Management statements in C, additionally known as management constructs in C, permit builders to handle this system’s execution circulate. These management directions in C, together with conditional management statements, simplify decision-making, looping, and branching, making executing directions conditionally or repeatedly doable. This text will focus on management statements in c with examples
Key Takeaways
- Management statements in C dictate the execution circulate of a program, enabling decision-making, looping, and branching primarily based on circumstances.
- There are three predominant varieties of management statements in C language: decision-making (
if, else if assertion, switch-case), iteration (for, whereas, do-while), and leap (break, proceed, goto). These kind the idea of management construction in C programming, enabling builders to deal with varied logical eventualities effectively. - The `
if-else` assertion executes blocks of code primarily based on a real or false situation, with syntax emphasizing the usage of parentheses for circumstances and braces for code blocks. - The `
switch-case` assertion supplies a structured methodology for multi-way branching utilizing integer values of expressions. Every case ends in a `break` to stop a fall-through. - Iteration statements like `
for`, `whereas`, and `do-while` loops facilitate the repeated execution of code blocks primarily based on conditional expressions, with every loop kind providing completely different management mechanisms. - Nested management buildings, together with nested if-else and switch-case inside loops, permit for complicated decision-making and repetitive duties inside various programming eventualities.
What Is Management Statements in C
Management statements in C are directions that handle the circulate of execution in a program primarily based on particular circumstances or repetitions. They permit builders to make choices, repeat duties, or leap to particular elements of the code.
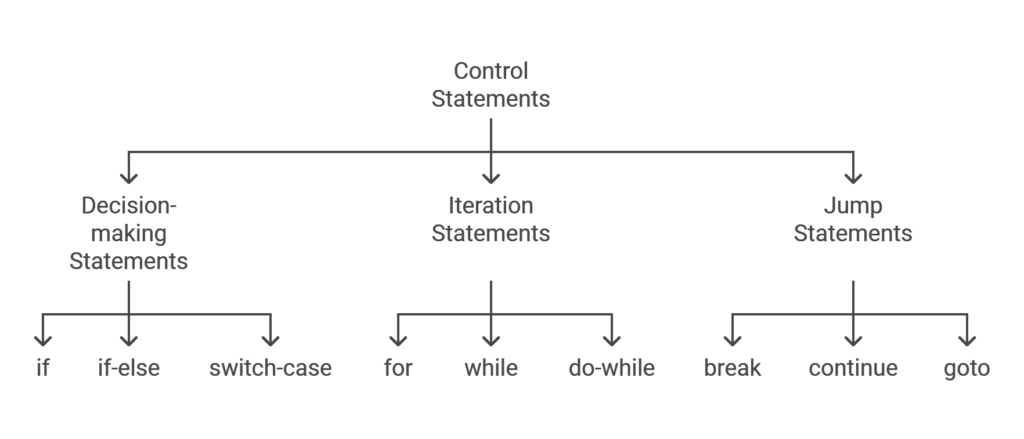
Forms of Management Statements
There are three varieties of management statements in C:
- Determination-making statements (
if, if-else, switch-case) - Iteration statements (
for, whereas, do-while) - Soar statements (
break, proceed, goto)
Determination-Making Statements
1. if-else Assertion
The if-else assertion, a significant a part of management circulate statements in C, executes blocks of code primarily based on a true or false situation. Advanced choices usually contain a number of if-else statements or an else-if assertion, making certain completely different outcomes for varied circumstances.
Syntax
if (situation) {
} else {
}- If the situation is true, the if block runs, and this system continues with the subsequent assertion after it.
- If the situation is fake and there’s no else block, this system merely skips the if block and strikes to the subsequent assertion.
- The else block is used solely when particular code must run if the situation is fake.
Instance 1: Verify Optimistic or Adverse Quantity
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant( ) {
int a;
printf("n Enter a quantity:");
scanf("%d", &a);
if(a>0)
{
printf( "n The quantity %d is constructive.",a);
}
else
printf("n The quantity %d is unfavourable.",a);
}
return 0;
}Instance 2: Examine Two Strings
#embrace <string.h>
int predominant( )
char a[20] , b[20];
printf("n Enter the primary string:");
scanf("%s",a);
printf("n Enter the second string:")
scanf("%s",b);
if((strcmp(a,b)==0))
{
printf("nStrings are the identical")
else
printf("nStrings are completely different");
}
return 0;
}The above program compares two strings to verify whether or not they’re similar. The strcmp perform is used for this function. It’s declared within the string.h file as:
int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2);It compares the string pointed to by s1 to the string pointed to by s2, and returns:
- 0 if the strings are equal.
- Adverse if the primary string is lower than the second.
- Optimistic if the primary string is larger than the second.
Notice: The comparability is case-sensitive. For case-insensitive comparisons, use strcasecmp() (non-standard).
Nested if and if-else Statements
Additionally it is doable to embed or to nest if-else statements one throughout the different. Nesting is beneficial when a number of circumstances have to be evaluated.
The final format of a nested if-else assertion is:
if(condition1) {
} else if(condition2) {
} else if(conditionN) {
} else {
}
}
else
{
}This construction can be known as the if-else ladder. Throughout the execution of a nested if-else assertion, execution stops on the first situation that evaluates to true, and the remaining blocks are skipped.
If neither of the circumstances is true, both the final else-block is executed, or if the else-block is absent, the management will get transferred to the subsequent instruction current instantly after the else-if ladder.
Instance: Discover the Best of Three Numbers
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int a = 6, b = 5, c = 10;
if(a > b) {
if(a > c) {
printf("nGreatest is: %d", a);
} else {
printf("nGreatest is: %d", c);
}
} else if(b > c) {
printf("nGreatest is: %d", b);
} else {
printf("nGreatest is: %d", c);
}
return 0;
}The above program compares three integer portions and prints the best. The primary if assertion compares the values of a and b.
- If a>b is true, it enters a nested if to match a and c.
- If a > c, prints a. In any other case, prints c.
- If the primary situation fails (a > b is fake), it checks b > c. If true, prints b, else c.
Finest Practices and Widespread Errors:
- Braces for Single Statements: At all times enclose statements in braces {} even when just one assertion follows an if or else.
- Keep away from Project As a substitute of Comparability: Use == for comparisons, not =, which assigns values.
- Indentation Issues: Keep constant indentation to enhance readability and keep away from errors.
- Take a look at Edge Instances: Validate inputs and outputs, particularly in nested if-else buildings, to deal with boundary circumstances.
2. Swap Assertion
The switch-case assertion is used for multi-way branching, the place a variable or expression’s worth is matched towards predefined instances. It’s ideally suited for changing lengthy chains of if-else when testing for equality.
Nevertheless, it’s a must to watch out when utilizing a change assertion since lacking a break assertion may cause fall-through behaviour, executing subsequent instances and resulting in surprising outcomes.
Syntax
change (expression) {
case value1:
break;
case value2:
break;
...
case valueN:
break;
default:
}The worth of this expression is both generated throughout program execution or learn in as consumer enter. The case whose worth is similar as that of the expression is chosen and executed. The non-compulsory default label is used to specify the code phase to be executed when the worth of the expression doesn’t match any of the case values.
If no break statements have been current on the finish of the third case, the change assertion prematurely executes all subsequent instances, inflicting unintended outcomes.
If the break is current, solely the required case is chosen and executed, after which the management will get transferred to the subsequent assertion instantly after the change assertion.
There is no such thing as a break after default as a result of, after the default case, the management will, both manner, get transferred to the subsequent assertion instantly after the change.
Instance 1: Print the Day of the Week
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant( ) {
int day;
printf("nEnter the variety of the day:");
scanf("%d",&day);
change(day)
{
case 1
printf("Sunday")
break;
case 2
printf("Monday");
break
case 3
printf("Tuesday");
break
case 4
printf"Wednesday"
break;
case 5
printf"Thursday"
break;
case 6
printf("Friday")
break;
case 7
printf("Saturday");
break
default
printf"Invalid selection"
return 0;
}This primary program demonstrates the usage of the switch-case assemble. The suitable case is executed primarily based on the consumer’s enter, and the break assertion prevents the execution of subsequent instances. As an illustration, if the enter is 5, the output might be Thursday.
All applications written utilizing the management construction in C, such because the switch-case assertion, will also be applied utilizing the if-else assertion.
Nevertheless, the management circulate statements in C, like switch-case, provide higher readability and efficiency in multi-way branching.
Swap-case statements are significantly efficient for menu-based purposes or dealing with particular consumer inputs. In comparison with nested if-else statements, they’re extra environment friendly and simpler to learn, particularly when choosing from a hard and fast set of decisions.
Instance 2: Menu-Pushed Program for File Processing
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int selection;
printf("nPlease choose from the next choices:");
printf("n1. Add a report on the finish of the file.");
printf("n2. Add a report initially of the file.");
printf("n3. Add a report after a selected report.");
printf("nPlease enter your selection (1/2/3): ");
scanf("%d", &selection);
change(selection) {
case 1:
break;
case 2:
break;
case 3:
break;
default:
printf("nWrong Selection");
}
return 0;
}The above instance of switch-case typically includes nesting the switch-case assemble inside an iteration assemble like do-while.
Finest Practices and Widespread Errors:
- At all times Use Break: Embrace a break after every case except intentional fall-through is required.
- Default Case Placement: Place the default on the finish to enhance readability.
- Take a look at All Enter Values: Guarantee inputs match legitimate case values and deal with invalid inputs correctly utilizing the default case.
- Keep away from Advanced Expressions: Use easy constants for instances, as variables or ranges should not supported.
- Indentation and Formatting: Comply with constant indentation to keep up readability.
Iteration Statements
Iteration statements are used to execute a selected set of directions repeatedly till a selected situation is met or for a hard and fast variety of iterations.
1. for Loop
The `for` loop is a pre-test loop, which evaluates the situation earlier than the loop executes. It’s best suited to conditions the place the variety of iterations is understood beforehand.
Syntax
for(initialization; termination; increment/decrement) { The for loop consists of three expressions:
- Initialization expression: Initializes the looping index. The looping index controls the looping motion. The initialization expression is executed solely as soon as when the loop begins.
- Termination expression: Represents a situation that have to be true for the loop to proceed execution.
- Increment/decrement expression: Executed after each iteration to replace the worth of the looping index.
Instance: Fibonacci Sequence
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int i, n, a = 0, b = 1, sum;
printf("Enter the variety of phrases: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d %d", a, b);
for(i = 2; i < n; i++) {
sum = a + b;
printf(" %d", sum);
a = b;
b = sum;
}
return 0;
}The above program makes use of the for loop to print the collection: 0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13 … to n phrases.
- Initialization: Units i = 2 as the primary two phrases (0 and 1) are already printed.
- Situation: Continues execution till i < n.
- Increment: Increments i by 1 after every iteration.
If the enter quantity is 7, the out put might be:
Variations of the for Loop
1. Omitting the Initialization Expression
On this case, the looping index is initialized earlier than the for loop. Thus, the for loop takes the next kind:
int i = 0;
for(; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", i);
}This methodology is beneficial when the loop variable is initialized outdoors the loop.
Notice: The semicolon that terminates the initialization expression is current earlier than the situation expression.
2. Omitting the Situation
On this case the situation is specified inside the physique of the for loop, typically utilizing an if assertion. The whereas or do-while statements can also be used to specify the situation. Thus the for loop takes the next kind:
for(int i = 0; ; i++) {
if(i == 5) break;
printf("%d ", i);
}That is helpful for conditions the place conditional exits are dealt with contained in the loop physique. Additionally, the semicolon that terminates the situation is current within the for assertion. The next program explains how the situation might be omitted:
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int i,n, a, b, sum=0;
printf("Enter the variety of phrases:");
scanf("%d",&n);
a=0;
b=1;
printf("%dn %d", a, b);
for(i=2; ;i++) {
if(i==(n-1)) {
break;
}
sum=a+b;
printf("npercentd",sum);
a=b;
b=sum;
}
return 0;
}3. Omitting the increment /decrement Expression:
On this case, the increment/decrement expression is written contained in the for loop’s physique. That is helpful once you solely must increment the loop rely primarily based on particular circumstances.
for(int i = 0; i < 5;) {
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
}4. Omitting all Three Expressions:
Additionally it is doable to omit all three expressions, however they need to be current within the methods mentioned above. If all three expressions are omitted solely — ie, they don’t seem to be talked about within the methods mentioned above — then the for loop turns into an infinite or unending loop.
On this case, the for loop takes the next kind:
Finest Practices and Widespread Errors:
- At all times Replace Loop Variables: Guarantee increments or decrements forestall infinite loops.
- Use Braces {} for Readability: Even for single statements contained in the loop.
- Keep away from Off-By-One Errors: Double-check termination circumstances, particularly with < or <=.
- Take a look at with Boundary Values: Validate conduct with minimal and most values.
2. whereas Loop
The whereas assertion executes a block of statements repeatedly whereas a selected situation is true.
The statements are executed repeatedly till the situation is true.
Instance 1: Sum of Digits
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int n, a, sum = 0;
printf("nEnter a quantity: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
whereas(n > 0) {
a = n % 10;
sum = sum + a;
n = n / 10;
}
printf("nSum of the digits = %d", sum);
return 0;
}The above program makes use of the whereas loop to calculate the sum of the digits of a quantity. For instance, if the quantity is 456, the whereas loop will calculate the sum in 4 iterations as follows.
Notice: % offers the rest and / the quotient.
- Iteration 1: n>0 Situation is true(n=456) a=npercent10=6; sum=sum+a=6; n=n/10= 45; New worth of n is 45.
- Iteration 2: n>0 Situation is true(n=45) a=npercent10=5; sum=sum+a=6+5=11; n=n/10= 4; New worth of n is 4.
- Iteration 3: n>0 Situation is true(n=4) a=npercent10=4; sum=sum+a=11+4=15; n=n/10= 0; ew worth of n is 0.
- Iteration 4: n>0 Situation is fake(n=0). After the fourth iteration management exits the whereas loop and prints the sum to be 15.
Instance 2: Palindrome Verify
A palindrome is a quantity that continues to be the identical when its digits are learn or written from proper to left or vice versa, eg 343 is a palindrome, however 342 isn’t.
The next program works on the logic that if the reverse of the quantity is similar as the unique quantity, then the entered quantity is a palindrome, in any other case it isn’t.
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int n, m, a, reverse = 0;
printf("nEnter a quantity: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
m = n;
whereas(n > 0) {
a = n % 10;
reverse = reverse * 10 + a;
n = n / 10;
}
if (m == reverse) {
printf("nThe quantity is a palindrome.");
} else {
printf("nThe quantity isn't a palindrome.");
}
return 0;
}The above program makes use of virtually the identical logic as this system of the sum of digits. As was seen in that program, n turns into 0 within the final iteration. Nevertheless, we have to examine the unique worth of n to the reverse of the quantity to find out whether or not it’s a palindrome or not.
Subsequently, the worth of n was saved in m earlier than getting into the whereas loop. The worth of m is later in contrast with the reverse to determine whether or not the entered quantity is a palindrome or not.
The whereas loop works within the following manner:
Let n=343;
- Iteration 1: a= npercent10=3; reverse=reverse*10+a=0*10+3=3; n=n/10=34;
- Iteration 2: a=npercent10=4; reverse=reverse*10+a=3*10+4=34; n=n/10=3;
- Iteration 3: a= npercent10=3; reverse=reverse*10+a=34*10+3=343; n=n/10=0;
- Iteration 4: n>0 situation false(n=0). Management exits from the whereas loop.
Finest Practices and Widespread Errors:
- Infinite Loops: Make sure the situation adjustments throughout the loop to keep away from infinite execution.
- Initialization: Initialize variables correctly earlier than getting into the loop.
- Break Situations: Use specific break statements when required for early exits.
- Edge Instances: Take a look at inputs like 0 or unfavourable values to deal with all eventualities.
3. do-while loop
The do-while loop is an exit-controlled loop, which means the loop physique executes a minimum of as soon as earlier than the situation is checked.
Syntax
The distinction between whereas and do-while is that the whereas loop is entry-controlled — it exams the situation initially of the loop and won’t execute even as soon as if the situation is fake, whereas the do-while loop is exit-controlled — it exams the situation on the finish of the loop after finishing the primary iteration.
For a lot of purposes, it’s extra pure to check for the continuation of a loop initially quite than on the finish of the loop. For that reason, the do-while assertion is used much less incessantly than the whereas assertion.
Instance 1: Sum of Digits
The next program calculates the sum of digits in the identical method, besides that it makes use of the do-while loop:
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int n, a, sum = 0;
printf("nEnter a quantity: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
do {
a = n % 10;
sum = sum + a;
n = n / 10;
} whereas(n > 0);
printf("nSum of the digits = %d", sum);
return 0;
}Nevertheless, the do-while assertion must be used solely when the loop have to be executed a minimum of as soon as, whether or not or not the situation is true.
A sensible use of the do-while loop is in an interactive menu-driven program the place the menu is offered a minimum of as soon as, after which, relying upon the consumer’s selection, the menu is displayed once more, or the session is terminated. Contemplate the identical instance that we noticed within the change case.
Instance 2: Menu-Pushed Program
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int selection;
char ch;
do {
printf("nMain Menu");
printf("n1. Add a report on the finish of the file.");
printf("n2. Add a report initially of the file.");
printf("n3. Add a report after a selected report.");
printf("nPlease enter your selection (1/2/3): ");
scanf("%d", &selection);
change(selection) {
case 1:
break;
case 2:
break;
case 3:
break;
default:
printf("nWrong Selection");
}
printf("nDo you wish to proceed updating data (y/n)? ");
scanf(" %c", &ch);
} whereas(ch == 'y' || ch == 'Y');
return 0;
}Finest Practices and Widespread Errors:
- Initialization: Guarantee variables are initialized earlier than getting into the loop.
- Situation Validation: Deal with edge instances the place enter would possibly trigger infinite loops.
- Interactive Packages: Desire do-while when the loop should execute a minimum of as soon as.
- Readability: Keep correct indentation and feedback for readability.
Soar Statements
Soar management circulate statements in C programming alter the circulate of a program unconditionally. These embrace `break`, `proceed`, and `goto`. , that are basic elements of management constructs in C.”
1. break Assertion
The break assertion is primarily used to exit early from a loop or a switch-case assertion. It stops the execution of the present assemble and transfers management to the assertion instantly following the assemble.
Syntax
When the break assertion is encountered, this system instantly exits the enclosing loop or switch-case construction and resumes execution after it.
Instance: Search in an Array
Contemplate a scenario the place you’re looking for a particular quantity in an array. As quickly because the quantity is discovered, the loop might be terminated utilizing break.
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int goal = 30;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (arr[i] == goal) {
printf("Discovered %d at index %dn", goal, i);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}Output
Right here, the break assertion ensures the loop doesn’t waste time checking the remaining components as soon as the goal is discovered.
Finest Practices:
- Use break Judiciously: Keep away from extreme use, as it will probably make code tougher to learn.
- Validate Situations: Make sure the situation triggering break is well-defined to stop logical errors.
- Doc Function: Add feedback to clarify why break is used to enhance maintainability.
2. proceed Assertion
The `proceed` assertion is used to skip the remaining statements within the present iteration of a loop and proceed to the subsequent iteration. When proceed is encountered, this system jumps again to the start of the loop, re-evaluates the loop situation, and begins the subsequent iteration.
Syntax
Instance: Printing solely odd numbers in a variety
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
proceed;
}
printf("%d ", i);
}
return 0;
}Right here, the proceed assertion ensures that even numbers are skipped with out terminating the loop.
Output
Finest Practices:
- Keep away from Overuse: Frequent use of proceed can cut back code readability.
- Simplify Situations: Optimize logic to scale back reliance on proceed.
- Remark Utilization: Add feedback to clarify why proceed is used, particularly in loops with a number of circumstances.
3. goto Assertion
The goto assertion performs an unconditional leap to a labeled assertion throughout the similar perform. Whereas thought-about dangerous for code readability, it may be helpful in particular instances like breaking out of deeply nested loops or error dealing with.
When the goto assertion is encountered, this system jumps on to the labeled assertion, skipping intermediate code.
Syntax
Instance: Exiting Nested Loops
In eventualities with a number of nested loops, exiting all loops concurrently might be difficult. The goto assertion simplifies this course of.
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (i == j) {
goto finish;
}
printf("i = %d, j = %dn", i, j);
}
}
finish:
printf("Exited nested loops.n");
return 0;
}#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (i == j) {
goto finish;
}
printf("i = %d, j = %dn", i, j);
}
}
finish:
printf("Exited nested loops.n");
return 0;
}Output
i = 0, j = 1
i = 0, j = 2
Exited nested loops.Right here, the loop Iterates by means of i and j. When i == j, the goto assertion jumps on to the finish label, skipping additional iterations.
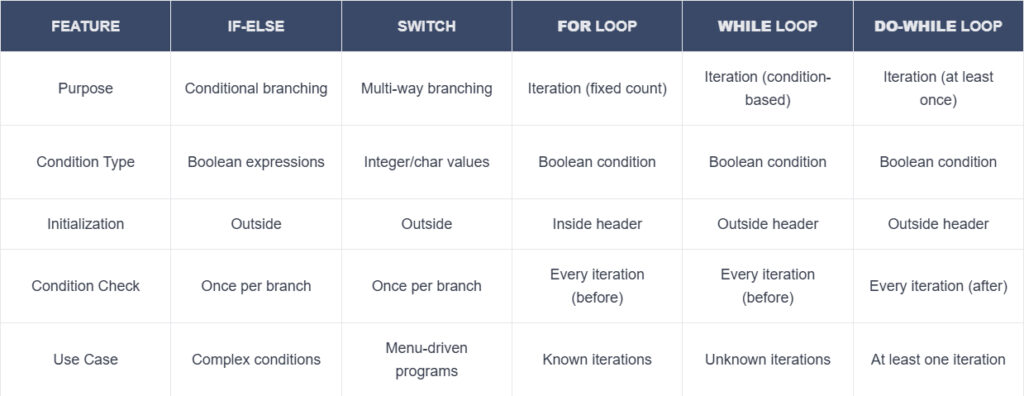
Comparability Desk
Superior Utilization and Interactions
1. Utilizing Management Statements with Arrays
Management statements in C, a key side of the C programming language, are sometimes paired with arrays for duties like looking, filtering, and processing. For instance, looping buildings like for and whereas are important elements of management directions in C, serving to to navigate array components effectively. As an illustration, right here is methods to discover the utmost aspect in an array:
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
int arr[] = {10, 20, 50, 40, 30};
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
printf("Most aspect: %dn", max);
return 0;
}The loop begins with the second aspect (index 1) for the reason that first aspect is assumed to be the utmost initially.
The if assertion compares every aspect with the present max.
If a bigger aspect is discovered, max is up to date.
2. Error Dealing with Utilizing Management statements in C
Though C lacks built-in exception dealing with, management statements in C like if and goto can deal with easy errors.
#embrace<stdio.h>
int predominant() {
FILE *file = fopen("knowledge.txt", "r");
if (file == NULL) {
printf("Error: File not discovered.n");
return 1;
}
printf("File opened efficiently.n");
fclose(file);
return 0;
}The if assertion checks if the file pointer is NULL, indicating the file couldn’t be opened.
If true, an error message is displayed, and this system exits early utilizing return 1.
FAQs About Management Statements in C
What Are Management Statements in C?
Management statements in C, sometimes called management construction in C, are programming constructs that help you management the circulate of a program. These management constructs in C language are important for decision-making, iteration, and branching.
What Is the Function of Conditional Statements in C?
Conditional statements, comparable to if, else if, and change, help you execute completely different blocks of code primarily based on specified circumstances. They allow your program to make choices and carry out actions accordingly.
How Do I Use the If Assertion in C?
if assertion, some of the used management directions in C, is used to execute a block of code if a specified situation is true. It may be adopted by an non-compulsory “else” assertion to specify another motion if the situation is fake.
What Is the Distinction Between If and Swap Statements?
if statements are used for common conditional branching, whereas change statements are used for multi-way branching primarily based on the worth of an expression. if statements are extra versatile and may deal with complicated circumstances, whereas change statements are perfect for conditions the place a variable can match particular values.
When Ought to I Use a Whereas Loop over A for Loop?
Use some time loop when that you must repeat a block of code so long as a situation stays true however and not using a fastened variety of iterations. for loops are extra appropriate for conditions with a recognized variety of iterations.
What Are the Widespread Errors to Keep away from When Utilizing Management Statements in C?
Widespread errors embrace not utilizing braces for code blocks in if and loop statements, forgetting to replace loop management variables, and creating infinite loops by not altering loop circumstances appropriately. Correctly structuring your code and dealing with nook instances are important.
How Do I Keep away from Infinite Loops?
Guarantee loop circumstances are up to date appropriately contained in the loop.
Debug by printing key variables concerned within the loop situation.
Use breakpoints in an IDE to watch the loop execution.
Can I Use A number of Else If Situations in an If Assertion?
Sure, you should use a number of else if circumstances in an if assertion to judge a collection of circumstances sequentially. This lets you select from a number of alternate options primarily based on the primary true situation.
What’s the Distinction Between Break and Proceed?
- break: Exits the loop solely and strikes management to the assertion after the loop.
- proceed: Skips the remainder of the loop physique for the present iteration and jumps to the subsequent iteration.



