Introduction
After I first began working with spreadsheets, I used to be baffled by how formulation behaved when copied throughout cells. Generally, they labored completely, whereas others went fully haywire. I didn’t notice it then, however by mastering spreadsheets, I perceive how references—relative, absolute, and blended—operate. As soon as I grasped this idea, my productiveness skyrocketed. In the event you’ve ever been confused by formulation that appear to vary unpredictably, you’re in the precise place. On this information, I’ll stroll you thru the ins and outs of those references, utilizing sensible examples that may assist you to take full management of your spreadsheets.
Overview
- The article discusses the significance of understanding cell references in spreadsheets to grasp formulation.
- Explains how relative references routinely alter when copied throughout cells.
- Describes absolute references that stay mounted no matter the place the method is copied.
- Covers blended references that mix parts of each relative and absolute references.
- Emphasizes mastering these references to enhance spreadsheet effectivity and scale back errors.
Understanding Cell References
In spreadsheet software program like Excel or Google Sheets, a cell reference tells this system which cell’s knowledge you wish to use in a method. These references may be categorized into three essential sorts: relative, absolute, and blended. Every kind behaves in another way whenever you copy or transfer a method to a different cell. Understanding these variations is important for correct knowledge evaluation and environment friendly workflow.
1. Relative References
What They Are: Relative references alter based mostly on the place the place they’re copied. While you transfer a method that incorporates relative references to a brand new cell, the references will routinely replace to replicate the brand new location.
Instance: Think about you might have knowledge in cells A1 and B1 and wish to sum them up in cell C1. You utilize the method =A1+B1. In the event you copy this method to cell C2, it is going to routinely alter to =A2+B2.
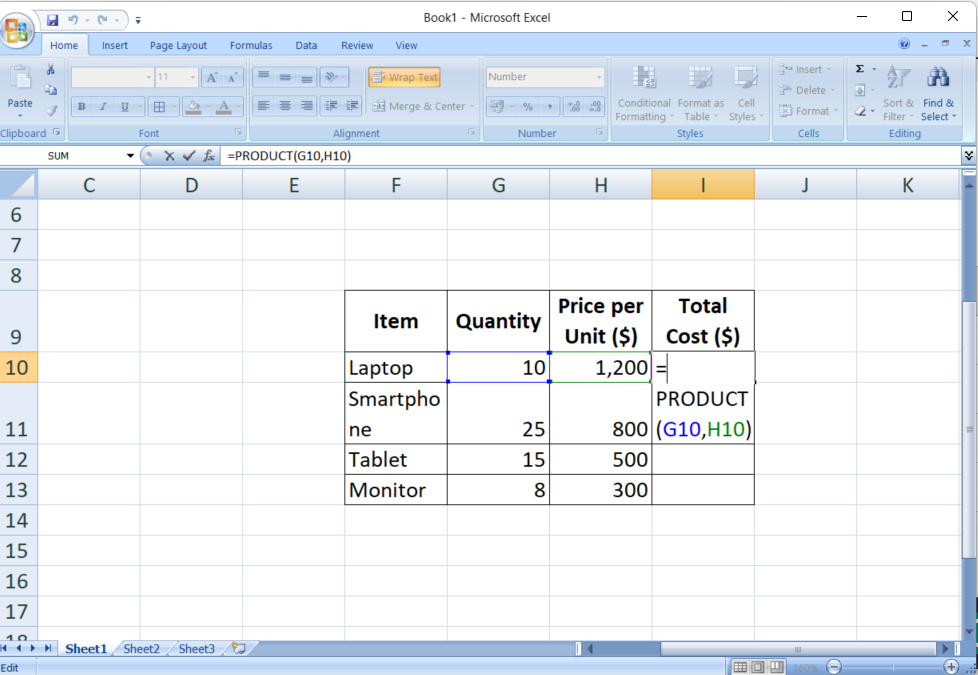
- Unique System:
=A1+B1in C1 - Copied System:
=A2+B2in C2
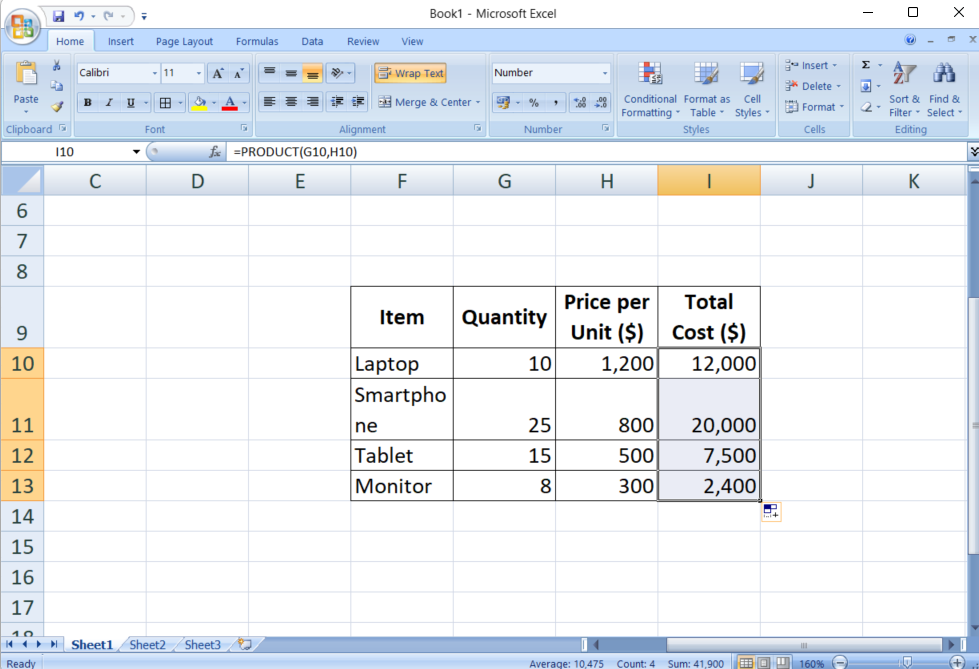
This adaptability is the core characteristic of relative references. They’re particularly helpful when performing the identical calculation throughout a number of rows or columns.
Additionally learn: Microsoft Excel for Knowledge Evaluation
2. Absolute References
What They Are: Absolute references don’t change when the method is copied to a different cell. They’re mounted to a selected cell, making them ideally suited whenever you want a continuing reference in a number of formulation.
How They Work: Absolute references are denoted by greenback indicators ($) earlier than the column letter and row quantity. As an illustration, $A$1 cell A1 will all the time check with that cell, regardless of the place you progress or copy the method.
Instance: If you wish to multiply every worth in column A by the fixed worth in cell B1, you’d use the method =A1*$B$1 in cell C1. While you copy this method right down to C2, C3, and so forth, it is going to alter solely the A1 half whereas it $B$1 stays fixed.
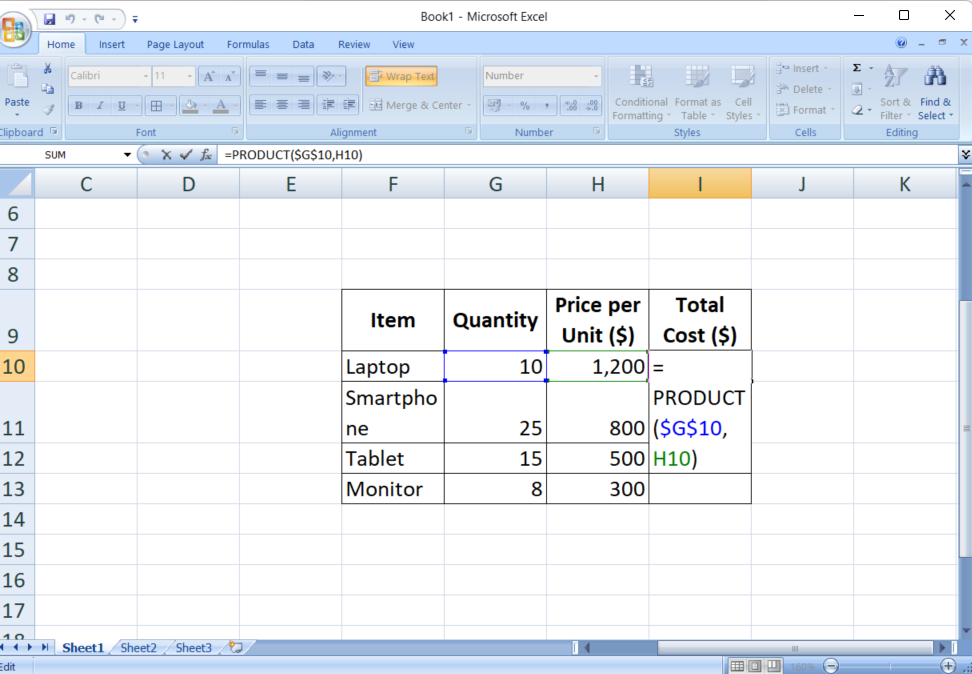
- Unique System:
=A1*$B$1in C1 - Copied System:
=A2*$B$1in C2
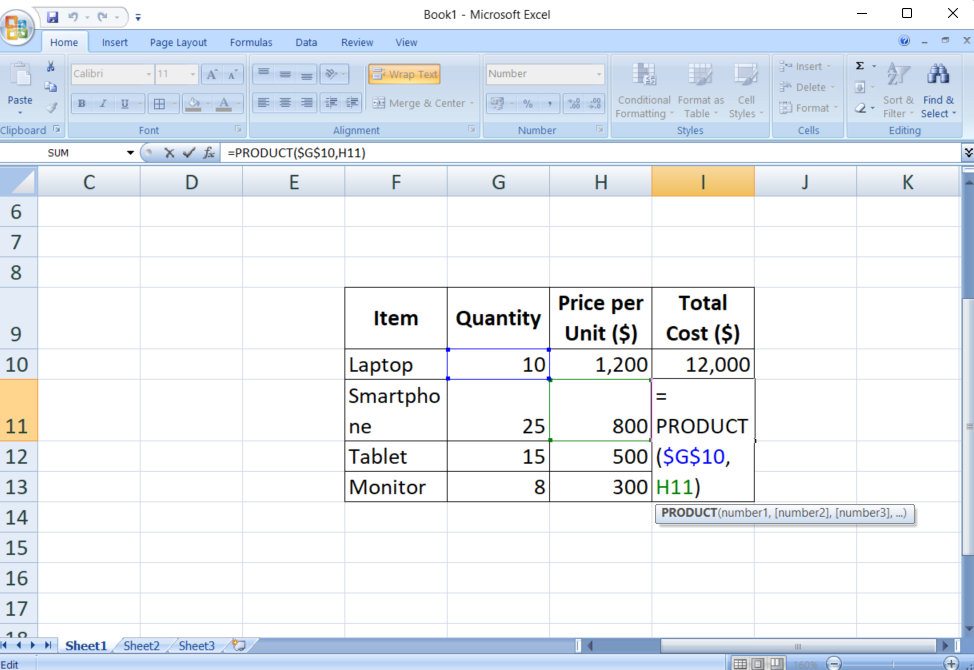
This ensures that each worth in column A is multiplied by the fixed worth in cell B1.
Additionally learn: Cheatsheet – Excel Capabilities & Keyboard Shortcuts
3. Blended References
What They Are: Blended references mix parts of each relative and absolute references. In a blended reference, the row or the column is mounted, however not each.
How They Work: There are two variations:
- Fixing the Column:
$A1– Right here, the column A is mounted, however the row quantity can change. - Fixing the Row:
A$1– Right here, row 1 is mounted, however the column letter can change.
Instance: Suppose you might have a desk the place you wish to multiply every row of knowledge by a price within the prime row. You possibly can use a method like =A$1*B1. When this method is copied throughout columns, the row reference stays mounted at 1, however the column adjusts. If copied down rows, the column adjusts usually.
- Unique System:
=A$1*B1in C1 - Copied System:
=B$1*C2in D2
Blended references are highly effective when it is advisable anchor one a part of the reference whereas permitting the opposite half to regulate.
Additionally learn: A Complete Information on Superior Microsoft Excel for Knowledge Evaluation.
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering these three sorts of cell references in Excel—relative, absolute, and blended—can considerably improve your effectivity when working with spreadsheets. They assist you to create dynamic and highly effective formulation that adapt to your wants, decreasing errors and saving you time. Subsequent time you’re engaged on a posh spreadsheet, strive experimenting with these references to see how they’ll simplify your workflow. Bear in mind, the extra you observe, the extra intuitive it is going to turn into.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
Ans. A relative reference in Excel refers to a cell deal with that adjustments when the method is copied to a different cell. For instance, in the event you use the method =A1+B1 in cell C1 after which copy it to C2, it is going to routinely alter to =A2+B2.
Ans. An absolute reference is a continuing cell deal with, no matter the place the method is copied. Including a greenback signal ($) earlier than the column letter and row quantity, corresponding to $A$1, achieves this. Regardless of the place you copy the method, the reference will all the time level to cell A1.
Ans. A blended reference is a mixture of relative and absolute references. You may lock both the column or the row, however not each. For instance, $A1 locks the column whereas the row adjustments, and A$1 locks the row whereas the column adjustments. Blended references are helpful whenever you want one a part of the reference to remain fixed and the opposite to regulate.
Ans. You may shortly toggle between relative, absolute, and blended references by choosing the cell reference within the method bar and urgent the F4 key. Every press of F4 will cycle by the completely different reference sorts.
Ans. A relative reference is most helpful whenever you need the method to regulate based mostly on its new place routinely. That is significantly useful when making use of the identical calculation throughout a number of rows or columns. Absolute or blended references are used when sure method components want to stay fixed.



