Deliver this undertaking to life
Introduction
Within the deep-learning discipline, the selection of the framework can considerably affect the effectivity, flexibility, and efficiency of machine-learning fashions. Through the years, this atmosphere has modified often, in style frameworks like TensorFlow slowly lose their place to new releases. Over the previous few years, PyTorch and JAX have emerged as two contenders among the many hottest frameworks, every providing distinctive benefits and capabilities to builders and researchers alike.
PyTorch, developed by Fb’s AI Analysis lab (FAIR), has gained widespread adoption attributable to its easy API, dynamic computation graph permitting simple debugging, and intensive ecosystem of libraries and instruments. PyTorch’s flexibility and ease of use have made it a go-to alternative for machine studying and A.I. practitioners.
Alternatively, JAX, an open-source undertaking from Google Analysis, has not too long ago gained recognition as a robust framework for high-performance numerical computing. Constructed on useful programming rules and composable transformations, JAX gives automated differentiation, just-in-time compilation, and parallel execution, making it notably well-suited for scalable and environment friendly mannequin coaching on fashionable {hardware} accelerators.
What’s the distinction between them?
JAX, a more recent framework, at a excessive -level is less complicated and extra versatile than PyTorch for creating high-performance machine studying code. Constructed on high of NumPy, its syntax follows the identical construction, making it a simple alternative for customers conversant in the favored numerical computing library. PyTorch presents a extra advanced syntax, which requires one thing of a studying curve. Nonetheless, PyTorch nonetheless has better flexibility for establishing dense neural community architectures and is much extra prevalent in use for open-source tasks.
Evaluating the efficiency and velocity of JAX and PyTorch, JAX works nicely on {hardware} accelerators resembling GPUs and TPUs, resulting in doubtlessly quicker efficiency in particular situations. Nonetheless, PyTorch’s longer tenure and bigger group translate to extra accessible assets for optimizing efficiency.
Moreover, automated differentiation stands as a major function in successfully coaching deep studying fashions. PyTorch’s autograd bundle gives an easy technique for computing gradients and adjusting mannequin parameters. In the meantime, JAX builds upon Autograd and elevates automated differentiation by integrating its XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) backend.
Furthermore, ecosystem and group help play essential roles. Each frameworks present lively communities, various instruments, and libraries for deep studying duties. Nonetheless, PyTorch’s longer institution and bigger consumer base end in richer assets for learners and well-established libraries in particular domains like pc imaginative and prescient or pure language processing.
What’s JAX? Why is it so in style?
JAX is a library developed by Google Analysis that may velocity up machine studying and AI duties. JAX can robotically differentiate Python and NumPy capabilities, even by way of advanced buildings like loops and branches. It additionally helps ahead and reverse mode differentiation, a.ok.a. again provocation, permitting for environment friendly gradient calculations.
Past differentiation, JAX can considerably velocity up code utilizing a specialised compiler referred to as Accelerated Linear Algebra or XLA. This compiler optimizes linear algebra operations, resembling fusing operations, to cut back reminiscence utilization and streamline processing. JAX goes additional by permitting just-in-time compilation of customized Python capabilities into optimized kernels utilizing just-in-time (JIT) compilation. Moreover, JAX supplies highly effective instruments like PMAP for parallel execution throughout units.
Now, what’s PMAP? PMAP permits JAX to execute single-program multiple-data (SPMD) packages. Making use of PMAP implies that the perform will get compiled by XLA like JIT, replicated, after which executed in parallel throughout units. That is what the P in PMAP stands for.
VMAP is used for automated vectorization, and Grad is used for gradient calculations. VMAP is used for automated vectorization, reworking a perform designed for a single knowledge level into one able to processing batches of various sizes utilizing a single wrapper perform.
These options make JAX a flexible framework for constructing and optimizing machine studying fashions.
For instance, when coaching a deep neural community on the MNIST dataset, JAX can deal with duties like batching knowledge effectively utilizing VMAP and optimizing mannequin coaching with JIT. Whereas JAX is a analysis undertaking and should have some tough edges, its capabilities are promising for researchers and builders alike.
Crucial Factors for Pytorch and JAX
- JAX efficiency will increase when utilizing GPUs to run the code and additional the efficiency will increase when utilizing JIT compilation. This supplies a better benefit as GPUs make the most of parallelization, which supplies quicker efficiency than CPUs.
- JAX has glorious built-in help for parallelism throughout a number of units, surpassing different frameworks generally utilized for machine studying duties like PyTorch and TensorFlow.
- JAX supplies Auto differentiation with the grad() perform, this perform turns out to be useful whereas coaching a deep neural community. As DNN requires backpropagation, JAX makes use of an analytical gradient solver as an alternative of utilizing different refined strategies. It primarily breaks down the perform’s construction and applies the chain rule to compute gradients.
- Pytorch combines Torch’s environment friendly and adaptable GPU-accelerated backend libraries with a user-friendly Python frontend. It supplies prototyping, clear code readability, and intensive help for various deep-learning fashions. –
- Tensors, much like multidimensional arrays, are a basic knowledge kind in PyTorch. They retailer and manipulate mannequin inputs, outputs, and parameters. They share similarities with NumPy’s ndarrays, with the added functionality of GPU acceleration for quicker computation.
Get began with JAX
We’ve offered hyperlinks to a few notebooks that can be utilized to begin experimenting with JAX.
Deliver this undertaking to life
To put in JAX run the beneath command,
!pip set up -U "jax[cuda12_pip]" -f https://storage.googleapis.com/jax-releases/jax_cuda_releases.htmlAs soon as the requirement is happy you possibly can import the required libraries,
# JAX's syntax is generally much like NumPy's!
# There's additionally a SciPy API help (jax.scipy)
import jax.numpy as jnp
import numpy as np
# Particular rework capabilities
from jax import grad, jit, vmap, pmap
# JAX's low degree API
from jax import lax
from jax import make_jaxpr
from jax import random
from jax import device_putInstance 1: JAX’s syntax is similar to NumPy’s,
L = [0, 1, 2, 3]
x_np = np.array(L, dtype=np.int32)
x_jnp = jnp.array(L, dtype=jnp.int32)
x_np, x_jnp(array([0, 1, 2, 3], dtype=int32), Array([0, 1, 2, 3], dtype=int32))
x_np = np.linspace(0, 10, 1000)
y_np = 2 * np.sin(x_np) * np.cos(x_np)
plt.plot(x_np, y_np)
Instance 2: Here is one other comparability code for JAX vs PyTorch with a velocity check:
The code beneath compares the execution time of matrix multiplication utilizing JAX and PyTorch. It generates massive matrices of 1000×1000 and measures the time taken to carry out the multiplication operation utilizing each libraries.
import time
import jax.numpy as jnp
from jax import jit, random
import torch
# Outline JAX matrix multiplication perform
def jax_matmul(A, B):
return jnp.dot(A, B)
# Add JIT compilation for efficiency
jax_matmul_jit = jit(jax_matmul)
# Outline PyTorch matrix multiplication perform
def torch_matmul(A, B):
return torch.matmul(A, B)
# Generate massive matrices
matrix_size = 1000
key = random.PRNGKey(0)
A_jax = random.regular(key, (matrix_size, matrix_size))
B_jax = random.regular(key, (matrix_size, matrix_size))
A_torch = torch.randn(matrix_size, matrix_size)
B_torch = torch.randn(matrix_size, matrix_size)
# Heat-up runs
for _ in vary(10):
jax_matmul_jit(A_jax, B_jax)
torch_matmul(A_torch, B_torch)
# Measure execution time for JAX
start_time = time.time()
result_jax = jax_matmul_jit(A_jax, B_jax).block_until_ready()
jax_execution_time = time.time() - start_time
# Measure execution time for PyTorch
start_time = time.time()
result_torch = torch_matmul(A_torch, B_torch)
torch_execution_time = time.time() - start_time
print("JAX execution time:", jax_execution_time, "seconds")
print("PyTorch execution time:", torch_execution_time, "seconds")JAX execution time: 0.00592041015625 seconds
PyTorch execution time: 0.017140865325927734 seconds
Instance 3: A comparability code for Computerized Differentiation in JAX and PyTorch
These codes display automated differentiation for the perform,
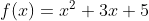
utilizing JAX and PyTorch. JAX’s grad perform is used to compute the spinoff within the JAX code, whereas PyTorch’s autograd mechanism is utilized within the PyTorch code
#for JAX
import jax.numpy as jnp
from jax import grad
# Outline the perform to distinguish
def f(x):
return x**2 + 3*x + 5
# Outline the spinoff of the perform utilizing JAX's grad perform
df_dx = grad(f)
# Check the spinoff at a particular level
x_value = 2.0
derivative_value = df_dx(x_value)
print("Spinoff (JAX) at x =", x_value, ":", derivative_value)
Spinoff (JAX) at x = 2.0 : 7.0
#for PyTorch
import torch
# Outline the perform to distinguish
def f(x):
return x**2 + 3*x + 5
# Convert the perform to a PyTorch tensor
x = torch.tensor([2.0], requires_grad=True)
# Calculate the spinoff utilizing PyTorch's autograd mechanism
y = f(x)
y.backward()
derivative_value = x.grad.merchandise()
print("Spinoff (PyTorch) at x =", x.merchandise(), ":", derivative_value)
Spinoff (PyTorch) at x = 2.0 : 7.0
Conclusion
In conclusion, each PyTorch and JAX provide highly effective frameworks for machine studying and growing deep neural networks. Every framework comes with its strengths and areas of experience. PyTorch excels in its ease of use, intensive group help, and adaptability for fast prototyping and experimentation, making it a super alternative for a lot of deep-learning tasks. Alternatively, JAX shines in its efficiency optimization, useful programming paradigm, and seamless integration with {hardware} accelerators, making it a most well-liked framework for high-performance computing and analysis at scale. In the end, the selection between PyTorch and JAX will depend on the undertaking’s particular necessities, balancing ease of growth towards efficiency and scalability wants. With each frameworks frequently evolving and pushing the boundaries of innovation, practitioners are lucky to have entry to such versatile instruments driving developments.



