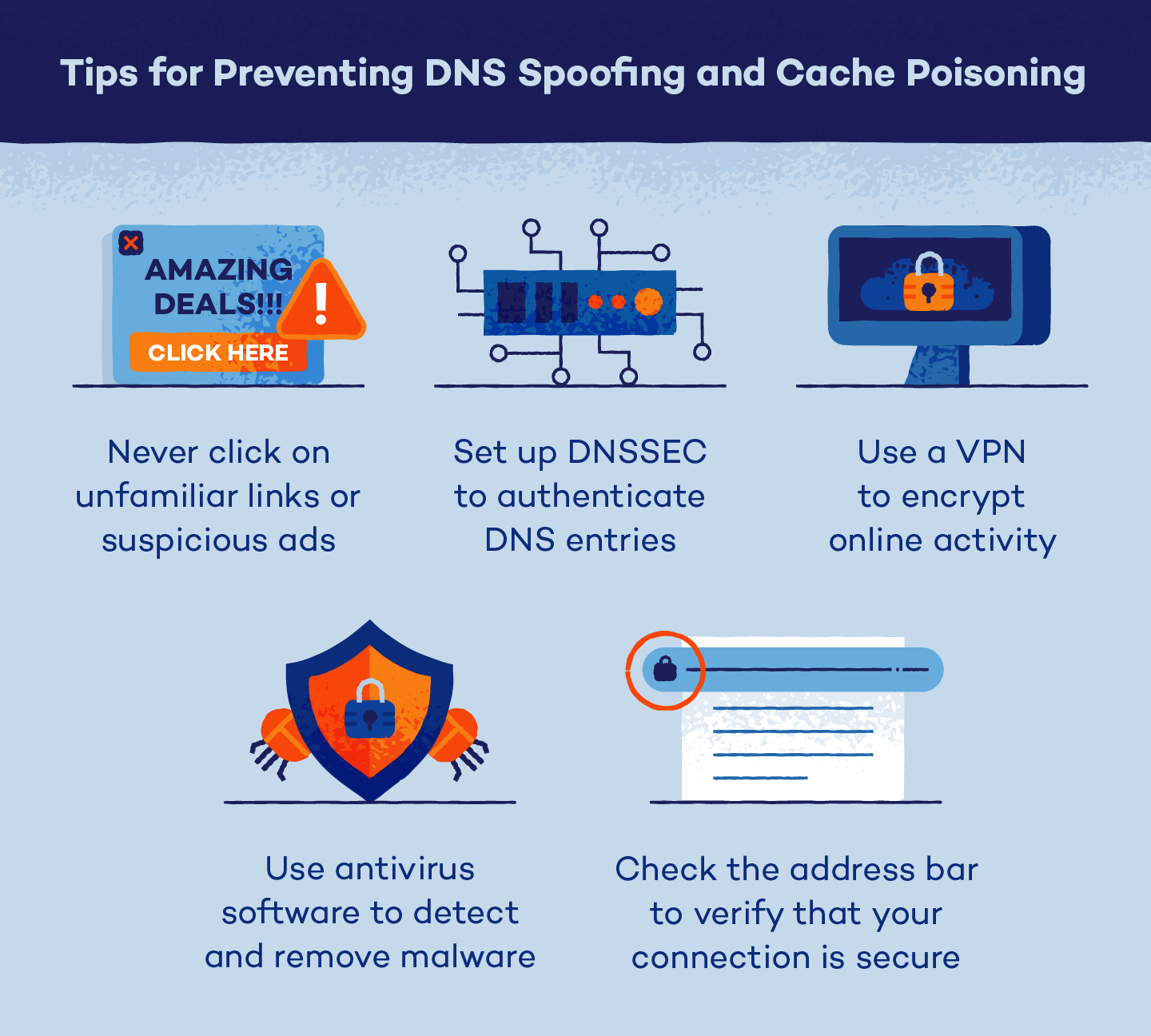 By no means Click on on Unfamiliar Hyperlinks
By no means Click on on Unfamiliar Hyperlinks
Malicious web sites typically show faux ads or notifications that immediate you to click on on a hyperlink. By clicking on unfamiliar hyperlinks, you could possibly expose your gadget to harmful viruses and different malware. Should you discover an unfamiliar hyperlink or commercial on a web site you usually use, it’s finest to keep away from it.
Set Up DNSSEC
Area homeowners and web suppliers can arrange DNS safety extensions (DNSSEC) to authenticate DNS entries. DNSSEC works by assigning a digital signature to DNS information and analyzing a root area’s certificates to confirm that every response is genuine. This ensures that every DNS response comes from a reliable web site. Sadly, DNSSEC just isn’t extensively used, so DNS information for many domains stays unencrypted.
Scan for and Take away Malware
As a result of attackers typically use DNS spoofing to put in viruses, worms and different kinds of malware, it’s essential to scan your units for these threats recurrently. You are able to do this by putting in antivirus software program that identifies and helps take away threats. Should you personal a web site or DNS server, it’s also possible to set up DNS spoofing detection instruments. These are designed to scan all outgoing information to make sure it’s reliable.
Use a VPN
A digital personal community (VPN) is an added safety measure that stops attackers from monitoring your on-line exercise. As a substitute of connecting your units to your web supplier’s native server, a VPN connects to non-public DNS servers around the globe that use end-to-end encrypted requests. This prevents attackers from intercepting site visitors and connects you to DNS servers which might be higher shielded from DNS spoofing.
Confirm That Your Connection Is Safe
Malicious web sites are sometimes equivalent to reliable ones at first look, however there are a number of methods to confirm that you simply’re related to a safe website. Should you’re utilizing Google Chrome, search for a small, grey padlock image within the handle bar to the left of the URL. This image exhibits that Google trusts the area host’s safety certificates and signifies that the web site just isn’t a reproduction.
In some circumstances, your browser will provide you with a warning if you happen to attempt to entry an unsecured website. Should you see a message warning that your connection isn’t safe, you shouldn’t ignore it. It might imply that the location you’re attempting to entry is a spoofed website with out a reliable SSL (Safe Sockets Layer) certificates.
DNS spoofing is likely one of the most troublesome kinds of cyberattacks to detect, however there are many methods you should utilize to guard your self and your data. Think about putting in dependable antivirus software program or a VPN to assist safe your on-line exercise and fend off future assaults.


