GitHub vs. Bitbucket
GitHub isn’t the one hosted enhanced Git service, and GitHub Enterprise isn’t the one on-premises product for corporations. Atlassian Bitbucket competes with each of them, with barely decrease pricing and with a free five-member workforce stage that features limitless personal repos and the usage of Bitbucket Pipelines for steady integration. GitHub is a extra well-liked web site for open supply tasks and it has a a lot bigger pool of open supply builders. Bitbucket’s pricing was extra favorable for small startups. Now that GitHub permits limitless personal repos on free and workforce accounts, that’s now not the case.
GitHub vs. GitLab
GitLab competes with each GitHub and Bitbucket, each hosted and on-premises. On the floor, GitLab seems to have extra lifecycle performance than the others, however the distinction from Bitbucket principally disappears in the event you embrace Jira once you consider Bitbucket. GitLab affords Gold-plan cloud options to open-source tasks totally free, however that further performance doesn’t actually compensate for the bigger open-source developer group on GitHub.
GitHub Desktop
GitHub Desktop, proven beneath, makes it simple to handle your GitHub.com and GitHub Enterprise repositories. Whereas it doesn’t implement all the options of the Git command line and the GitHub net GUI, it does implement all of the operations you’ll do every day out of your desktop whereas contributing to tasks. Sometimes, you’ll clone repos from GitHub to GitHub Desktop, sync them as wanted, create branches on your work, commit your work, and infrequently revert a number of commits.
To work with repos for which you lack commit and collaborate privileges, you usually begin by forking the repo on GitHub and cloning the fork to your desktop. Then you definately add any branches you want in GitHub Desktop, commit any adjustments you would like, take a look at your work, push the commits again to your distant forked repo, and eventually generate a pull request to the mum or dad undertaking.
You may see the Pull Request button on the higher proper of the GitHub Desktop interface. You may also see many commits within the Neo4j undertaking that had been merges of branches or pull requests. That’s typical of open-source tasks with few committers and plenty of contributors.
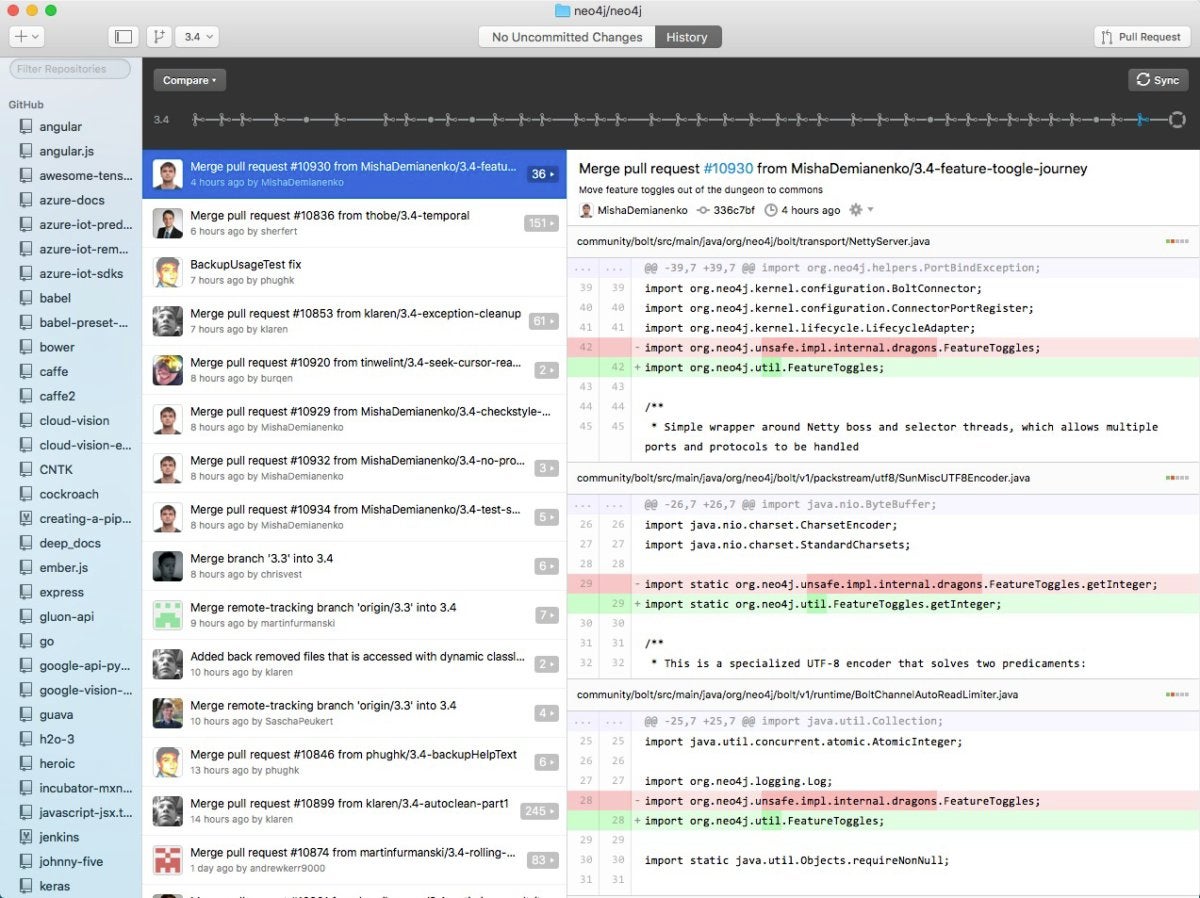
GitHub Desktop provides you a helpful GUI for including or cloning repos, navigating branches, pushing adjustments, and managing pull requests.
GitHub for open-source tasks
Open-source software program tasks usually want methods to implement high quality management whereas nonetheless accepting contributions from exterior the core workforce of committers. The necessity for contributors is large, however bringing new contributors into the undertaking whereas sustaining the integrity of the codebase is a troublesome and doubtlessly harmful endeavor. On the identical time, the necessity for suggestions from customers of the undertaking can also be enormous.
GitHub has a variety of mechanisms that may assist grease the wheels of open supply tasks. For instance, customers can add points to the undertaking on GitHub to report bugs or request options. Another programs name these tickets. Venture managers working with points can generate process lists, assign points to particular contributors, point out different contributors in order that they’re notified of adjustments, add labels, and add milestones.
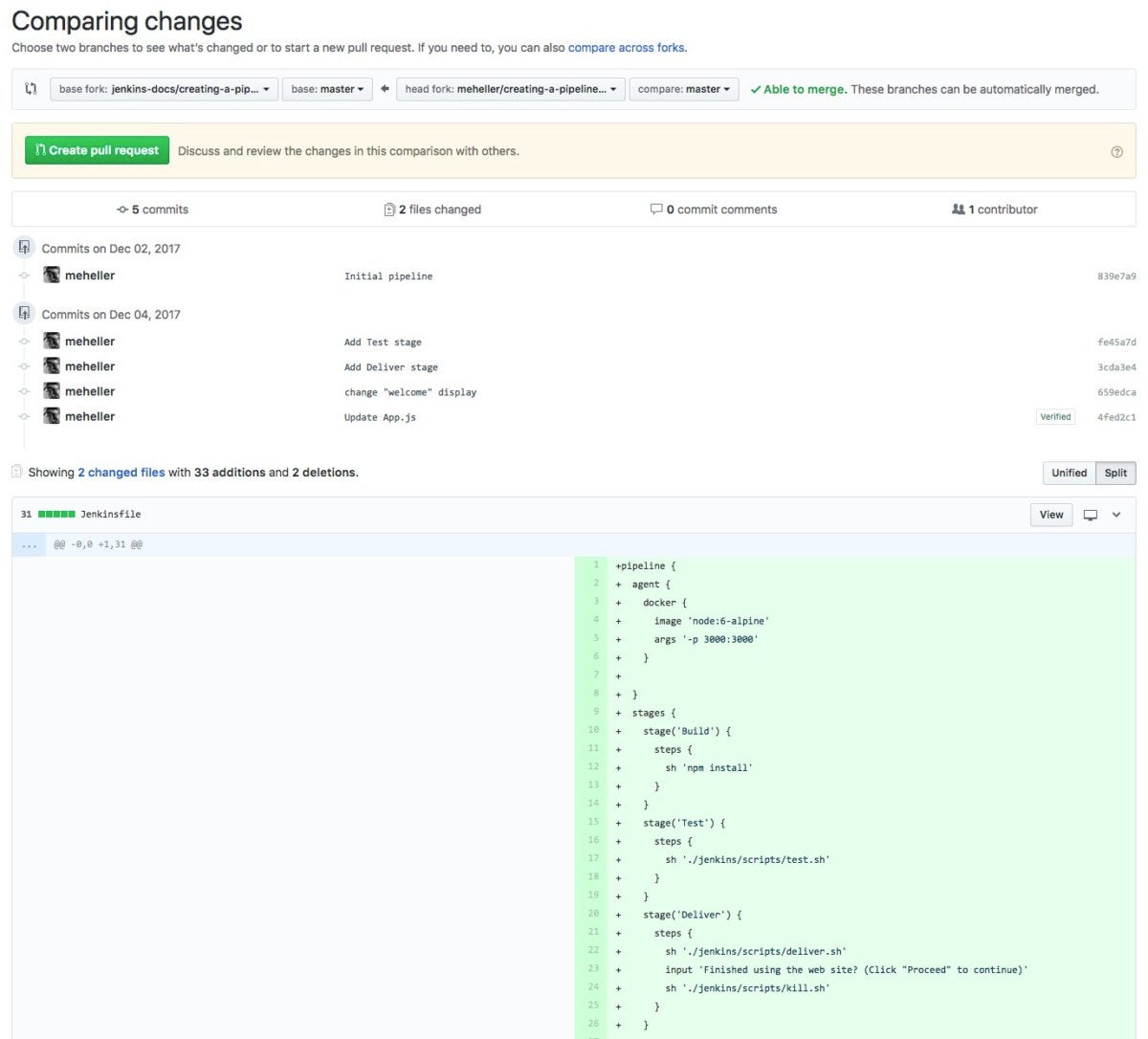
To contribute to a undertaking, you mainly begin from a subject head department that incorporates the dedicated adjustments that you really want added to the undertaking base department and initialize a pull request from the pinnacle department, as proven beneath. Then you definately push your commits and add them to the undertaking department. Different contributors can assessment your proposed adjustments, add assessment feedback, contribute to the pull request dialogue, and add their very own commits to the pull request.
As soon as everybody concerned is pleased with the proposed adjustments, a committer can merge the pull request. The merge can protect all of the commits, squash all adjustments right into a single commit, or rebase the commits from the pinnacle department into the bottom department. If the merge generates conflicts, you possibly can resolve them on GitHub or utilizing the command line.
Code critiques on GitHub enable a distributed workforce to collaborate asynchronously. Helpful GitHub instruments for reviewers embrace diffs (the decrease half of the screenshot beneath), historical past (the higher half), and blame view (a technique to view the evolution of a file commit by commit). Code discussions on GitHub go into feedback which are introduced consistent with your code adjustments. If the built-in instruments don’t suffice on your undertaking, you possibly can add code assessment and steady integration instruments from the GitHub market. Market add-ons are sometimes free for open supply tasks.
GitHub supplies a variety of helpful views into your code together with a commit historical past (high) and a diff view (backside).
GitHub gists
Gists are particular GitHub repositories for sharing your work (public) or for saving work for later reuse (secret). They’ll include single recordsdata, elements of recordsdata, or full purposes. You may obtain gists, clone them, fork them, and embed them.
Public gists might be found and located in searches. You should use key phrases to slim down what you discover, together with prefixes to limit the outcomes to gists from particular customers, gists with at the very least N stars, gists with particular filenames, and so forth.
Secret gists aren’t searchable, however anybody with the URL can see them. In the event you really need your code to be protected, use a non-public repository.
As we’ve seen, GitHub supplies Git repositories as a service, together with options for code assessment, undertaking administration, integrations with different developer instruments, workforce administration, social coding, and documentation. Whereas GitHub shouldn’t be the one product in its class, it’s the dominant repository for open-source software program growth.



