
Introduction
Technique overloading and methodology overriding are two elementary ideas in object-oriented programming (OOP) you have to know. They will enormously improve the flexibleness and performance of your code, particularly in fields like information science and synthetic intelligence, which require environment friendly and maintainable code. Though these two phrases may sound related, their underlying mechanisms are considerably completely different. They even have very completely different use instances. On this article, we are going to be taught what methodology overloading and overriding are, whereas understanding their variations and exploring their purposes.
New to OOP? Right here’s a beginner-level article to get you began with the fundamentals: Object-Oriented Programming in Python For Absolute Freshmen
Overview
- Perceive what methodology overloading and methodology overriding are.
- Know the syntax and implementation of every of them.
- Know the advantages and sensible purposes of each.
- Be taught the important thing variations between methodology overloading and overriding.
What’s Technique Overloading?
Technique overloading, also referred to as compile-time polymorphism, is a characteristic in OOP that enables a category to have a number of strategies with the identical title however completely different parameters. The compiler differentiates these strategies primarily based on the quantity, kind, and order of parameters. This lets you carry out related actions by means of a single methodology title, which improves the readability and reusability of your code.
Technique overloading is fairly simple in most programming languages like Java and C++. Python, nevertheless, doesn’t help it in the identical method. In Python, you’ll be able to outline strategies with the identical title, however the final methodology outlined will overwrite the earlier ones. As an alternative, Python makes use of default arguments, variable-length arguments, and key phrase arguments to attain related performance.
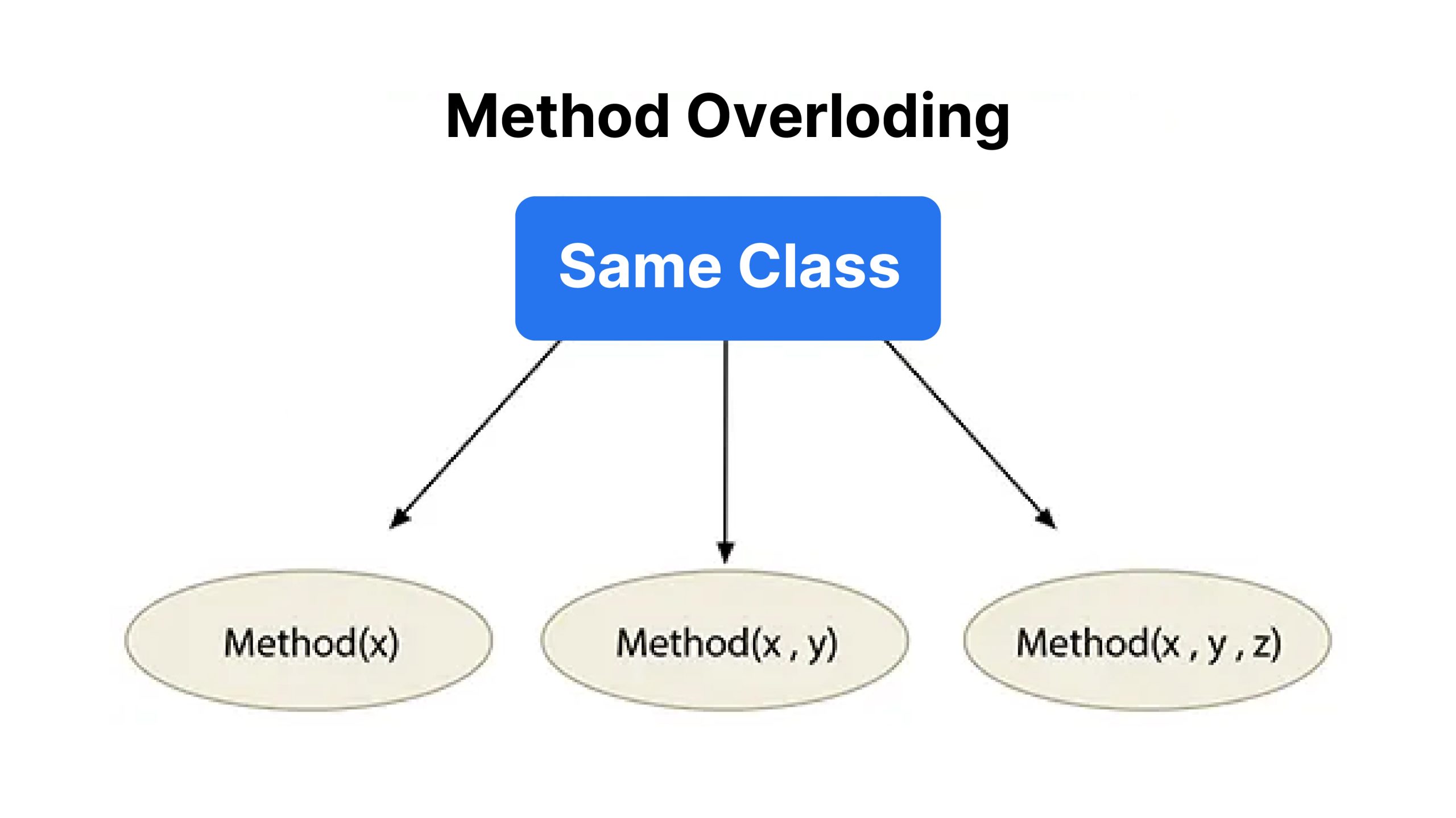
Syntax
Right here’s an instance of methodology overloading in Java:
class MathOperations {
// Technique so as to add two integers
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
// Overloaded methodology so as to add three integers
int add(int a, int b, int c) {
return a + b + c;
}
// Overloaded methodology so as to add two doubles
double add(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
}On this instance, the add methodology is overloaded with completely different parameter lists. The suitable methodology is invoked primarily based on the arguments handed throughout the methodology name.
Advantages of Technique Overloading
- Code Readability: Utilizing the identical methodology title for related operations makes the code extra intuitive and simpler to grasp.
- Reusability: Overloaded strategies can carry out completely different duties with out the necessity for distinctive methodology names. This reduces code redundancy.
- Flexibility: Builders can add new performance by introducing new overloaded strategies with out affecting the prevailing code.
Sensible Purposes of Technique Overloading
- Mathematical Libraries: To carry out operations on completely different information sorts resembling integers, floats, and many others.
- String Manipulation Libraries: To deal with numerous types of enter information resembling substrings, character arrays, and many others.
- Utility Features: For basic utility strategies that have to deal with numerous information sorts.
- Constructor Overloading: To instantiate objects in numerous methods primarily based on the supplied parameters.
What’s Technique Overriding?
Technique overriding, also referred to as runtime polymorphism, is a characteristic in OOP that enables a subclass to supply a selected implementation of a way already outlined in its superclass. That is required for polymorphism, or dynamic methodology dispatch, the place the tactic to be executed is set at runtime primarily based on the article’s kind. On this case, the overriding methodology within the subclass ought to have the identical title, return kind, and parameter checklist as the tactic within the superclass.
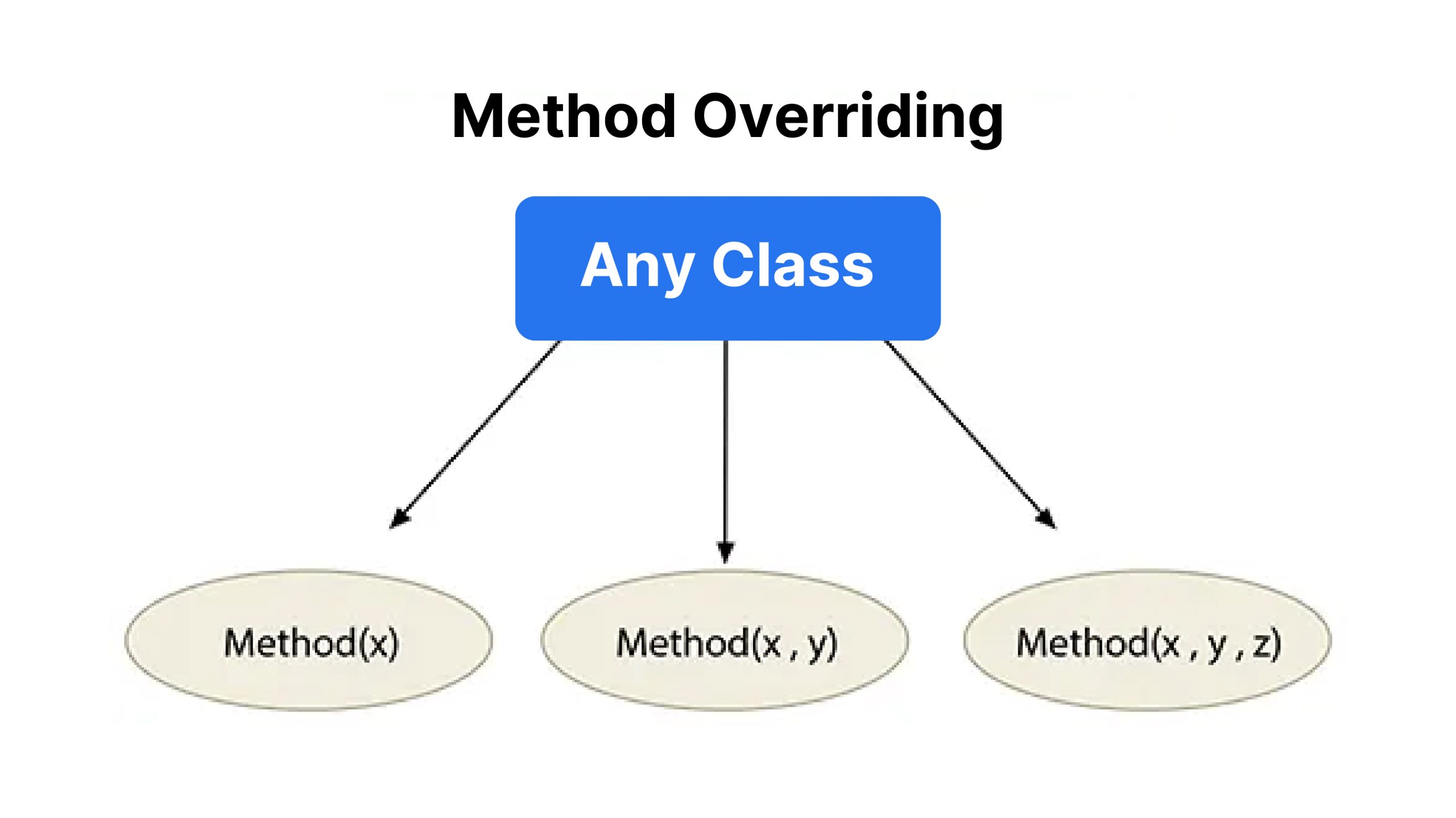
Syntax
Right here’s an instance of overriding in Python:
class Mum or dad:
def present(self):
print("That is the father or mother class")
class Baby(Mum or dad):
def present(self):
print("That is the kid class")On this case, the present methodology within the Baby class overrides the present methodology within the Mum or dad class.
Advantages of Technique Overriding
- Dynamic Polymorphism: Offers flexibility by enabling the collection of the suitable methodology at runtime.
- Extensibility: Permits subclasses to increase or modify the performance of a superclass methodology.
- Code Maintainability: Permits subclasses to supply particular implementations whereas reusing the interface outlined by the superclass.
- Inheritance Utilization: Promotes the usage of inheritance by permitting subclasses to refine or substitute the habits of superclass strategies.
- Reusability: Inherits strategies from the superclass and modifies them solely when crucial.
Sensible Purposes of Technique Overriding
- Customized Conduct: To tailor a superclass methodology to satisfy the particular wants of a subclass.
- Framework Improvement: To increase or modify base framework lessons and customise the habits of pre-defined strategies.
- GUI Libraries: To deal with person interactions in a different way in numerous parts.
- API Design: To supply default implementations in base lessons and permit overrides in subclasses for particular behaviors.
- Design Patterns: To override the steps of an algorithm by subclasses in patterns just like the Template Technique sample.
Key Variations Between Technique Overloading and Overriding
| Function | Technique Overloading | Technique Overriding |
| Definition | A number of strategies with the identical title however completely different parameter lists. | A subclass offers a selected implementation of a way outlined within the superclass. |
| Binding Time | Compile-time | Runtime |
| Parameters | Should differ in quantity, kind, or order | Should be the identical |
| Return Sort | Might be completely different | Should be the identical |
| Inheritance | Not required | Required |
| Function | To carry out related duties with completely different inputs | To supply a selected implementation for a superclass methodology |
Conclusion
It is very important know use methodology overloading and overriding for writing environment friendly and maintainable object-oriented code. Technique overloading enhances code readability and reusability by permitting related operations by means of a single methodology title. In the meantime, methodology overriding allows dynamic polymorphism, permitting subclasses to customise or substitute the habits of superclass strategies.
These ideas will show you how to develop functionalities and create versatile, reusable code constructions. They’re actually helpful in complicated fields like information science and synthetic intelligence. By studying these strategies, you’ll be able to improve your programming expertise and produce extra maintainable, scalable, and adaptable software program options.
Continuously Requested Questions
A. Whereas Python doesn’t help conventional methodology overloading, you’ll be able to obtain related habits utilizing default arguments or variable-length argument lists.
A. Technique overriding permits a subclass to supply a selected implementation for a way already outlined in its superclass.
A. No, methodology overloading just isn’t thought of polymorphism. Technique overriding, nevertheless, is.
A. Though Python doesn’t help methodology overloading within the conventional sense, you’ll be able to simulate it utilizing default arguments or by dealing with completely different numbers of arguments manually.
A. A typical instance of methodology overriding is a graphical person interface framework the place a base class has a draw methodology, and completely different subclasses like Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle override this methodology to attract particular shapes.


